Abstract
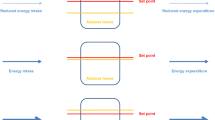
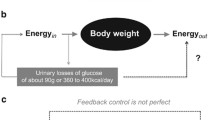
Mammals have evolved complex mechanisms to obtain energy from food; store excess energy in the forms of glycogen, fat, and protein; and utilize energy efficiently for vital functions. Obesity develops when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. While obesity treatment is mostly focused on reducing food intake, studies suggest that increasing energy expenditure through physical activity and adaptive thermogenesis is an important strategy for weight loss and maintenance of health. This chapter will describe fundamental concepts of bioenergetics and provide a framework for understanding the pathogenesis and treatment of metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahima RS. Digging deeper into obesity. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2076-2079. doi: 10.1x172/JCI58719.
Amatruda JM, Statt MC, Welle SL. Total and resting energy expenditure in obese women reduced to ideal body weight. J Clin Invest. 1993;92(3):1236-1242. doi:10.1172/JCI116695.
Astrup A. Thermogenesis in human brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle induced by sympathomimetic stimulation. Acta Endocrinol Suppl. 1986;278:1-32.
Astrup A, Bulow J, Madsen J, et al. Contribution of BAT and skeletal muscle to thermogenesis induced by ephedrine in man. Am J Physiol. 1985;248(5 Pt 1):E507-515.
Astrup A, Gotzsche PC, van de Werken K, et al. Meta-analysis of resting metabolic rate in formerly obese subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69(6):1117-1122.
Baba S, Tatsumi M, Ishimori T, et al. Effect of nicotine and ephedrine on the accumulation of 18F-FDG in brown adipose tissue. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(6):981-986. doi:10.2967/jnumed.106.039065.
Bal NC, Maurya SK, Sopariwala DH, et al. Sarcolipin is a newly identified regulator of muscle-based thermogenesis in mammals. Nat Med. 2012;18(10):1575-1579. doi:10.1038/nm.2897.
Batsis JA, Mackenzie TA, Barre LK, et al. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and mortality in older adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014;68(9):1001-1007. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2014.117.
Bogardus C, Lillioja S, Ravussin E, et al. Familial dependence of the resting metabolic rate. N Engl J Med. 1986;315(2):96-100. doi:10.1056/NEJM198607103150205.
Bosy-Westphal A, Eichhorn C, Kutzner D, et al. The age-related decline in resting energy expenditure in humans is due to the loss of fat-free mass and to alterations in its metabolically active components. J Nutr. 2003;133(7):2356-2362.
Bosy-Westphal A, Reinecke U, Schlorke T, et al. Effect of organ and tissue masses on resting energy expenditure in underweight, normal weight and obese adults. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(1):72-79. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802526.
Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, et al. Genetic effect in resting and exercise metabolic rates. Metab Clin Exper. 1989;38(4):364-370.
Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP, et al. The response to long-term overfeeding in identical twins. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(21):1477-1482. doi:10.1056/NEJM199005243222101.
Brundin T, Thorne A, Wahren J. Heat leakage across the abdominal wall and meal-induced thermogenesis in normal-weight and obese subjects. Metab Clin Exper. 1992;41(1):49-55.
Caleyachetty R, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Tait CA, et al. Prevalence of behavioural risk factors for cardiovascular disease in adolescents in low-income and middle-income countries: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(7):535-544. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00076-5.
Cypess AM, Lehman S, Williams G, et al. Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(15):1509-1517. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810780.
Eckel RH, Kahn SE, Ferrannini E, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes: what can be unified and what needs to be individualized? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(6):1654-1663. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0585.
Elia M, Cummings JH. Physiological aspects of energy metabolism and gastrointestinal effects of carbohydrates. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61(Suppl 1):S40-74. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602938.
Enerback S, Jacobsson A, Simpson EM, et al. Mice lacking mitochondrial uncoupling protein are cold-sensitive but not obese. Nature. 1997;387(6628):90-94. doi:10.1038/387090a0.
FAO. Human energy requirements: report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Food Nutr Bull. 2005;26(1):166.
Feldmann HM, Golozoubova V, Cannon B, et al. UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality. Cell Metab. 2009;9(2):203-209. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.12.014.
Flatt JP, Ravussin E, Acheson KJ, et al. Effects of dietary fat on postprandial substrate oxidation and on carbohydrate and fat balances. J Clin Invest. 1985;76(3):1019-1024. doi:10.1172/JCI112054.
Frayn KN. Adipose tissue as a buffer for daily lipid flux. Diabetologia. 2002;45(9):1201-1210. doi:10.1007/s00125-002-0873-y.
Golozoubova V, Hohtola E, Matthias A, et al. Only UCP1 can mediate adaptive nonshivering thermogenesis in the cold. FASEB J. 2001;15(11):2048-2050. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0536fje.
Green DE, Zande HD. Universal energy principle of biological systems and the unity of bioenergetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981;78(9):5344-5347.
Harms M, Seale P. Brown and beige fat: development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat Med. 2013;19(10):1252-1263. doi:10.1038/nm.3361.
Harper ME, Green K, Brand MD. The efficiency of cellular energy transduction and its implications for obesity. Annu Rev Nutr. 2008;28:13-33. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155357.
Hill JO, Peters JC, Reed GW, et al. Nutrient balance in humans: effects of diet composition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;54(1):10-17.
Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Peters JC. Energy balance and obesity. Circulation. 2012;126(1):126-132. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.087213.
Jequier E, Acheson K, Schutz Y. Assessment of energy expenditure and fuel utilization in man. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:187-208. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.001155.
Johannsen DL, Ravussin E. Spontaneous physical activity: relationship between fidgeting and body weight control. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2008;15(5):409-415. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e32830b10bb.
Johnstone AM, Murison SD, Duncan JS, et al. Factors influencing variation in basal metabolic rate include fat-free mass, fat mass, age, and circulating thyroxine but not sex, circulating leptin, or triiodothyronine. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82(5):941-948.
Joint WHOFAOUNUEC. Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2007;935:1-265.
Keys A, Taylor HL, Grande F. Basal metabolism and age of adult man. Metab Clin Exp. 1973;22(4):579-587.
Kim TN, Choi KM. The implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity on cardiometabolic disease. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(7):1171-1178. doi:10.1002/jcb.25077.
Kontani Y, Wang Y, Kimura K, et al. UCP1 deficiency increases susceptibility to diet-induced obesity with age. Aging Cell. 2005;4(3):147-155. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00157.x.
Kopecky J, Clarke G, Enerback S, et al. Expression of the mitochondrial uncoupling protein gene from the aP2 gene promoter prevents genetic obesity. J Clin Invest. 1995;96(6):2914-2923. doi:10.1172/JCI118363.
Kummitha CM, Kalhan SC, Saidel GM, et al. Catheter-based induction of renal ischemia/reperfusion in swine: description of an experimental model. Physiol Rep. 2014;2(9):pii: e121590.
Larson DE, Ferraro RT, Robertson DS, et al. Energy metabolism in weight-stable postobese individuals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;62(4):735-739.
Leibel RL, Rosenbaum M, Hirsch J. Changes in energy expenditure resulting from altered body weight. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(10):621-628. doi:10.1056/NEJM199503093321001.
Levine JA, Eberhardt NL, Jensen MD. Role of nonexercise activity thermogenesis in resistance to fat gain in humans. Science. 1999;283(5399):212-214.
Lin J, Wu H, Tarr PT, et al. Transcriptional co-activator PGC-1 alpha drives the formation of slow-twitch muscle fibres. Nature. 2002;418(6899):797-801. doi:10.1038/nature00904.
Livesey G, Elia M. Estimation of energy expenditure, net carbohydrate utilization, and net fat oxidation and synthesis by indirect calorimetry: evaluation of errors with special reference to the detailed composition of fuels. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988;47(4):608-628.
Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518(7538):197-206. doi:10.1038/nature14177.
Loos RJ, Bouchard C. FTO: the first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes Rev. 2008;9(3):246-250. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2008.00481.x.
Loos RJ, Lindgren CM, Li S, et al. Common variants near MC4R are associated with fat mass, weight and risk of obesity. Nature genetics. 2008;40(6):768-775. doi:10.1038/ng.140.
Maurya SK, Bal NC, Sopariwala DH, et al. Sarcolipin is a key determinant of the basal metabolic rate, and its overexpression enhances energy expenditure and resistance against diet-induced obesity. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(17):10840-10849. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.636878.
Plasqui G, Bonomi AG, Westerterp KR. Daily physical activity assessment with accelerometers: new insights and validation studies. Obes Rev. 2013;14(6):451-462. doi:10.1111/obr.12021.
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, et al. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 1998;92(6):829-839.
Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Anderson TE, et al. Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. Methods and results using a respiratory chamber. J Clin Invest. 1986;78(6):1568-1578. doi:10.1172/JCI112749.
Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Knowler WC, et al. Reduced rate of energy expenditure as a risk factor for body-weight gain. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(8):467-472. doi:10.1056/NEJM198802253180802.
Ravussin E, Harper IT, Rising R, et al. Energy expenditure by doubly labeled water: validation in lean and obese subjects. Am J Physiol. 1991;261(3 Pt 1):E402-409.
Redman LM, Heilbronn LK, Martin CK, et al. Metabolic and behavioral compensations in response to caloric restriction: implications for the maintenance of weight loss. PLoS One. 2009;4(2), e4377. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004377.
Rising R, Keys A, Ravussin E, et al. Concomitant interindividual variation in body temperature and metabolic rate. Am J Physiol. 1992;263(4 Pt 1):E730-734.
Rolfe DF, Brown GC. Cellular energy utilization and molecular origin of standard metabolic rate in mammals. Physiol Rev. 1997;77(3):731-758.
Rosenbaum M, Goldsmith R, Bloomfield D, et al. Low-dose leptin reverses skeletal muscle, autonomic, and neuroendocrine adaptations to maintenance of reduced weight. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3579-3586. doi:10.1172/JCI25977.
Saad MF, Alger SA, Zurlo F, et al. Ethnic differences in sympathetic nervous system-mediated energy expenditure. Am J Physiol. 1991;261(6 Pt 1):E789-794.
Saito M, Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Matsushita M, et al. High incidence of metabolically active brown adipose tissue in healthy adult humans: effects of cold exposure and adiposity. Diabetes. 2009;58(7):1526-1531. doi:10.2337/db09-0530.
Schoeller DA. Recent advances from application of doubly labeled water to measurement of human energy expenditure. J Nutr. 1999;129(10):1765-1768.
Schulz LO, Schoeller DA. A compilation of total daily energy expenditures and body weights in healthy adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994;60(5):676-681.
Shekelle PG, Hardy ML, Morton SC, et al. Efficacy and safety of ephedra and ephedrine for weight loss and athletic performance: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2003;289(12):1537-1545. doi:10.1001/jama.289.12.1537.
Sims EA, Danforth E Jr, Horton ES, et al. Endocrine and metabolic effects of experimental obesity in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1973;29:457-496.
Smith SR, de Jonge L, Zachwieja JJ, et al. Fat and carbohydrate balances during adaptation to a high-fat. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(2):450-457.
Speakman JR. The history and theory of the doubly labeled water technique. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;68(4):932S-938S.
Spiller RC. Intestinal absorptive function. Gut. 1994;35(1 Suppl):S5-9.
Spraul M, Ravussin E, Fontvieille AM, et al. Reduced sympathetic nervous activity. A potential mechanism predisposing to body weight gain. J Clin Invest. 1993;92(4):1730-1735. doi:10.1172/JCI116760.
Swinburn BA, Sacks G, Hall KD, et al. The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):804-814. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60813-1.
Tataranni PA, Larson DE, Snitker S, et al. Thermic effect of food in humans: methods and results from use of a respiratory chamber. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;61(5):1013-1019.
Tataranni PA, Young JB, Bogardus C, et al. A low sympathoadrenal activity is associated with body weight gain and development of central adiposity in Pima Indian men. Obes Res. 1997;5(4):341-347.
van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Vanhommerig JW, Smulders NM, et al. Cold-activated brown adipose tissue in healthy men. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(15):1500-1508. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808718.
van Ooijen AM, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, van Steenhoven AA, et al. Cold-induced heat production preceding shivering. Br J Nutr. 2005;93(3):387-391.
Villablanca PA, Alegria JR, Mookadam F, et al. Nonexercise activity thermogenesis in obesity management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90(4):509-519. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.02.001.
Virtanen KA, Lidell ME, Orava J, et al. Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(15):1518-1525. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0808949.
Vybiral S, Lesna I, Jansky L, et al. Thermoregulation in winter swimmers and physiological significance of human catecholamine thermogenesis. Exp Physiol. 2000;85(3):321-326.
Westerterp KR, Speakman JR. Physical activity energy expenditure has not declined since the 1980s and matches energy expenditures of wild mammals. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32(8):1256-1263. doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.74.
Weststrate JA. Resting metabolic rate and diet-induced thermogenesis: a methodological reappraisal. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993;58(5):592-601.
Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Snitker S, et al. Increase in insulin action and fat oxidation after treatment with CL 316,243, a highly selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist in humans. Diabetes. 1998;47(10):1555-1561.
Weyer C, Pratley RE, Salbe AD, et al. Energy expenditure, fat oxidation, and body weight regulation: a study of metabolic adaptation to long-term weight change. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(3):1087-1094. doi:10.1210/jcem.85.3.6447.
Wijers SL, Schrauwen P, Saris WH, et al. Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial uncoupling is associated with cold induced adaptive thermogenesis. PLoS One. 2008;3(3), e1777. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001777.
Zingaretti MC, Crosta F, Vitali A, et al. The presence of UCP1 demonstrates that metabolically active adipose tissue in the neck of adult humans truly represents brown adipose tissue. FASEB J. 2009;23(9):3113-3120. doi:10.1096/fj.09-133546.
Zurlo F, Ferraro RT, Fontvielle AM, et al. Spontaneous physical activity and obesity: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies in Pima Indians. Am J Physiol. 1992;263(2 Pt 1):E296-300.
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by grant P01-DK-049210 from the National Institutes of Health, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this entry
Cite this entry
Ahima, R.S. (2016). Principles of Energy Homeostasis. In: Ahima, R.S. (eds) Metabolic Syndrome. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11251-0_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11251-0_48
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-11250-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-11251-0
eBook Packages: MedicineReference Module Medicine