Abstract
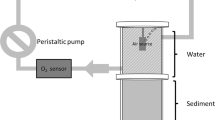
Sediment cores containing different densities of Chironomus plumosus, ranging from 0 to 12 000 ind. m−2, were incubated in the laboratory, with 100 and 39% O2 saturation in the overlying water. Rates of O2 uptake, and fluxes of the various inorganic N species were measured after addition of 15NO su−inf3 to the overlying water. The animals enhanced O2 and NO su−inf3 uptake, due to irrigation. Denitrification of NO su−inf3 coming from the overlying water (Dw) and dissimilatory NO su−inf3 reduction to NH sup+inf4 (DNRA) represented 20–30 and 4–10% of the NO su−inf3 uptake, respectively. Only 20–40% of the measured NH sup+inf4 effluxes corresponded to DNRA, the rest was probably due to animal excretion. Nitrite production, mostly from dissimilatory NO sup−inf3 reduction, was detected at both 39 and 100% oxygen saturation. Higher rates of NO su−inf2 production at the lower oxygen concentrations, were probably due to a thinner oxic layer, compared to fully oxygenated waters. The presence of Chironomus plumosus increased nitrification rates, relative to non-inhabited microcosms. However, nitrification rates were low compared to Dw, probably due to low numbers of nitrifiers in the sediment. At 39% oxygen saturation, rates of nitrification and denitrification of NO su−inf3 generated within the sediment were not measurable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarhus Amtskommune, 1981. Almind Sø og Slåen Sø, undersøgelser of vandkemi, fytoplankton, sediment og bundfauna.
Andersen, J. M., 1977. Importance of the denitrification process for the rate of degradation of organic matter in lake sediments. In H. L. Golterman (ed.), Interactions between sediments and freshwater. Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 357–362.
Blackburn, T. H., 1993. Turnover of 15NH +4 tracer in sediments. In P. Kemp, B. F. Sherr, E. B. Sherr & J. J. Cole (eds), Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology, pp. 643–648. Boca Raton, Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Bower, C. E. & T. Holm-Hansen, 1980. A salicylate-hypochlorite method for determining ammonia in seawater. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 794–798.
Brennan, A. & A. J. McLachlan, 1979. Tubes and tube-building in a lotic chironomid (Diptera) community. Hydrobiologia 67: 173–178.
Christensen, P. B., L. P. Nielsen, J. Sørensen & N. P. Revsbech, 1990. Denitrification in nitrate-rich sediments: diurnal and seasonal variation related to benthic oxygen metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 640–651.
Edwards, R. W., 1958. The effect of larvae of Chironomus riparius Meigen on the redox potentials of settled activated sludge. Ann. appl. Biol. 46: 457–464.
Edwards, R. W. & H. L. J. Rolley, 1965. Oxygen consumption of river muds. J. Ecol. 53: 1–19.
Fenchel, T. & T. H. Blackburn, 1979. The nitrogen cycle. In T. Fenchel & T. H. Blackburn (eds), Bacteria and mineral cycling. Academic Press, London: 101–126.
Fisher, J. B., 1982. Effects of macrobenthos on the chemical diagenesis of freshwater sediments. In P. L. McCall & M. J. S. Tevesz (eds), Animal Sediment Relations, Plenum Press, New York: 177–218.
Focht, D. D. & W. Verstraete, 1977. Biochemical ecology of nitrification and denitrification. In M. Alexander (ed.), Advances in microbial ecology. Plenum Press, New York 1: 135–214.
Fukuhara, H. & K. Yasuda, 1989. Ammonium excretion by some freshwater zoobenthos from a eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 173: 1–8.
Gamble, J. C., 1970. Effect of low dissolved oxygen concentrations on the ventilation rhythm of three tubicolous crustaceans, with special reference to the phenomenon of intermittent ventilation. Mar. Biol. 6: 121–127.
Gardner, W. S., T. F. Nalepa, D. R. Slavens & G. A. Laird, 1983. Patterns and rates of nitrogen release by benthic chironomids and oligochaeta. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 40: 259–266.
Granéli, W., 1979. The influence of Chironomus plumosus larvae on the oxygen uptake of sediment. Arch. Hydrobiol. 87: 385–403.
Grasshoff, K., M. Erhard & K. Kremling, 1983. Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Hargrave, B. T., 1975. Stability in structure and function of the mud-water interface. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 1073–1079.
Henriksen, K. & M. Kemp, 1988. Nitrification in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. In T. H. Blackburn & J. Sørensen (eds), Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine environments. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester: 207–249.
Koike, I. & A. Hattori, 1978. Simultaneous determination of nitrification and nitrate reduction in coastal sediments by a 15N dilution technique. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 35: 853–857.
Matisoff, G., J. B. Fisher & S. Matis, 1985. Effects of benthic macroinvertebrates on the exchange of solutes between sediments and freshwater. Hydrobiologia 122: 19–33.
McCall, P L. & M. J. S. Tevesz, 1982. The effects of benthos on physical properties of freshwater sediments. In P. L. McCall & M. J. S. Tevesz (eds), Animal Sediment Relations. Plenum Press, New York: 105–176.
Newell, R. C., C. L. Moloney, J. G. Field, M. I. Lucas & T. A. Probyn, 1988. Nitrogen models at the community level: plant-animal-microbe interactions. In T. H. Blackburn & J. Sørensen (eds), Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine environments. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester: 379–414.
Nielsen, L. P., 1992. Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 86: 357–362.
Pelegrí, S. P., L. P. Nielsen & T. H. Blackburn, 1994. Denitrification in estuarine sediment stimulated by the irrigation activity of the amphipod Corophium volutator (Pallas). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 105: 285–290.
Revsbech, N. P., P. B. Christensen, L. P. Nielsen & J. Sørensen, 1989. Denitrification in a trickling filter biofilm studied by a microsensor for oxygen and nitrous oxide. Water Res. 23: 867–871.
Risgaard-Petersen, N., S. Rysgaard & N. P. Revsbech, 1993. A sensitive assay for determination of 14N/15N isotope distribution in NO −4 . J. Microbiol. Meth. 17: 155–164.
Risgaard-Petersen, N., S. Rysgaard & N. P. Revsbech, 1995. A combined microdiffusion-hypobromite oxidation method for determination of 15N atom% in NH +4 . Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 59: 1077–1080.
Russel-Hunter, W. D., 1970. Aquatic productivity. Macmillan, London.
Rysgaard, S., N. Rysgaard-Petersen & N. P. Sloth, In press. Nitrification, denitrification and nitrate ammonification in sediments of two coastal lagoons in Southern France. In P Caumette, J. Castel & R. Herbert (eds), Coastal lagoon eutrophication and anaerobic processes. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dev. Hydrobiol.
Tátrai, I., 1982. Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of herbivorous chironomid larvae in Lake Balaton. Hydrobiologia 96: 129–135.
Tátrai, I., 1986. Rates of ammonia release from sediments by chironomid larvae. Freshwat. Biol. 16: 61–66.
Tátrai, I., 1987. The role of fish and benthos in the nitrogen budget of Lake Balaton, Hungary. Arch. Hydrobiol. 110: 291–302.
Walshe, B. M., 1950. The feeding habitats of certain chironomid larvae subfamily Tendipedinae. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 121: 63–79.
Weiss, R. F., 1970. The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res. 17: 721–735.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelegrí, S.P., Blackburn, T.H. Nitrogen cycling in lake sediments bioturbated by Chironomus plumosus larvae, under different degrees of oxygenation. Hydrobiologia 325, 231–238 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014989
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014989