Summary
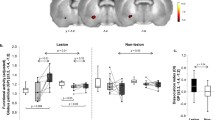
Regional cerebral glucose metabolism (rCMRGlu-18FDG) was measured in 6 cases with rigid type Parkinson’s disease(PD) (2 cases with dopa-induced dyskinesia = DID), 6 cases with chorea(Ch), 5 cases with essential tremor (EssT) and 2 cases with normal subjects(N). The effects of L-Dopa on rCMRGlu was studied in 3 cases with PD. With the aid of depth microrecording study, stereotactic pallidotomy was performed in all cases with PD. Thalamotomy was performed in 3 cases with Ch. In the EssT and N group, the metabolic pattern was high in the frontal cortex (FCx) but low in the lenticular nucleus (LN). In contrast, all cases with a rigid type PD showed lower rCMRGlu in FCx(premotor, prefrontal area). However, 4 out of 6 cases were higher in LN than the control group. Administration of L-Dopa shifted rCMRGlu toward the normal pattern in this group. Five out of 6 cases with Ch represented higher rCMRGlu in FCx(3 focal, 2 diffuse) but lower in LN. Moreover, when DID occurred, it showed almost the same pattern as in Ch. Electrophysiological studies showed high background neuronal activity (BNA) in the medial segment of the globus pallidus(GP) but low BNA in the lateral segment of the GP in the rigid type of PD. In cases with Ch, irregular burst discharges were often encountered in ventro-oral thalamus. From these results, the on-going changes of basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit in cases with a rigid type PD, DID and Ch are discussed. The underlying mechanisms of Parkinsonian rigidity was considered to contrast with those of DID and Ch within the same motor circuit.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeLong MR (1990) Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trend Neurosci 13: 281–285
Hirato M, Ohye C et al (1993) Defferent cerebral metabolism between parkinsonian rigidity and hyperkinesia (DID, chorea, dystonia). A PET study. Adv Neurol 60: 511–514
Ohye C, Hirato M, et al (1994) Neural activity of the human basal ganglia in Parkinsonism compared to other motor disorders. In: Percheron G et al (eds) Basal ganglia 4. Plenum, New York, pp 383–391
Page RD (1992) The use of thalamotomy in the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 114: 77–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer-Verlag
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hirato, M., Ishihara, J., Horikoshi, S., Shibazaki, T., Ohye, C. (1995). Parkinsonian Rigidity, Dopa-Induced Dyskinesia and Chorea — Dynamic Studies on the Basal Ganglia-Thalamocortical Motor Circuit Using PET Scan and Depth Microrecording. In: Meyerson, B.A., Ostertag, C. (eds) Advances in Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery 11. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum, vol 64. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-9419-5_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-9419-5_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-9421-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-9419-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive