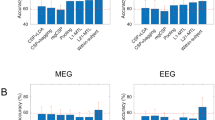
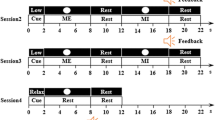
Abstract
We discuss a novel movement imagery brain-computer/ma-chine-interface (BCI/BMI) paradigm learning procedure with utilization of real- and quasi-movements of subjects’ thumbs. In the proposed procedure volitional movements are slowly minimized by the subjects to a very low level so that finally they become undetectable by objective measures such as electromyography (EMG). The procedure allows the subjects to understand motion imagery process, which follows after the training. The procedure allows also to control the final movement imagery protocol and to detect any possible movements in case subject would not learn to suppress them completely. We present also a discussion on electroencephalography (EEG) signals pre-processing steps with common spatial pattern (CSP) method improvements. Promising results were obtained with subjects who could not perform the motion imagery paradigm as well with those who never tried it before conclude the paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pfurtscheller, G., Aranibar, A.: Event-related cortical desynchronization detected by power measurements of scalp EEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 42 (1977) 817–826
Wolpaw, J.R., Birbaumer, N., McFarland, D.J., Pfurtscheller, G., Vaughan, T.M.: Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 113 (2002) 767–791
Cichocki, A., Washizawa, Y., Rutkowski, T., Bakardjian, H., Phan, A.H., Choi, S., Lee, H., Zhao, Q., Zhang, L., Li, Y.: Noninvasive BCIs: Multiway signal-processing array decompositions. Computer 41(10) (2008) 34–42
Wolpaw, J.R., McFarland, D.J.: Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 101(51) (December 2004) 17849–17854
Nikulin, V.V., Hohlefeld, F.U., Jacobs, A.M., Curio, G.: Quasi-movements: A novel motor-cognitive phenomenon. Neuropsychologia 46 (2008) 727–742
Niedermeyer, E., Da Silva, F.L., eds.: Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields, 5 edn. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2004)
Ramoser, H., Mueller-Gerking, J., Pfurtscheller, G.: Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined hand movement. IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng. Rehab. Eng 8(4) (2000) 441–446
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper was supported in part by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science grant no. 21360179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Higashi, H., Rutkowski, T.M., Washizawa, Y., Tanaka, T., Cichocki, A. (2011). Imagery Movement Paradigm User Adaptation Improvement with Quasi-movements Phenomenon. In: Wang, R., Gu, F. (eds) Advances in Cognitive Neurodynamics (II). Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9695-1_101
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9695-1_101
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-9694-4
Online ISBN: 978-90-481-9695-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)