Abstract
Intracerebral injections of high concentrations of thrombin cause brain edema but, in vitro, low concentrations of thrombin may be neuroprotective. This study investigated whether a low dose of thrombin might induce tolerance to subsequent large doses of thrombin (thrombin preconditioning; TPC) in a manner analogous to ischemic preconditioning. The study involved five parts. The first tested the effect of intracerebral infusion of a small dose (1 U) of thrombin on brain water content. In the second part, the effect of such a small dose of thrombin on subsequent edema formation from a large dose of thrombin (5 U) was evaluated. The time course of TPC was examined in the third part. In the fourth part, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, HSP32 and HSP70 were quantitated by Western blotting analysis while the fifth identified the cell types expressing HSPs.
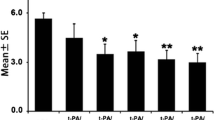
Injection of a low dose of thrombin alone did not cause brain edema. However, TPC significantly attenuated the edema induced by a subsequent injection of a large dose of thrombin. This effect of TPC was abolished by co-injection of a thrombin inhibitor, hirudin. The maximal effect of TPC on edema formation was seven days after pretretment. This time course was similar to that for a marked up-regulation in astrocytic HSP27. TPC also induced HSP32, but this effect occurred earlier than the effect on edema formation. TPC had no effect on HSP70. These results suggest that thrombin-induced brain tolerance may be related to HSP27 induction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham NG, Lavrovsky Y, Schwartzman ML, Stoltz RA, Levere RD, Gerritsen ME, Shibahara S, Kappas A (1995) Transfection of the human heme oxygenase gene into rabbit coronary microvessel endothelial cells: protective effect against heme and hemoglobin toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 6798–6802
Brophy CM, Woodrum D, Dickinson M, Beali A (1998) Thrombin activates MAPKAP2 kinase in vascular smooth muscle. J Vascular Surg 27: 963–969
Cavanaugh KP, Gurwitz D, Cunningham DD, Bradshaw RA (1990) Reciprocal modulation of astrocyte stellation by thrombin and protease nexin-1. J Neurochem 54: 1735–1743
Donovan FM, Cunningham DD (1998) Signaling pathways involved in thrombin-induced cell protection. J Biol Chem 273: 12746–12752
Guay J, Lambert H, Gingras-Breton G, Lavoie JN, Huot J, Landry J (1997) Regulation of actin filament dynamics by p38 map kinase-mediated phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27. J Cell Sci 110: 357–368
Huot J, Houle F, Marceau F, Landry J (1997) Oxidative stress-induced actin reorganization mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/heat shock protein 27 pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Circulation Res 80: 383–392
Huot J, Houle F, Spitz DR, Landry J (1996) HSP27 phosphorylation-mediated resistance against actin fragmentation and cell death induced by oxidative stress. Cancer Res 56: 273–279
Johnston RN, Kucey BL (1988) Competitive inhibition of hsp 70 gene expression causes thermosensitivity. Science 242: 1551–1554
Kato H, Liu Y, Kogure K, Kato K (1994) Induction of 27-kDa heat shock protein following cerebral ischemia in a rat model of ischemic tolerance. Brain Res 634: 235–244
Kirino T, Tsujita Y, Tamura A (1991) Induced tolerance to ischemia in gerbil hippocampal neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11: 299–307
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Tagaya M, Hata R, Ueda H, Niinobe M, Handa N, Fukunaga R, Kimura K, Mikoshiba K, et al (1990) ‘Ischemic tolerance’ phenomenon found in the brain. Brain Res 528: 21–24
Landry J, Chretien P, Lambert H, Hickey E, Weber LA (1989) Heat shock resistance conferred by expression of the human HSP27 gene in rodent cells. J Cell Biol 109: 7–15
Lavoie JN, Lambert H, Hickey E, Weber LA, Landry J (1995) Modulation of cellular thermoresistance and actin filamant stability accompanies phosphorylation-induced changes in the oligomeric structure of heat shock protein 27. Mol Cell Biol 15: 505–516
Lee KR, Colon GP, Betz AL, Keep RF, Kim S, Hoff JT (1996) Edema from intracerebral hemorrhage: the role of thrombin. J Neurosurg 84: 91–96
Martin JL, Mestril R, Hilal-Dandan R, Brunton LL, Dillmann WH (1997) Small heat shock proteins and protection against ischemic injury in cardiac myocytes. Circulation 96: 4343–4348
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74: 1124–1136
Plumier JC, David JC, Robertson HA, Currie RW (1997) Cortical application of potassium chloride induces the low-molecular weight heat shock protein (Hsp27) in astrocytes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17: 781–790
Plumier JC, Hopkins DA, Robertson HA, Currie RW (1997) Constitutive expression of the 27-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp27) in sensory and motor neurons of the rat nervous system. J Comp Neurol 384:409–428
Reiser G, Breder J, Reymann KG, Striggow F (1998) The protease thrombin is involved in neuroprotection again ischemia-induced cell death. Soc Neurosci Abstr 24: 2144
Sharp FR, Massa SM, Swanson RA (1999) Heat-shock protein protection. TINS 22: 97–99
Vaughan PJ, Pike CJ, Cotman CW, Cunningham DD (1995) Thrombin receptor activation protects neurons and astrocytes from cell death produced by environmental insults. J Neurosci 15: 5389–5401
Xi G, Keep RF, Hoff JT (1998) Erythrocytes and delayed brain edema formation following intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. J Neurosurg 89: 991–996
Xi G, Wagner KR, Keep RF, Hua Y, de Courten-Myers GM, Broderick JP, Brott TG, Hoff JT (1998) The role of blood clot formation on early edema development following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 29: 2580–2586
Yenari MA, Fink SL, Sun GH, Chang LK, Patel MK, Kunis DM, Onley D, Ho DY, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (1998) Gene therapy with HSP72 is neuroprotective in rat models of stroke and epilepsy. Ann Neurol 44: 584–591
Yoshida K, Maaieh MM, Shipley JB, Doloresco M, Bernardo NL, Qian YZ, Elliott GT, Kukreja RC (1996) Monophosphoryl lipid A induces pharmacologic ‘preconditioning’ in rabbit hearts without concomitant expression of 70-kDa heat shock protein. Mol Cell Biochem 159: 73–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xi, G., Keep, R.F., Hua, Y., Hoff, J.T. (2000). Thrombin Preconditioning, Heat Shock Proteins and Thrombin-Induced Brain Edema. In: Mendelow, A.D., et al. Brain Edema XI. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 76. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6346-7_107
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6346-7_107
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7257-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6346-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive