Abstract
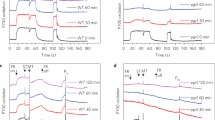
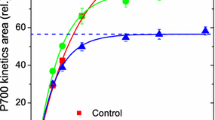
Oxygen evolving photosystem II particles were exposed to 100 and 250 W m−2 white light at 20°C under aerobic, anaerobic and strongly reducing (presence of dithionite) conditions. Three types of photoinactivation processes with different kinetics could be distinguished: (1) The fast process which occurs under strongly reducing (t 1/2≅1–3 min) and anaerobic conditions (t 1/2≅4–12 min). (2) The slow process (t 1/2≅15–40 min) and (3) the very slow process (t 1/2>100 min), both of which occur under all three sets of conditions.
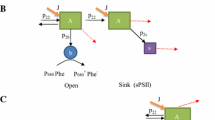
The fast process results in a parallel decline of variable fluorescence (F v) and of Hill reaction rate, accompanied by an antiparallel increase of constant fluorescence (F o). We assume that trapping of QA in a negatively charged stable state, (QA −)stab, is responsible for the effects observed.
The slow process is characterized by a decline of maximal fluorescence (F m). In presence of oxygen this decline is due to the well known disappearance of F v which proceeds in parallel with the inhibition of the Hill reaction; F o remains essentially constant. Under anaerobic and reducing conditions the decline of F m represents the disappearance of the increment in F o generated by the fast process. We assume that the slow process consists in neutralization of the negative charge in the domain of QA in a manner that renders QA non-functional. The charge separation in the RC is still possible, but energy of excitation becomes thermally dissipated.
The very slow photoinactivation process is linked to loss of charge separation ability of the PS II RC and will be analyzed in a forthcoming paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F :
-
chlorophyll a fluorescence
- F o, F v, F m :
-
constant, variable, maximum fluorescence
- F′ o, F′ v, F′ m :
-
the same, measured in presence of dithionite (F′ v suppression method)
- PS II:
-
photosystem II
- RC:
-
reaction centre (P680. Pheo)
- P680:
-
primary electron donor
- Pheo:
-
pheophytin, intermediary electron acceptor
- QA, QB :
-
the primary and secondary electron acceptor
- Z, D:
-
electron donors to P680
- (QA)stab, (QA H)stab :
-
hypothetical modifications of QA resulting from photoinactivation
- O-, A- and R-conditions:
-
aerobic, anaerobic and strongly reducing (presence of dithionite) conditions
- MES:
-
2-(N-morpholine) ethanesulphonic acid
- DCPIP:
-
2,6-dichlorphenolindophenol
- GGOC:
-
mixture of glucose, glucose oxidase and catalase
- DT-20:
-
oxygen-evolving PS II particles
References
Allakhverdiev SA, Šetlíková E, Klimov VV and Šetlík I (1987) In photoinhibited photosystem II particles pheophytin photoreduction remains unimpaired. FEBS Lett 226: 186–190
Arntz B and Trebst A (1986) On the role of the QB protein of PS II in photoinhibition. FEBS Lett 194: 43–49
Barényi B and Krause GH (1985) Inhibition of photosynthetic reactions by light. A study with isolated spinach chloroplasts. Planta 163: 218–226
Björkman O and Powles SB (1984) Inhibition of photosynthetic reactions under water stress: interaction with light level. Planta 161: 490–504
Callahan FE and Cheniae GM (1985) Studies on the photoinactivation of the water-oxidizing enzyme. I. Processes limiting photoinactivation in hydroxylamine-extracted leaf segments. Plant Physiol 79: 777–786
Callahan FE, Becker DW and Cheniae GM (1986) Studies on photo-inactivation of the water-oxidizing enzyme. II. Characterization of weak light photoinhibition of PS II and its light-induced recovery. Plant Physiol 82: 261–269
Cleland RE (1988) Molecular events of photoinhibitory inactivation in the reaction centre of photosystem II. Aust J Plant Physiol 15: 135–150
Cleland RE and Critchley C (1985) Studies on the mechanism of photoinhibition in higher plants. Inactivation by high light of photosystem II reaction center function in isolated chloroplasts. Photobiochem Photobiophys 10: 83–92
Critchley C (1981) Studies on the mechanism of photoinhibition in higher plants. Plant Physiol 67: 1161–1165
Critchley C (1988) The molecular mechanism of photoinhibition - facts and fiction. Aust J Plant Physiol 15: 27–41
Demeter S, Neale PJ and Melis A (1987) Photoinhibition: Impairment of the primary charge separation between P680 and pheophytin in PS II of chloroplasts. FEBS Lett 214: 370–374
Demmig B and Björkman O (1987) Comparison of the effect of excessive light on chlorophyll fluorescence (77 K) and photon yield of O2 evolution in leaves of higher plants. Planta 171: 171–187
Edelman M (1987) The primary in vivo cleavage site of the rapidly turning-over 32 kDa protein. In: Ohad I and Edelman M (eds) Dynamics of Photosystem II, EMBO Workshop, p 43. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Karapetjan NV and Klimov VV (1973) On the nature of the reversible and irreversible fluorescence quenching in chloroplasts illuminated under reducing conditions (in Russ). Fiziol Rast 20: 545–553
Klimov VV, Allakhverdiev SI and Pashchenko VZ (1978) Measurement of activation energy and life-time of chlorophyll fluorescence from PS II (in Russ). Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 242: 1204–1207
Kok B, Gassner EB and Rurainski HJ (1965) Photoinhibition of chloroplast reactions. Photochem Photobiol 4: 215–227
Krause GH, Köster S and Wong SC (1985) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis under anaerobic conditions studied with leaves and chloroplasts of Spinacia oleracea L. Planta 165: 430–438
Krause GH and Laasch H (1987) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis. Studies of mechanisms of damage and protection in chloroplasts. In: Biggins J (ed) Progress in Photosynthesis Research, Vol IV, pp 19–20. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk Publishers
Kuhn M, Thiel A and Böger P (1988) The 9-kDa phosphoprotein involved in photoinhibition. Z Naturforsch 43c: 413–417
Kyle DJ, Ohad I and Arntzen CJ (1984) Membrane protein damage and repair: selective loss of a quinone-protein function in chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 4070–4074
Mattoo AK, Hoffman-Falk H, Marder JB and Edelman M (1984) Regulation of protein metabolism: coupling of photosynthetic electron transport to in vivo degradation of the rapidly metabolized 32-kD protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1380–1384
Nedbal L, Šetlíková E, Masojídek J and Šetlík I (1986) The nature of photoinhibition in isolated thylakoids. Biochim Biophys Acta 848: 108–119
Renger G (1987) On the reaction pattern of system II and its modifications by exogenous substances. In: Ohad I and Edelman M (eds) Dynamics of Photosystem II, EMBO Workshop p 29. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Renger G, Koike H, Yuasa M and Inoue Y (1983) Studies on the mechanism of the fluorescence decline induced by strong actinic light in PS II particles under different redox conditions. FEBS Lett 163: 89–93
Rutherford AW, Zimmermann JA and Mathis P (1984) EPR of PS II—interactions, herbicide effects and a new signal. In: Sybesma C (ed) Advances in Photosynthesis Research, Vol I, pp 445–448. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk Publishers
Satoh K (1970) Mechanism of photoinhibition in photosynthetic system II. The occurrence and properties of two different types of photoinactivation. Plant Cell Physiol 11: 29–38
Satoh K (1971) Mechanism of photoinactivation in photosynthetic systems. IV. Light-induced changes in the fluorescence transient. Plant Cell Physiol 12: 13–27
Satoh K and Fork DC (1982) Photoinhibition of reaction centers of photosystems I and II in intact Bryopsis chloroplasts under anaerobic conditions. Plant Physiol 70: 1004–1008
Šetlík I, Nedbal L, Masojídek J and Šetlíková E (1984) Irradiance dependent changes in photosystem 2 caused by chloramphenicol and uncouplers in photosynthesizing cells. In: Sybesma C (ed) Advances in Photosynthesis Research, Vol III, pp 259–262. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk Publishers
Šetlík I, Nedbal L, Šetlíková E, Sofrová D and Masojídek J (1987) The kinetics of photosystem 2 photoinactivation in whole cells, thylakoids and PS 2 particles of a thermophilic blue green alga Synechococcus elongatus. In: Biggins J (ed) Progress in Photosynthesis Research, Vol IV, pp 55–58. Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
Šetlíková E, Masojídek J, Nedbal L and Šetlík I (1984) The irradiance dependent control of the Q-B-polypeptide turnover is a widespread phenomenon in oxygenic photosynthesis. In: Sybesma C (ed) Advances in Photosynthesis Research, Vol III, pp 255–258. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk Publishers
Theg SM, Filar LJ and Dilley RA (1986) Photoinactivation of chloroplasts already inhibited on the oxidizing side of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 849: 104–111
Trissl HW, Breton J, Deprez J and Leibl W (1987) An electronic two-step charge separation in photosystem II: Implications for the Klimov backreaction. In: Ohad I and Edelman M (eds) Dynamics of Photosystem II, EMBO Workshop p 27. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Tytler EM, Whitelam GC, Hipkins MF and Codd GA (1984) Photoinactivation of photosystem II during photoinhibition in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Planta 160: 229–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šetlík, I., Allakhverdiev, S.I., Nedbal, L. et al. Three types of Photosystem II photoinactivation. Photosynth Res 23, 39–48 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00030061
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00030061