Abstract
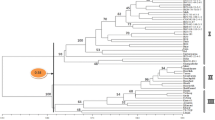
AFLP and RAPD marker techniques have been used to evaluate and study the diversity and phylogeny of 54 lentil accessions representing six populations of cultivated lentil and its wild relatives. Four AFLP primer combinations revealed 23, 25, 52 and 48 AFLPs respectively, which were used to partition variation within and among Lens taxa. The results of AFLP analysis is compared to previous RAPD analysis of the same material. The two methods provide similar conclusions as far as the phylogeny of Lens is concerned. The AFLP technique detected a much higher level of polymorphyism than the RAPD analysis. The use of 148 AFLPs arising from four primer combinations was able to discriminate between genotypes which could not be distinguished using 88 RAPDs. The level of variation detected within the cultivated lentil with AFLP analysis indicates that it may be a more efficient marker technology than RAPD analysis for the construction of genetic linkage maps between carefully chosen cultivated lentil accessions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-elwafa A, Murai, K, Shimada T (1995) Intra- and inter-specific variations in Lens revealed by RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:335–340
Black WCIV (1993) PCR with arbitrary primers: approach with care. Insect Mol Biol 2:1–6
Genstat 5 Committee (1987) Genstat 5 Manual. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Havey MJ, Muehlbauer FJ (1989) Variability for restriction fragment lengths and phylogenies in lentils. Theor Appl Genet 77:839–843
Hoffman DL, Soltis E, Muehlbauer FJ, Ladizinsky G (1986) Isozyme polymorphism in Lens (Leguminosae). Syst Bot 11:172–176
Kempton R, McNicol J (1990) Graphical method for multivariate data. Scottish Agricultural Stastistics Service
Ladizinsky G (1979) The genetics of several morphological traits in the lentil. J Hered 70:135–137
Ladizinsky G (1993) Wild lentils. Crit Rev Plant Sci 12:169–184
Ladizinsky G, Cohen D, Muehlbauer FJ (1984) The biological species of the genus Lens. Bot Gaz 145:253
Mayer MS, Soltis PS (1994) Chloroplast DNA phytogeny of Lens (Leguminosae); origin and diversity of cultivated lentil. Theor Appl Genet 87:773–781
Muehlbauer FJ, Kaiser WJ Clement SL, Summerfield RJ (1995) Production and breeding of lentil. Adv Agron 54:284–332
Muench DG, Slinkard AE, Scoles GJ (1991) Determination of genetic variation and taxonomy in lentil (Lens Miller) species by chloroplast DNA polymorphism. Euphytica 56:213–218
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in sub-divided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M, Li W (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Pinkas R, Zamir D, Ladizinsky G (1985) Allozyme divergence and evolution of the genus Lens. 151:131–140
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sharma SK, Dawson IK, Waugh R (1995) Relationship among cultivated and wild lentils revealed by RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 91:647–654
Simon CJ, Tahir M, Muehlbauer FJ (1993) Linkage map of lentil (Lens culinaris) 2n = 14. In:O'Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps. Locus maps of complex genomes, 6th edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 6.96–6.100
Swofford D (1989) BIOSYS-1, Release 1.7. Illinois Natural History Survey, University of Illinois, Champaign, Illinois, USA
Tahir M, Simon CJ, Muehlbauer FJ (1993) Gene map of lentil:a review. Lens Newslett 20:3–10
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kupier M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Zabeau M, Vos P (1993) Selective restriction fragment amplification: a general method for DNA fingerprinting. European Patent Application 924026 29.7 (Publication number:0534 858 A 1)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S.K., Knox, M.R. & Ellis, T.H.N. AFLP analysis of the diversity and phylogeny of Lens and its comparison with RAPD analysis. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 93, 751–758 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224072
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224072