Abstract
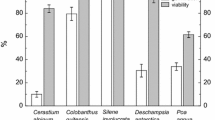
The percentage germination of seeds of parsley cv. Imperial Curled was higher in the light than in the dark, the high temperature limits for germination being 30 and 28°C for light and dark respectively. At the higher temperatures, the germination rate was slower in the dark. At 30°C, treatment with a gibberellin A4/7 mixture at 2 × 10−4 M partially alleviated the inhibiting effect of darkness on the germination percentage. Pre-incubation of parsley seeds at 35°C in the dark for 30 h increased the rate, but decreased the percentage, of germination of seeds incubated at 15°C in the light. Germination and seedling emergence studies were made on seed harvested from four different umbel positions. Although heavier seeds were produced from primary umbels than from other umbel orders, they were less viable as measured by seedling emergence in the glasshouse. The rate of emergence was decreased with increasing umbel order i.e. with later seed development: this was reflected in subsequent seedling weights, with seedlings from quarternary umbel seeds being about half the weight of those from primary umbel seeds. The upper temperature limit for dark germination was only slightly affected by umbel order, with quarternary umbel seeds being the most thermo-inhibited.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
N6-benzyladenine
- GA4/7 :
-
a mixture of gibberellins A4 and A7
- SD8339:
-
6-benzyl-amino-9-(tetrahydropyran-2-yl)-9H-purine
References
Biddington NL and Thomas TH (1979) Residual effects of high temperature pretreatment on the germination of celery seeds (Apium graveolens). Physiol Plant 47: 211–214
Durrant MJ and Mash SJ (1990) Sugar-beet seed treatments and early sowing. Seed Sci Technol 18: 839–850
Gray D and Steckel JRA (1985) Parsnip (Pastinaca sativa) seed production: effects of seed crop plant density, seed position on the mother plant, harvest date and methods, and seed grading on embryo and seed size and seedling performance. Ann App Biol 107: 559–570
Orchard TJ (1977) Estimating the parameters of plant seedling emergence. Seed Sci Technol 5: 61–69
Soffer H and Smith OE (1974) Studies on lettuce seed quality. III Relationships between flowering pattern, seed yield and seed quality. Am Soc Hort Sci 90: 114–117
Thomas TH (1994) Responses of Florence fennel (Foeniculum vulgaris azoricum) seeds to light, temperature and gibberellin GA4/7. Plant Growth Regul 14: 139–143
Thomas TH, Biddington NL and O'Toole DF (1979) Relationship between position on the parent plant and dormancy characteristics of seeds of three cultivars of celery (Apium graveolens). Physiol Plant 45: 492–496
Thomas TH, Gray D and Biddington NL (1978) The influence of the position of the seed on the mother plant on seed and seedling performance. Acta Hortic 83: 57–66
Thomas TH, Palevitch D, Biddington NL and Austin RB (1975) Growth regulators and the phytochrome-mediated dormancy of celery seeds. Physiol Plant 35: 101–106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, T.H. Relationships between position on the parent plant and germination characteristics of seeds of parsley (Petroselinium crispum Nym.). Plant Growth Regul 18, 175–181 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024379
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024379