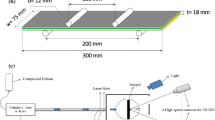
Abstract
The increasing need for high performance structures, in the energy and transport industry, demands a continuous development of new engineering materials. Unique mechanical properties together with low specific weight can be achieved by the combination of various constituent materials into one macroscopic composite material. Coupling of the high strength reinforcement with supporting matrix creates a novel material with the improved characteristics, which could never be obtained using either of the constituents separately. These types of materials are particularly desirable in structures where a high strength to weight ratio is of great importance. In this chapter, two case studies are provided one on nanophased sandwich composites with polyurethane/layered silicate foam cores and the other on thermoplastic glass-fibre and nano-silica reinforced nanocomposites.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, K., Desai, S.: Nanofiller‐reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 19(8), 947--959 (2008)
Leszczyńska, A., Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, K., Banerjee, J.R.: Polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites with improved thermal properties: Part II. Thermal stability of montmorillonite nanocomposites based on different polymeric matrixes. Thermochimica Acta. 454(1), 1–22 (2007/2/15)
Leszczyńska, A., Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, K., Banerjee, J.R.: Polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites with improved thermal properties: Part I. Factors influencing thermal stability and mechanisms of thermal stability improvement. Thermochimica Acta. 453(2), 75–96 (2007/2/1)
Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, K., Desai, D.: Nanofiller-reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 19(8), 947–959 (2008)
Mamalis, A.G.: Crashworthiness of composite thin-walled structural components. Technomic Pub. Co., Lancaster, Pa (1998)
Njuguna, J.: Crashworthiness of composite materials, Cranfield University, School of Applied Sciences, lecture notes ( 2012)
Farley, G.L.: Effect of fiber and matrix maximum strain on the energy absorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 20(4), pp. 322 (1986)
Meressi, T., Paden, B.: Buckling control of a flexible beam using piezoelectric actuators. J. Guidance Control and Dyn. 16(5), 977–980 (1993)
Farley, G. L.: The effects of crushing speed on the energy-absorption capability of composite tubes. J. Compos. Mater. 25(10), pp. 1314 (1991)
Thornton, P.: The crush behavior of pultruded tubes at high strain rates. J. Compos. Mater. 24(6), pp. 594 (1990)
Thornton, P.: Energy absorption in composite structures. J. Compos. Mater. 13(3), pp. 247 (1979)
Hamada, H., Coppola, J., Hull, D., Maekawa, Z., Sato, H.: Comparison of energy absorption of carbon/epoxy and carbon/PEEK composite tubes. Compos. 23(4), 245--252 (1992)
Yuan, Q., Misra, R.: Impact fracture behavior of clay-reinforced polypropylene nanocomposites. Polym. 47(12), 4421--4433 (2006)
Sun, L., Gibson, R.F., Gordaninejad, F., Suhr, J.: Energy absorption capability of nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69(14), 2392--2409 (2009)
Bartczak, Z., Argon, A.S., Cohen, R.E., Weinberg, M.: Toughness mechanism in semi-crystalline polymer blends: I. High-density polyethylene toughened with rubbers. Polym. 40(9), 2331--2346 (1999)
Bartczak, Z., Argon, A.S., Cohen, R.E., Weinberg, M.: Toughness mechanism in semi-crystalline polymer blends: II. High-density polyethylene toughened with calcium carbonate filler particles. Polym. 40(9), 2347--2365 (1999)
Viana, J.: Polymeric materials for impact and energy dissipation. Plast., Rubber Compos. 35(6--7), 260--267 (2006)
Wang, J., Fang, Z., Gu, A., Xu, L., Liu, F.: Effect of amino‐functionalization of multi‐walled carbon nanotubes on the dispersion with epoxy resin matrix. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 100(1), 97--104 (2006)
Cooper, C.A., Ravich, D., Lips, D., Mayer, J., Wagner, H.D.: Distribution and alignment of carbon nanotubes and nanofibrils in a polymer matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 62(7--8), 1105--1112 (2002)
Kireitseu, M., Hui, D., Tomlinson, G.: Advanced shock-resistant and vibration damping of nanoparticle-reinforced composite material. Compos. B Eng. 39(1), 128--138 (2008)
Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Friedrich, K., Eger, C.: Property improvements of in situ epoxy nanocomposites with reduced interparticle distance at high nanosilica content. Acta Mater. 54(7), 1833--1842 (2006)
Javni, I., Zhang, W., Karajkov, V., Petrovic, Z., Divjakovic, V.: Effect of nano-and micro-silica fillers on polyurethane foam properties. J. Cell. Plast. 38(3), pp. 229 (2002)
Chen, J., Huang, Z., Zhu, J.: Size effect of particles on the damage dissipation in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 67(14), 2990--2996 (2007)
Caprino, G., Teti, R.: Impact and post-impact behavior of foam core sandwich structures. Compos. Struct. 29(1), 47–55 (1994)
Anderson, T., Madenci, E.: Experimental investigation of low-velocity impact characteristics of sandwich composites, Composite Structures. 50(3), 239–247 (2000/11)
Mines, R.A.W., Worrall, C.M., Gibson, A.G.: Low velocity perforation behaviour of polymer composite sandwich panels. Int. J. Impact Eng. 21(10), 855–879 (1998)
Lee, L.J., Zeng, C., Cao, X., Han, X., Shen, J., Xu, G.: Polymer nanocomposite foams. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65(15–16), 2344–2363 (2005)
Cao, X., James Lee, L., Widya, T., Macosko, C.: Polyurethane/clay nanocomposites foams: Processing, structure and properties. Polymer 46(3), 775–783 (2005)
Mahfuz, H., Islam, M.S., Rangari, V.K., Saha, M.C., Jeelani, S.: Response of sandwich composites with nanophased cores under flexural loading, Composites Part B: Engineering. 35(6–8), 543–550 (2004/0)
Hosur, M.V., Mohammed, A.A., Zainuddin, S., Jeelani, S.: Processing of nanoclay filled sandwich composites and their response to low-velocity impact loading. Compos. Struct. 82(1), 101--116 (2008)
Wetzel, B., Rosso, P., Haupert, F., Friedrich, K.: Epoxy nanocomposites-fracture and toughening mechanisms. Eng. Fract. Mech. 73(16), 2375--2398 (2006)
Subramaniyan, A.K., Sun, C.: Toughening polymeric composites using nanoclay: Crack tip scale effects on fracture toughness. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 38(1), 34--43 (2007)
Njuguna, J., Michalowski, S., Pielichowski, K., Kayvantash, K., Walton, A.: Improved car crash protection. SPE Plastic Research Online (2010). 10.1002/spepro.003061
Hussain, F., Hojjati, M., Okamoto, M., Gorga, R.E.: Review article: Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing, and application: An overview. J. Compos. Mater. 40(17), pp. 1511 (2006)
Ng, C., Schadler, L., Siegel, R.: Synthesis and mechanical properties of TiO2-epoxy nanocomposites. Nanostruct. Mater. 12(1--4), 507--510 (1999)
Ma, J., Mo, M.S., Du, X.S., Rosso, P., Friedrich, K., Kuan, H.C.: Effect of inorganic nanoparticles on mechanical property, fracture toughness and toughening mechanism of two epoxy systems. Polym. 49(16), 3510--3523 (2008)
Guo, Y., Li, Y.: Quasi-static/dynamic response of SiO2-epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 458(1--2), 330--335 (2007)
Han, J., Cho, K.: Nanoparticle-induced enhancement in fracture toughness of highly loaded epoxy composites over a wide temperature range. J. Mater. Sci. 41(13), 4239--4245 (2006)
Njuguna, J., Silva, F., Sachse, S.: Nanocomposites for vehicle structural applications” in nanofibers—production, properties and functional applications, Lin, T. (ed.) In Tech Press, (ISBN: 978-953 307 420 7) (2011)
Silva, F., Sachse, S., Njuguna, J.: Energy absorption characteristics of nano-composite conical structures, IOP Conf. Ser.: Materials Science and Engineering 40 012010 doi:10.1088/1757-899X/40/1/012010 (2012)
Silva, F., Njuguna, J., Sachse, S., Pielichowski, K., Leszczynska, A., Gianocolli, M.: The influence of multiscale fillers reinforcement into impact resistance and energy absorption properties of polyamide 6 and polypropylene nanocomposite structures. Mater. Des. 50, 244–252 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the European Commission financial support through the FP7 Project- CP-FP, Project Reference No.: 228536– 2. Support from Research Councils Unite Kingdom (RCUK) and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) equipment pool is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Njuguna, J., Sachse, S., Silva, F. (2013). Energy Absorption and Low-Velocity Impact Performance of Nanocomposites: Cones and Sandwich Structures. In: Njuguna, J. (eds) Structural Nanocomposites. Engineering Materials. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40322-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40322-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-40321-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-40322-4
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)