Abstract
Glutathione, termed the “ultimate” or “master” antioxidant, is a vital intracellular tripeptide molecule and plays a central role in cellular physiologic functions. Currently the undeniable connection between glutathione and good health is very well established.
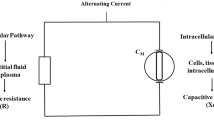
Bioelectrical impedance data indicative of cellular physiologic organ function (status), using an Electro Interstitial Scanning (EIS) system, were acquired from two cohort volunteers. Cohort 1 comprised of 10 subjects: 1 male and 9 females, 18-86 (mean 58) years of age while Cohort 2 were 20 subjects: 4 males and 16 females, 19-80 (mean 54) years of age. Cellular physiologic function in subjects were evaluated in 8 organs (pancreas, liver, gall bladder, intestines, left and right adrenal glands, hypothalamus and pituitary gland) while wearing the glutathione patch for a period of 4 weeks. Physiologic function testing was repeated each week. Cohort 1 wore the glutathione patch for 12 hours/day daily, while Cohort 2 wore the glutathione patch for 12 hours/day on weekdays. Cellular physiologic function baseline data were acquired from all subjects at the beginning of the study period before the glutathione patch was worn. Subjects were instructed to keep well hydrated during the study period. All subjects served as their own control. The hypothesis to be tested was: The glutathione patch worn 12 hours daily for 4 weeks significantly improves cellular physiologic functional status in different organs.
The overall data in Cohort 1 in this study demonstrated that glutathione patches worn 12 hours daily over a period of 4 weeks produced a highly significant improvement in physiologic functional status of pancreas, liver, gall bladder, intestines, left and right adrenals, hypothalamus and pituitary gland and very significant improvement in pancreas with a statistical power of at least 72%. Stated differently all organs achieved significant cellular physiologic functional status improvement compared to baseline with a statistical power of at least 91%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nazeran, H., Blake-Greenberg, S. (2010). Nanoscale Glutathione Patches Improve Organ Function. In: Herold, K.E., Vossoughi, J., Bentley, W.E. (eds) 26th Southern Biomedical Engineering Conference SBEC 2010, April 30 - May 2, 2010, College Park, Maryland, USA. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 32. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14998-6_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14998-6_35
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-14997-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-14998-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)