Abstract
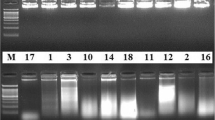
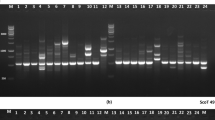
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs), also known as microsatellites, are highly variable DNA sequences that can be used as markers for the genetic analysis of plants. Three approaches were followed for the development of PCR primers for the amplification of DNA fragments containing SSRs from sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]: a search for sorghum SSRs in public DNA databases; the use of SSR-specific primers developed in the Poaceae species maize (Zea mays L.) and seashore paspalum grass (Paspalum vaginatum Swartz); and the screening of sorghum genomic libraries by hybridization with SSR oligonucleotides. A total of 49 sorghum SSR-specific PCR primer pairs (two designed from GenBank SSR-containing sequences and 47 from the sequences of genomic clones) were screened on a panel of 17 sorghum and one maize accession. Ten primer pairs from paspalum and 90 from maize were also screened for polymorphism in sorghum. Length polymorphisms among amplification products were detected with 15 of these primer pairs, yielding diversity values ranging from 0.2 to 0.8 with an average diversity of 0.56. These primer pairs are now available for use as markers in crop improvement and conservation efforts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkaya MS, Bhagwat AA, Cregan PB (1992) Length polymorphisms of simple sequence repeat DNA in soybean. Genetics 132:131–139
Akkaya MS, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE, Bhagwat AA, Cregan PB (1995) Integration of simple sequence repeat DNA markers into a soybean linkage map. Crop Sci 35:1439–1445
Altschul, SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–10
Ammer H, Schwaiger F-W, Kammerbauer C, Arriens A, Lazary S, Epplen JT (1992) Exonic polymorphism versus intronic hypervariability in DRB genes: evolutionary persistence and group-specific organization in simple repeat sequences. Immunogenetics 35:330–337
Bell CS, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of arabidopsis. Genomics 19:137–144
Condit RC, Hubbell SP (1991) Abundance and DNA sequence of two-base repeat regions in tropical tree genomes. Genome 34:66–71
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for labeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Hulbert SH, Richter TE, Axtell JD, Bennetzen JL (1990) Genetic mapping and characterization of sorghum and related crops by means of maize DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4251–4255
Karper RE (1949) Registration of sorghum varieties V. Agron J 41:536–540
Karper RE (1953) Registration of sorghum varieties VI. Agron J 45:322–323
Kondo Y, Mori M, Kuramoto T, Yamada J, Beckmann JS, Simon-Chazottes D, Montagutelli X, Guenet JL, Serikawa T (1993) DNA segments mapped by reciprocal use of microsatellite primers between mouse and rat. Mammal Genome 4:571–576
Kresovich S, Szewc-McFadden AK, Bliek SM, McFerson JR (1995) Abundance and characterization of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) isolated from a size-fractionated genomic library of Brassica napus L. (Rapeseed). Theor Appl Genet 91:206–211
Lagercrantz U, Ellegren H, Andersson L (1993) The abundance of various polymorphic microsatellite motifs differs between plants and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1111–1115
Lavi U, Akkaya M, Bhagwat A, Lahav E, Cregan PB (1994) Methodology of generation and characteristics of simple sequence repeat DNA markers in avocado (Persea americana M.). Euphytica 80:171–177
Litt M, Luty JA (1989) A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet 44:397–401
Liu ZW, Jarret RL, Kresovich S, Duncan RR (1995) Characterization and analysis of simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Swartz). Theor Appl Genet 91:47–52
Mellersh C, Sampson J (1993) Simplifying detection of microsatellite length polymorphisms. BioTechniques 15:582–584
Moore SS, Sargeant LL, King TJ, Mattick JS, Georges M, Hetzel DJS (1991) The conservation of dinucleotide microsatellites among mammalian genomes allows the use of heterologous PCR primer pairs in closely related species. Genomics 10:654–660
Pereira MG, Lee M, Bramel-Cox P, Woodman W, Doebley J, Whitkus R (1994) Construction of an RFLP map in sorghum and comparative mapping in maize. Genome 37:236–243
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Saghai-Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhang Q, Allard RW (1994) Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barley: species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5466–5470
Schlötterer C, Amos B, Tautz D (1991) Conservation of polymorphic simple sequence loci in cetacean species. Nature 354:63–65
Scheuring JF, Miller FR (1978) Fertility restorers and sterility maintainers to the milo-kafir genetic cytoplasmic male-sterility system in the sorghum world collection. Texas Agric Expt Stn MP-1367
Senior ML, Heun M (1993) Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CT primer. Genome 36:884–889
Senior ML, Chin ECL, Smith,JSC (1995) Simple sequence repeats in maize — a progress report. Maize Genet Coop Newslett 69:119–120
Stephens JC, Miller FR, Rosenow DT (1967) Conversion of alien sorghums to early combine genotypes. Crop Sci 7:396
Thomas MR, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphisms when analyzed as sequence-tagged sites. Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Wang Z, Weber JL, Zhong G, Tanksley SD (1994) Survey of plant short tandem DNA repeats. Theor Appl Genet 88:1–6
Weber JL (1990) Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n·(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics 7:524–530
Whitkus R, Doebley J, Lee M (1992) Comparative genome mapping of sorghum and maize. Genetics 132:1119–1130
Zhao X, Kochert G (1993) Phylogenetic distribution and genetic mapping of a (GGC)n microsatellite from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 21:607–614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. E. Hart
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, S.M., Hopkins, M.S., Mitchell, S.E. et al. Multiple methods for the identification of polymorphic simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 93, 190–198 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225745
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225745