Abstract
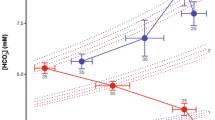
The aim of this chapter is to provide a brief introduction to the wide range of environmental oxygen and carbon dioxide partial pressures (PO2, PCO2) that certain vertebrates experience as a part of their natural life history. Various biological and physical features of the environment, particularly of aquatic systems, can lead to marked oscillations in the ambient gas tensions both daily and seasonally, and these in turn can have profound effects on the regulation of gas exchange in a number of these animals. In some instances, unfavourable gas concentrations in the environment (e.g. low O2 levels) can place restrictions on the activity range of an animal or limit the overall success of a species. On the other hand, animals that can tolerate the less than optimal gas composition of certain secluded habitats are often freed from risks of predation. Whereas some animals choose to live in confined, sometimes hypoxic areas (e.g. fossorial mammals), others are subject to periodic extremes of the medium in which they live (e.g. overwintering fish).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman RA (1977) The respiratory gas exchange of sea turtle nests (Chelonia, Caretta). Respir Physiol 31: 19–38
Arieli R (1979) The atmospheric environment of the fossorial mole rat (Spalax ehrenbergi): effects of season, soil texture, rain, temperature and activity. Comp Biochem Physiol 63 A: 569–575
Arieli R, Ar A (1979) Ventilation of a fossorial mammal (Spalax ehrenbergi) in hypoxic and hypercapnic conditions. J Appl Physiol 47: 1011–1017
Arieli R, Ar A (1981) Blood capillary density in heart and skeletal muscles of the fossorial mole rat. Physiol Zool 54: 22–27
Atkinson RJA (1976) Some preliminary field observations of the burrows of the Red Band fish, Cepola rubescens L. J Fish Biol 9: 181–183
Atkinson RJA, Pullin RSV, Dipper FA (1977) Studies on the Red Band fish, Cepola rubescens. J Zool (Lond) 182: 369–384
Babin J, Prepas EE (1985) Modelling winter oxygen depletion rates in icecovered temperate zone lakes in Canada. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42: 239–249
Baird DJ, Gates TE, Davies RW (1987) Oxygen conditions in two prairie pothole lakes during winter ice cover. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44: 1092–1095
Barica J, Mathias JA (1979) Oxygen depletion and winterkill risk in small prairie lakes under extended ice cover. J Fish Res Board Can 36: 980–986
Bennett AF, Dawson WR (1976) Metabolism. In: Gans C, Dawson WR (eds) Biology of the Reptilia, vol 5. Physiology. Academic Press, New York, pp 127–233
Bentley PJ, Herreid CF, Schmidt-Nielsen K (1967) Respiration of a monotreme, the echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus. Am J Physiol 212: 957–961
Birchard GF, Kilgore DL (1980) Conductance of water vapor in eggs of burrowing and non-burrowing birds: Implications for embryonic gas exchange. Physiol Zool 53: 284–292
Black CP, Tenny SM (1980) Oxygen transport during progressive hypoxia in high-altitude and sea-level waterfowl. Respir Physiol 39: 217–239
Boggs DF, Kilgore DL Jr (1983) Ventilatory responses of the burrowing owl and bobwhite to hypercarbia and hypoxia. J Comp Physiol B 149: 527–533
Boggs DF, Kilgore DL Jr, Birchard GF (1984) Respiratory physiology of burrowing mammals and birds. Comp Biochem Physiol 77A: 1–7
Boutilier RG, Randall DJ, Shelton G, Toews DP (1979) Acid-base relationships in the blood of the toad Bufo marinus. III. The effects of burrowing. J Exp Biol 82: 357–365
Bridges CR, Taylor AC, Atkinson RJA (1982) Respiratory properties of the blood of the burrowing red band fish Cepola rubescens L. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 59: 51–60
Burggren W (1985) Gas exchange, metabolism, and “ventilation” in gelatinous frog egg masses. Physiol Zool 58: 503–514
Carr AF (1967) So excellent a fishe. Natural History Press, New York, 248 pp
Darden TR (1972) Respiratory adaptations of a fossorial mammal, the pocket gopher (Thomomys bottae). J Comp Physiol 78: 121–137
Dejours P (1981) Principles of comparative respiratory physiology, 2nd edn. North Holland/Elsevier, Amsterdam New York, 265 pp
Dejours P (1982) Mount Everest and beyond: breathing air. In: Taylor CR, Johansen K, Bolis L (eds) A companion to animal physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 17–30
Dethlefsen V, von Westernhagen H (1983) Oxygen deficiency and effects on bottom fauna in the eastern German Bight 1982. Meeresforschung 30: 42–53
Felger RS, Cliffton K, Regal PJ (1976) Winter dormancy in sea turtles: independent discovery and exploitation in the Gulf of California by two local cultures. Science 191: 283–285
Furilla RA (1980) Ecological and physiological correlates of tunnel nesting in the bank swallow, Riparia riparia, with reference to the cliff swallow, Petrochelidon pyrrhonata. M Sc Thesis, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, 54 pp
Gans C (1969) Amphisbaenians - reptiles specialized for a burrowing existence. Endeavour 28 (105): 146–151
Garey WF, Rahn H (1970) Gas tensions in the tissues of trout and carp exposed to diurnal changes in oxygen tension of the water. J Exp Biol 52: 575–582
Gatten RE Jr (1981) Anaerobic metabolism in freely diving painted turtles (Chrysemys picta). J Exp Zool 216: 377–385
Gnaiger E (1983) In situ measurement of oxygen profiles in lakes: microstratifications, oscillations, and the limits of comparison with chemical methods. In: Gnaiger E, Forstner H (eds) Polarographic oxygen sensors. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 245–264
Grasshoff K (1975) The hydrochemistry of landlocked basins and fjords. In: Riley JP, Skirrow G (eds) Chemical Oceanography, Vol 2, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 456–598
Harper DE Jr, McKinney LD, Salzer RR, Case RJ (1981) The occurrence of hypoxic bottom water off the upper Texas coast and its effects on the benthic biota. Contrib Mar Sci 24: 53–79
Harvey HW (1957) The chemistry and fertility of sea waters. Cambridge University Press, London, 240 pp
Hayward J (1966) Abnormal concentrations of respiratory gases in rabbit burrows. J Mammal 47: 723–724
Heisler N, Forcht G, Ultsch GR, Anderson JF (1982) Acid-base regulation in response to environmental hypercapnia in two aquatic salamanders, Siren lacertina and Amphiuma means. Respir Physiol 49: 141–158
Hill RW, Wyse GA (1989) Animal physiology, 2nd edn. Harper and Row, New York, 656 pp
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (1984) Biochemical adaptation. Princeton University Press, Princeton, 537 pp
Howe S, Kilgore DL Jr (1987) Convective and diffuse gas exchange in nest cavities of the northern flicker ( Colaptes auratus ). Physiol Zool 60: 707–712
Jackson DC (1986) Acid-base regulation of reptiles. In: Heisler N (ed) Acid-base regulation in animals. Elsevier Scientific, Amsterdam, pp 235–263
Johansen K, Lykkeboe G, Weber RE, Maloiy GMO (1976) Respiratory properties of blood in awake and estivating lungfish, Protopterus amphibius. Respir Physiol 27: 335–345
Kendeigh SC (1961) Energy of birds conserved by roosting in cavities. Wilson Bull 73: 140–147
Kennerley TE (1964) Microenvironmental conditions of the pocket gopher burrow. Texas J Sci 16: 395–441
Kramer DL, Lindsey CC, Moodie GEE, Stevens ED (1978) The fishes and the aquatic environment of the central Amazon basin, with particular reference to respiratory patterns. Can J Zool 56: 717–729
Lee AK, Mercer EH (1967) Cocoon surrounding desert-dwelling frogs. Science 157: 87–88
Lüling KH (1975) Ichthyologische und gewässerkundliche Beobachtungen und Untersuchungen an der Yarina Cocha, in der Umgebung von Pucallpa und am Rio Pacaya (mittlerer und unterer Ucayali, Ostperu). Zool Beitr 21: 29–96
Maclean GS (1978) Respiratory physiology of a semi-fossorial mammal, Tamias striatus. Physiologist 21: 75
Moodie GEE (1978) Observations on the life history of the caecilian Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Dumeril and Bibron) in the Amazon basin. Can J Zool 56: 1005–1008
Officer CB, Biggs RB, Taft JL, Cronin LE, Tyler MA, Boynton WR (1984) Chesapeake Bay anoxia: origin, development, and significance. Science 223: 22–27
Parer JT, Hodson WA (1974) Respiratory studies of monotremes. IV. Normal respiratory function of echidnas and ventilatory response to inspired oxygen and carbon dioxide. Respir Physiol 21: 307–316
Penny DG (1987) Frogs and turtles: Different ectotherm overwintering strategies. Comp Biochem Physiol 86A: 609–615
Pullin RSV, Morris DJ, Bridges CR, Atkinson RJA (1980) Aspects of the respiratory physiology of the burrowing fish Cepola rubescens L. Comp Biochem Physiol 66A: 35–42
Rahn H (1966) Aquatic gas exchange: theory. Respir Physiol 1: 1–12
Rawitcher FK (1944) Problemas de fitoecologia com consideracoes especiais sobre o Brazil meridional. Bol Fac Filos Cienc Univ Sāo Paulo 4: 1–153
Reid GK (1961) Ecology of inland waters and estuaries, D. Van Nostrand, New York, 375 pp
Reimers CE, Fischer KM, Merewether R, Smith KL, Jahnke RA (1986) Oxygen microprofiles measured in situ in deep ocean sediments. Nature 320: 741–744
Revsbech NP (1983) In situ measurement of oxygen profiles of sediments by use of oxygen microelectrodes. In: Gnaiger E, Forstner H (eds) Polarographic oxygen sensors. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 265–273
Revsbech NP, Sorensen J, Blackburn TH, Lomholt JP (1980 a) Distribution of oxygen in marine sediments measured with microelectrodes. Limnol Oceanogr 25: 403–411
Revsbech NP, Jorgensen BB, Blackburn TH (1980 b) Oxygen in the seabottom measured with a microelectrode. Science 207: 1355–1356
Seki H, Tsuji T, Hattori A (1974) Effects of Zooplankton grazing on the formation of the anoxic layer of Tokyo Bay. Estuarine Coastal Mar Sci 2: 145–151
Seliger HH, Boggs JA, Biggley WH (1985) Catastrophic anoxia in the Chesapeake Bay in 1984. Science 228: 70–73
Smith HW (1961) From Fish to Philosopher. The Natural History Library, Anchor Books, Doubleday, Garden City NY, 293 pp
Stephenson TA, Zoond A, Eyre J (1934) The liberation and utilization of oxygen by the popul0061tion of rock-pools. J Exp Biol 11: 162–172
Studier EH, Baca TP (1968) Atmospheric conditions in artificial rodent burrows. Southwest Nat 13: 401–410
Toews DP, Macintyre DH (1978) Respiration and circulation in an apodan amphibian. Can J Zool 56: 998–1004
Truchot JP, Duhamel-Jouve A (1980) Oxygen and carbon dioxide in the marine intertidal envi-ronment: diurnal and tidal changes in rockpools. Respir Physiol 39: 241–254
Ultsch GR (1973) The effects of water hyacinths (Eichhornia crassipes) on the microenvironment of aquatic communities. Arch Hydrobiol 72: 460–473
Ultsch GR (1976) Eco-physiological studies of some metabolic and respiratory adaptations of sirenid salamanders. In: Hughes GM (ed) Respiration of Amphibious Vertebrates. Academic Press, New York, pp 287–312
Vogel S, Ellington CP, Kilgore DL (1973) Wind-induced ventilation of the burrow of the prairie- dog, Cyanomys ludovicianus. J Comp Physiol 85: 1–14
Weber RE, Johansen K, Abe AS (1981) Myoglobin from the burrowing reptile Amphisbaena alba. Concentrations and functional characteristics. Comp Biochem Physiol 68A: 159–165
White FN, Bartholomew GA, Kinney JL (1978) Physiological and ecological correlates of tunnel-nesting in the European bee-eater, Merops apiaster. Physiol Zool 51: 140–148
White FN, Kinney J, Siegfried WR, Kemp AC (1984) Thermal and gaseous conditions of horn-bill nests. Natl Geogr Res Rep 17: 931–936
Wickler SJ, Marsh RL (1981) Effects of nestling age and burrow depth on CO2 and O2 concentrations in the burrows of bank swallows (Riparia riparia). Physiol Zool 54: 132–136
Williams DD, Rausch RL (1973) Seasonal carbon dioxide concentrations in the dens of hibernating mammals ( Sciuridae ). Comp Biochem Physiol 44: 1227–1235
Withers PC (1978) Models of diffusion-mediated gas exchange in animal burrows. Am Nat 112: 1101–1112
Wood CM, Boutilier RG (1985) Osmoregulation, ionic exchange, blood chemistry, and nitrogenous waste excretion in the land crab Cardisoma carnifex: A field and laboratory study. Biol Bull 169: 267–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1990 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Boutilier, R.G. (1990). Respiratory Gas Tensions in the Environment. In: Boutilier, R.G. (eds) Vertebrate Gas Exchange. Advances in Comparative and Environmental Physiology, vol 6. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75380-0_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75380-0_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-75382-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-75380-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive