Abstract
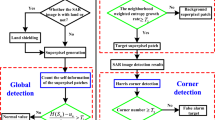
A Ship detection method was proposed in this paper by combining top-down recognition with bottom-up image segmentation, which will work on Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images and Space-borne Optical (SO) images. There are two steps in this method: a hypothesis generation step and a verification step. In the top-down hypothesis generation step, we design an improved Shape Context feature, which is more robust to ship deformation and background clutter. The improved Shape Context is used to generate a set of hypotheses of ship locations and figure ground masks, which have high recall and low precision rate. In the verification step, we first compute a set of feasible segmentations that are consistent with top-down ship hypotheses, and then we propose a False Positive Pruning (FPP) procedure to prune out false positives. We exploit the fact that false positive regions typically do not align with any feasible image segmentation. Experiments show that this simple framework is capable of achieving both high recall and high precision with only a few positive training examples and that this method can be generalized to many ship classes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viola, P.A., Jones, M.J.: Rapid ship detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In: CVPR (2001)
Borenstein, E., Ullman, S.: Class-Specific, Top-Down Segmentation. In: Heyden, A., Sparr, G., Nielsen, M., Johansen, P. (eds.) ECCV 2002, Part II. LNCS, vol. 2351, pp. 109–122. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Levin, A., Weiss, Y.: Learning to Combine Bottom-Up and Top-Down Segmentation. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006, Part IV. LNCS, vol. 3954, pp. 581–594. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Leibe, B., Seemann, E., Schiele, B.: Ship detection in crowded scenes. In: CVPR (2005)
Ferrari, V., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: Object Detection by Contour Segment Networks. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006, Part III. LNCS, vol. 3953, pp. 14–28. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Kokkinos, I., Maragos, P., Yuille, A.L.: Bottom-up & top-down ship detection using primal sketch features and graphical models. In: CVPR (2006)
Zhao, L., Davis, L.S.: Closely coupled ship detection and segmentation. In: ICCV (2005)
Ren, X., Berg, A.C., Malik, J.: Recovering human body configurations using pairwise constraints between parts. In: ICCV (2005)
Mori, G., Ren, X., Efros, A.A., Malik, J.: Recovering human body configurations: Combining segmentation and recognition. In: CVPR (2004)
Srinivasan, P., Shi, J.: Bottom-Up Recognition and Parsing of the Human Body. In: Yuille, A.L., Zhu, S.-C., Cremers, D., Wang, Y. (eds.) EMMCVPR 2007. LNCS, vol. 4679, pp. 153–168. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Huttenlocher, D.P.: Pictorial structures for ship recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision 61(1) (2005)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: CVPR (2005)
Belongie, S., Malik, J., Puzicha, J.: Shape matching and ship recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(4) (2002)
Mori, G., Belongie, S.J., Malik, J.: Efficient shape matching using shape contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(11) (2005)
Thayananthan, A., Stenger, B., Torr, P.H.S., Cipolla, R.: Shape context and chamfer matching in cluttered scenes. In: CVPR (2003)
Rubner, Y., Tomasi, C., Guibas, L.J.: A metric for distributions with applications to image databases. In: ICCV (1998)
Ramanan, D.: Using segmentation to verify ship hypotheses. In: CVPR (2007)
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. In: CVPR (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer India
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sreedevi, Y., Reddy, B.E. (2013). Ship Detection from SAR and SO Images. In: Kumar M., A., R., S., Kumar, T. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Computing. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 174. Springer, New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-0740-5_125
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-0740-5_125
Publisher Name: Springer, New Delhi
Print ISBN: 978-81-322-0739-9
Online ISBN: 978-81-322-0740-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)