Abstract
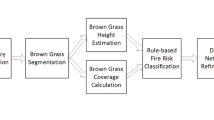
Roadside grass fire is a major hazard to the security of drivers and vehicles. However, automatic assessment of roadside grass fire risk has not been fully investigated. This paper presents an approach, for the first time to our best knowledge, that automatically estimates and classifies grass biomass for determining the fire risk level of roadside grasses from video frames. A major novelty is automatic measurement of grass coverage and height for predicting the biomass. For a sampling grass region, the approach performs two-level grass segmentation using class-specific neural networks. The brown grass coverage is then calculated and an algorithm is proposed that uses continuously connected vertical grass pixels to estimate the grass height. Based on brown grass coverage and grass height, a set of threshold based rules are designed to classify grasses into low, medium or high risk. Experiments on a challenging real-world dataset demonstrate promising results of our approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vazirabad, Y.F., Karslioglu, M.O.: LIDAR for biomass estimation. In: Biomass - Detection, Production and Usage. INTECH Open Access Publisher (2011)
Bond, W.J., Van Wilgen, B.W.: Fire and Plants. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2012)
Royo, C., Villegas, D.: Field measurements of canopy spectra for biomass assessment of small-grain cereals. In: Biomass - Detection, Production and Usage. INTECH Open Access Publisher (2011)
Sannier, C., Taylor, J., Plessis, W.D.: Real-time monitoring of vegetation biomass with NOAA-AVHRR in Etosha National Park, Namibia, for fire risk assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 23, 71–89 (2002)
Verbesselt, J., Somers, B., Van Aardt, J., Jonckheere, I., Coppin, P.: Monitoring herbaceous biomass and water content with SPOT VEGETATION time-series to improve fire risk assessment in savanna ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 101, 399–414 (2006)
Schneider, P., Roberts, D.A., Kyriakidis, P.C.: A VARI-based relative greenness from MODIS data for computing the fire potential index. Remote Sens. Environ. 112, 1151–1167 (2008)
Hernandez-Leal, P.A., Arbelo, M., Gonzalez-Calvo, A.: Fire risk assessment using satellite data. Adv. Space Res. 37, 741–746 (2006)
Zhang, L., Verma, B., Stockwell, D.: Spatial contextual superpixel model for natural roadside vegetation classification. Pattern Recognit. 60, 444–457 (2016)
Winn, J., Criminisi, A., Minka, T.: Object categorization by learned universal visual dictionary. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1800–1807 (2005)
Tilly, N., Hoffmeister, D., Cao, Q., Lenz-Wiedemann, V., Miao, Y., Bareth, G.: Transferability of models for estimating paddy rice biomass from spatial plant height data. Agriculture 5, 538–560 (2015)
Tilly, N., Aasen, H., Bareth, G.: Fusion of plant height and vegetation indices for the estimation of barley biomass. Remote Sens. 7, 11449–11480 (2015)
Zhang, L., Verma, B., Stockwell, D.: Class-semantic color-texture textons for vegetation classification. In: Arik, S., et al. (eds.) ICONIP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9489, pp. 354–362. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-26532-2_39
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from ARC and DTMR. This research was supported under Australian Research Council’s Linkage Projects funding scheme (project number LP140100939).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, L., Verma, B. (2016). Rule-Based Grass Biomass Classification for Roadside Fire Risk Assessment. In: Hirose, A., Ozawa, S., Doya, K., Ikeda, K., Lee, M., Liu, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9950. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46681-1_75
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46681-1_75
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-46680-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-46681-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)