Summary
Objective. Drug resistant epilepsy associated with hypothalamic hamartoma (HH) can be cured by microsurgical resection of the lesion. Morbidity and mortality risks of microsurgery in this area are significant. Gamma Knife Surgery’s (GKS) reduced invasivity seems to be well adapted. In view of the severity of the disease and risks of surgical resection it is crucial to evaluate GKS for this indication. A first retrospective study has shown a very good safety and efficacy level but for a more reliable evaluation a prospective study would be required.
Methods. Between Oct 1999 and July 2002, 30 patients with HH and associated severe epilepsy were included. Seizure semiology (video EEG ) and frequency, behavioural disturbances, neuro-psychological performance, endocrinological status. sleep electroclinical abnormalities, MR imaging, and visual function were systematically evaluated before and after GKS (6, 12, 18, 24, 36 months). Twenty patients had experienced precocious puberty at a median age of 3.7 (0–9). Range of maximum diameter was from 7.5 to 23 mm with only 3 larger than 18 mm. The median marginal dose was 17 gy (14–20).
Results. Sufficient follow up for final evaluation is not yet available. Only 6 patients have a follow-up of more than 12 months and 19 more than 6 months. However a lot of very dramatic changes did occur during that period in this group. Among the 19 patients with more than 6 month s of follow-up, a lot had already experienced an increase of gelastic seizures around 3 months (3), an improvement in their seizure rate (18), behaviour (9), sleep (3), and EEG background activity (3), a cessation of part ial complex seizures (7). No complications have occurred till now except one patient experiencing at 5 months a hyperthermi a without infection and concomitant increase of gelastic seizures both ceasing suddenly and spontaneously after 15 days.
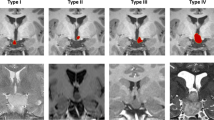
Conclusion. Our first results indicate that GKS is as effective as microsurgical resection and very much safer. GKS also allows to avoid the vascular risk related to radiofrequency lesioning or stimulation. The disadvantage of radiosurgery is its delayed action. Longer follow-up is mandatory for a serious evaluation of the role of GKS. Results are faster and more complete in patients with smaller lesions inside the 3rd ventricle (grade II). The early effect on subclinical discharges turns out to play a major role in the dramatic improvement of sleep quality, behaviour, developmental accelerat ion at school.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright A, Lee P (1993) Neurosurgical treatment of hypothalamic hamartomas causing precocious puberty [published erratum appeared in J Neurosurg 1993 Jul;79(1):156]. J Neurosurg 78: 77–82
Albright A, Lee P (1998) Surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas [letter]. J Neurosurg 88: 353
Arita K, Ikawa F, Kurisu K et al (1999) The relationship between magnetic resonance imaging findings and clinical manifestations of hypothalamic hamartoma. J Neurosurg 91: 212–220
Arita K, Kurisu K. Iida K et al (1998) Subsidence of seizure induced by stereotactic radiation in a patient with hypothalamic hamartoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 89: 645–648
Arroyo S. Santamaria J. Sanmarti F et al (1997) Ictal laughter associated with paroxysmal hypothalamopituitary dysfunction. Epilepsia 38: 114–117
Beningfield S. Bonnici F. Cremin B (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging of hypothalamic hamartomas. Br J Radiol 61: 1177–1180
Berkovic S. Kuzniecky R. Andermann F (1997) Human epileptogenesis and hypothalamic hamartomas: new lessons from an experiment of nature [editorial]. Epilepsia 38: 1–3
Berkovic SF. Andermann F. Melanson D et al (1988) Hypothalamic hamartoma and associated ictal laughter. Evolution of a characteristic epileptic syndrome and diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 23: 429–439
Brada M. Ford D. Ashley S et al (1992) Risk of second brain tumor after conservative radiotherapy for pituitary adenoma. Br Med J 304: 1343–1346
Cascino GD, Andermann F, Berkovic SF et al (1993) Gelastic seizures and hypothalamic hamartomas: evaluation of patients undergoing chronic intracranial EEG monitoring and outcome of surgical treatment. Neurology 43: 747–750
Cerullo A, Tinuper P, Provini F et al (1998) Autonomic and hormonal ictal changes in gelastic seizures from hypothalamic hamartomas. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 107: 317–322
Cheng K. Sawarnura Y. Yamauchi T et al (1993) Asymptomatic large hypoth alamic hamartoma associated with polydactyly in an adult. Neuro surgery 32: 458–460: discussion 460
Commentz JC, Helmke K (1995) Precocious puberty and decreased melatonin secretion due to a hypothalamic hamartoma. Horm Res 44: 271–275
Culler FL, James HE, Simon ML et al (1985) Identification of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in neurons of a hypothalamic hamartoma in a boy with precocious puberty. Neurosurgery 17: 408–412
Debeneix C, Bourgeois M, Trivin C et al (2001) Hypothalamic hamartoma: comparison of clinical presentation and magnetic resonance images. Horm Res 56: 12–18
Degerblad M, Rähn T. Bergstrand G et al (1986) Long-term results of stereotactic radiosurgery to the pituit ary gland in Cushing’s disease. Acta Endocrinol 112: 310–314
Delalande O, Fohlen M, Jalin C et al (1998) Surgical treatment of Epilepsy due to Hypothalamic hamartoma: Technique and preliminary results in five cases. Epilepsia 39: 90–91
Deonna T, Ziegler AL (2000) Hypothalamic hamartoma, precocious puberty and gelastic seizures: a special model of ‘epileptic’ developmental disorder. Epileptic Disord 2: 33–37
DiFazio MP, Davis RG (2000) Utility of early single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in neonatal gelastic epilepsy associated with hypothalamic hamartoma. J Child Neurol 15: 414–417
Donley D, Kuzniecky R, Mountz J et al (1994) Ictal SPECT findings in hypothalamic hamartoma and epilepsy (Abstract). Epilepsia 35 [Suppl]8: 146
Dunoyer C, Ragheb J. Resnick T et al (2002) The usc of stereotactic radiosurgery to treat intractable childhood partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 43: 292–300
Flickinger J, Kondziolka D, Lunsford L (1998) Clinical applications of stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer Treat Res 93: 283–297
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (1998) Radiosurgery management of brain metastasis from systemic cancer. In: Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC (eds) Progress in neurological surgery: gamma knife brain surgery. Karger, Basel. pp 145–159
Frattali CM, Liow K, Craig GH et al (2001) Cognitive deficits in children with gelastic seizures and hypothalamic hamartoma. Neurology 57: 43–46
Grob J, Regis J, Laurans R et al (1998) Rad iosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy in melanom a brain metastases. Eur J Cancer 34: 1187–1192
Harada K, Yoshida J, Wakabayashi T et al (1995) A super longacting LH-RH analogue induces regression of hypothalamic hamartoma associated with precocious puberty. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 137: 102–105
Hayashi M, Bartolomei F, Rey M et al (2002) MR changes after gamma knife radiosurgery for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: an evidence for the efficacy of subnecrotic doses. In: Kondziolka D (ed) Radiosurgery. Karger, Basel. pp 192–202
Kahane P, Munari C, Minotti L et al (1997) Role of the hypothalamic hamart oma in the genesis of gelastic and dacrystic seizures. In: Tuxhorn I, Holthausen H, Boenigk H (eds) Pediatric epilepsy syndromes and their surgical treatment. John Libbey, London. pp 447–461
Kahane P, Tassi L, Hoffmann D et al (1994) Crises dacrystiques et harna rtome hypoth alamique: à propos d’un e observation vidéo-stéréo-EEG. Epilepsies 6: 259–279
Kondziolka D, Lunsford L, McLaughlin M et al (1998) Long-term outcomes after rad iosurgery for acou stic neuromas [see comments]. N Engl J Med 339: 1426–1433
Kondziolka D. Niranjan A. Lunsford L et al (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery for meningiomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am 10: 317–325
Kuzniecky R, Guthrie B, Mountz J et al (1997) Intrinsic epileptogenesis of hypothalamic hamartomas in gelastic epilepsy. Ann Neurol 42: 60–67
Kuzniecky R, Guthrie B, Mountz J et al (1995) Hypothalamic hamartomas and gelastc seizures: evidence for subcortical seizure generation by ictal SPECT and cerebral stimulation. Epilepsia 36 [Suppl] 3: 266
Kuzniecky R, Mountz J, Wheatley G et al (1993) Ictal Single Photon emission computed tomography demonstrates localized epileptogenesis in cort icaldysplasia. Ann Neurol 34: 627–631
Kyuma Y, Kato E, Sekido K et al (1985) Hypothalamic hamartoma successfully treated by operation. Case report. J Neurosurg 62: 288–290
Laws E, Vance M (1999) Radio surgery for pituitary tumors and craniopharyngiomas. Neuro surg Clin N Am 10: 327–336
Leksell L (1951) The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand 102: 316–319
Leksell L (1971) Stereotaxis and radiosurgery. An operative system. In: Thomas CC (ed) Springfield
Lunsford LD (1990) Stereotactic radiosurgery of intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery update. Mc GrawHill, New York. pp 175–185
Machado HR, Hoffmann HJ, Hwang PA (1991) Gelastic seizures treated by resection of a hypothal amic hamartoma. Child’s Nervous System 7: 462–465
Mattia O, Olivier A, Avoli M (1995) Seizure-like discharges recorded in human dysplastic neocortex maint ained in vitro. Neurology 45: 1391–1395
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J et al (1998) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis from renal cell carcinoma [see comments]. Cancer 83: 344–353
Munari C, Kahane P, Francione S et al (1995) Role of the hypothalamic hamartoma in the genesis of gelastic fits (a videostereo-EEG study). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 95: 154–160
Murphy JV, Wheless JW, Schmoll CM (2000) Left vagal nerve stimulation in six patients with hypothalamic hamartomas. Pediatr Neurol 23: 167–168
Nishio S, Fujiwara S, Aiko Y et al (1989) Hypothalamic hamartoma. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 70: 640–645
Nishio S, Morioka T, Fukui M et al (1994) Surgical treatment of intractable seizures due to hypothalamic hamartoma. Epilepsia 35: 514–519
Nishio S, Shigeto H, Fukui M (1993) Hypothalami c hamartoma: the role of surgery. Neurosurg Rev 16: 157–160
Noren G (1996) Gamma knife radiosurgery for acoustic neurinomas. In: Gildenberg PL Tasker RR (eds) Textbook of stereotactic and functional neurosurgery. Mc Graw-Hill, New York. pp 835–844
Paillas JE, Roger G, Toga M et al (1969) Hamarthome de l’hypothalamus. Rev Neurol 120: 177–194
Pallini R, Bozzini V, Colicchio G et al (1993) Callosotomy for generalized seizures associated with hypothalamic hamartoma. Neurol Res 15: 139–141
Palmini A, Andermann F, Olivier A (1991) Focal neuronal migration disorders and intractable par tial epilepsy: results of surgical treatment. Ann Neurol 30: 750–757
Palmini A, Chandler C, Andermann F et al (2002) Resection of the lesion in patien ts with hypothalamic hamartomas and catastrophic epilepsy. Neurology 58: 1338–1347
Palmini A. Gambardella A. Andermann F (1995) Intrinsic epileptogenicity of human dysplastic cortex as suggested by corticography and surgical results. Ann Neurol 37: 476–487
Parrent AG (1999) Stereotacti c radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of gelastic seizures associated with hypothalamic hamartoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 91: 881–884
Pascual-Castroviejo I, Moneo JH, Viano J et al (2000) [Hypothalamic hamartomas: cont rol of seizures after part ial removal in one case]. Rev Neurol 31: 119–122
Plouin P, Ponsot G. Dulac O et al (1983) Hamartomes hypothalamiques et crises de rire. Rev. EEG Neurophysiol 13: 312–316
Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD el al (1994) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pituitary adenomas: imaging. visual and endocrine results. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 62: 33–38
Prasad D, Steiner M, Steiner L (2000) Gamma surgery for vestibular schwannoma [see comments]. J Neurosurg 92: 745–759
Regis J, Bartolomei F, de Toffol B et al (2000) Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Neurosurgery 47: 1343–1351; discussion 1351-1342
Regis J, Bartolomei F, Hayashi M et al (2000) The role of gamma knife surgery in the treatm ent of severe epilepsies. Epileptic Disord 2: 113–122
Régis J, Bartolomei F, Kida Y et al (2000) Radiosurgery of Epilepsy Associated with Caverno us Malformati on: Retrospective study in 49 patients. Neurosurgery 47: 1091–1097
Regis J, Bartolomei F, Metellus P et al (1999) Radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia and epilepsy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 10: 359–377
Régis J, Peragut J, Rey M et al (1994) First selective amygdalehippocampic radiosurgery for mesial temp oral lobe epilepsy. Stereo tact and Functional Neurosurg 64[Suppl] 1: 191–201
Régis J, Peragut JC, Rey M et al (1994) First selective amygda lohippocampic radiosurgery for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Stereotact Funct Neuro surg 64: 191–201
Regis J, Semah F, Bryan R et al (1999) Early and delayed MR and PET changes after selective lemporomesial radiosurgery in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20: 213–216
Roche PH, Regis J, Dufour H et al (2000) Gamm a knife Radiosur gery in the man agement of caverno us sinus men ingiomas. J Neurosurg 93: 68–73
Rosenfeld JV, Harvey AS, Wrennall J et al (2001) Transcallosal resection of hypoth alamic hamartomas, with control of seizures, in children with gelastic epilepsy. Neuro surgery 48: 108–11 8
Rutigliano MJ, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D et al (1995) Th e cost effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery versus surgical resection in the treatment of solitary meta static brain tumors. Neurosurgery 37: 445–455
Sato M, Ushio Y, Arita N et al (1985) Hypothalamic hamartoma: report of two cases. Neurosurgery 16: 198–206
Simmons NE, Laws E (1998) Gliomas Occurence after sellar Irradiation: case report and review. Neurosurgery 42: 172–178
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Adler J et al ( 1992) Clinical outcome of radiosurgery for cerebral arte riovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 77: 1–8
Stewart L, Steinbok P, Daaboul J (1998) Role of surgical resection in the treatment of hypothalamic hamartomas causing precocious puberty. Report of six cases. J Neurosurg 88: 340–345
Tasch E, Cendes F, Li LM et al (1998) Hypothalamic hamar tomas and gclastic epilepsy: a spectroscopic study. Neurology 51: 1046–1050
Tassi L, Quarato P, Francione S (1995) Chronological relationships between ictal laughing and smiling and intralesional discharges: stereo-EEG study of a patient with gelastic epilepsy and hypothalamic hamartoma. Epilepsia 36: 239–240
Tassinari CA, Riguzzi P, Rizzi R et al (1997) Gelastic seizures. In: Tuxhorn I, Holthausen H, Boenigk H (eds) Current problems in epilepsy. John Libbey, London. pp 429–446
Turjman F, Xavier J, Froment J et al (1996) Late MR follow-up of hypothalamic hamartomas. Childs Nerv Syst 12: 63–68
Unger F, Schrottner O, Haselsberger K et al (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery for hypothalamic hamartom as in patients with medically intractable epilepsy and precocious puberty. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 92: 726–731
Valdueza J, Cristante L, Dammann O et al (1994) Hypothalamic hamartomas: with special reference to gelastic epilepsy and surgery. Neurosurgery 34: 949–958; discussion 958
Watanabe T, Enomoto T, Uemura K et al (1998) [Gelastic seizures treated by partial resection of a hypothalamic hamartoma]. No Shinkei Geka 26: 923–928
Weissenberger AA, Dell ML, Liow K et al (2001) Aggression and psychiatric comorbidity in children with hypothalamic hamartomas and their unaffected siblings. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40: 696–703
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Régis, J. et al. (2004). Gamma Knife Surgery for Epilepsy Related to Hypothalamic Hamartomas. In: Wowra, B., Muacevic, A., Tonn, JC. (eds) Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 91. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0583-2_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0583-2_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7200-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-0583-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive