Abstract
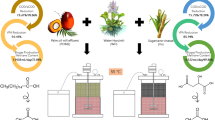
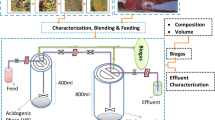
This study aims to investigate the potential methane yield by mono-anaerobic digestion of rice straw washwater (RSWW) and pineapple waste extract (PWE) as well as the co-digestion of both RSWW and PWE at a ratio of 50:50 (v/v). The experiment was conducted at a controlled mesophilic temperature of 37 °C in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor for a period of approximately 55 days. The process performances were evaluated based on the efficiency of COD removal and methane production in relation to other parameters such as pH, organic loading rate (OLR) and alkalinity ratio. This study confirmed that the rate of COD removal for RSWW, PWE, and RSWW:PWE (50:50) were achieved the stable condition at 81, 89, and 86% respectively. The alkalinity ratio value and pH throughout the experimental period remained below 0.30 and kept in the range of 6.5–7.0 indicated the stable and good environment existed for anaerobic digestion within the UASB reactor. This study implies that the co-digestion of RSWW:PWE found to improve the efficiency of COD removal and production of methane during the mono-digestion of RSWW from 81 to 86% and 0.093 to 0.13 LCH4/g CODrem by the increment of 6.2 and 40%, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binod, P., et al.: Bioresource Technology Bioethanol production from rice straw: an overview”. Biores. Technol. 1011(13), 4767–4774 (2010)
Tipayarom, D., Oanh, N.T.K.: Effects from open rice straw burning emission on air quality in the Bangkok metropolitan region. Sci. Asia 33(3), 339–345 (2007)
Arai, H., Hosen, Y., Hong Van, N.P., Nga, T.T., Chiem, N. H., Inubushi, K.: Greenhouse gas emissions from rice straw burning and straw-mushroom cultivation in a triple rice cropping system in the Mekong Delta. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 61, 1–17 (2015)
Gadde, B., Menke, C., Wassmann, R.: Rice straw as a renewable energy source in India, Thailand, and the Philippines: overall potential and limitations for energy contribution and greenhouse gas mitigation. Biomass Bioenerg. 33(11), 1532–1546 (2009)
Bardiya, N., Somayaji, D., Khanna, S.: Biomethanation of banana peel and pineapple waste. Biores. Technol. 58, 73–76 (1996)
Upadhyay, A., Lama, J.P., Tawata, S.: Utilization of pineapple waste: a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. Nepal 6, 10–18 (2013)
Mussoline, W., Esposito, G., Lens, P., Giordano, A.: Enhanced methane production from pilot-scale anaerobic digester loaded with rice straw. Open Environ. Eng. J. 6, 32–39 (2013)
Menardo, S., Cacciatore, V., Balsari, P.: Batch and continuous biogas production arising from feed varying in rice straw volumes following pre-treatment with extrusion. Biores. Technol. 180, 154–161 (2015)
Rosli, N.S., Idrus, S., Nik, Daud N., Ahsan, A.: Assessment of potential biogas production from rice straw leachate in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (UASB). Int. J. Smart Grid Clean Energy 5(3), 135–143 (2016)
Mussoline, W., Esposito, G., Giordano, A., Lens, P.: The anaerobic digestion of rice straw-a review. Crit. Rev. Enviro. Sci. Technol. 43(9), 895–915 (2012)
Idrus, S., Banks, C.J., Heaven, S.: Assessment of the potential for biogas production from wheat straw leachate in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 66(12), 2737–2744 (2012)
Babaee, A., Shayegan, J.: Effect of organic loading rates (OLR) on production of methane from anaerobic digestion of vegetables waste. In: World renewable energy Congress 2011, pp. 411–417. Bioenergy Technology, Sweden (2011)
Lay, J.J., Li, Y.Y., Noike, T.: Influences of pH and moisture content on the methane production in high- solids sludge digestion. Water Res. 6(31), 1518–1524 (1997)
Drosg, B.: Process monitoring in biogas plants, IEA Bioenergy (2013). [Online]. Available: http://www.iea-biogas.net/files/daten-redaktion/download/Technical Brochures/Technical Brochure process_montoring.pdf. Accessed 24 Mar 2017
Martín-González, L., Font, X., Vicent, T.: Alkalinity ratios to identify process imbalances in anaerobic digesters treating source-sorted organic fraction of municipal wastes. Biochem. Eng. J. 76, 1–5 (2013)
Cheng, J.: Anaerobic digestion for biogas production in biomass to renewable energy processes. In: Cheng, J. (ed.) CRC Press, New York, pp. 151–208 (2009)
Chong, H. C.: Nutritional characteristics evaluation of Malaysian commercial pineapple cultivars. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (2013)
Khalid, A., Arshad, M., Anjum, M., Mahmood, T., Dawson, L.: The anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste. Waste Manag. 31(8), 1737–1744 (2011)
España-Gamboa, E.I., Mijangos-Cortés, J.O., Hernández-Zárate, G., Maldonado, J.D., Alzate-Gaviria, L.M.: Methane production by treating vinasses from hydrous ethanol using a modified UASB reactor. Biotechnol. Biofuels 5(92), 1–9 (2012)
Hills, D.J., Roberts, D.W.: Anaerobic digestion of dairy manure and field crop residues. Agric. Wastes 3(3), 179–189 (1981)
Somani, D., Srivastava, H., Sabumon, P.C., Anjali, G.: A short review of anaerobic co-digestion and feasibility of anaerobic co-digestion of sewage and food waste for sustainable waste management. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 9(3), 55–70 (2016)
Zhan-jiang, P., et al.: High-solid Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and rice straw for biogas production. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 21(4), 61–66 (2014)
Jenkins, B.M., Bakker, R.R., Wei, J.B.: On the properties of washed straw. Biomass Bioenerg. 10(4), 177–200 (1996)
Said, N., Bishara, T., García-Maraver, A., Zamorano, M.: Effect of water washing on the thermal behavior of rice straw. Waste Manag. 33(11), 2250–2256 (2013)
Saravanan, P., Muthuvelayudham, R., Viruthagiri, T.: Enhanced Production of cellulase from pineapple waste by response surface methodology. J. Eng. (United States), (2013)
Senthilkumaar, S., Bharathi, S., Nithyanandhi, D., Subburam, V.: Biosorption of toxic heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Biores. Technol. 75(2), 163–165 (2000)
Levén, L., Eriksson, A.R.B., Schnürer, A.: Effect of process temperature on bacterial and archaeal communities in two methanogenic bioreactors treating organic household waste. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 59(3), 683–693 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge and thank the Putra Grant funded by the Universiti Putra Malaysia, vote number of 9,444,200 for providing the financial support in conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rosli, N.S., Idrus, S., Md Dom, A., Nik Daud, N.N. (2019). Potential of Pineapple Waste Extract (PWE) as Co-substrate in Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw Washwater (RSWW): Enhancement of Biogas Production. In: Pradhan, B. (eds) GCEC 2017. GCEC 2017. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering , vol 9. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8016-6_107
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8016-6_107
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-8015-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-8016-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)