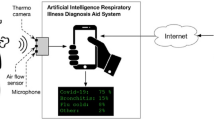
Abstract
Artificial intelligence has developed in recent years. It is mostly enviable to discover the facility of contemporaneous state-of-the-art techniques and to examine lung nodule features in terms of a large population. Now a days lung plays a major role all over the world in early prevention in disease identification. The latest progress of deep learning sustains the recognition and categorization of medical images of respiratory problems. There are varieties of lung diseases to be analyzed to select the high mortality rate among them. In this paper, we have provided a comprehensive study of several lung ailments, in particular lung cancer, pneumonia, and COVID-19/SARS, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Existing deep learning methodology used to diagnose lung diseases are clearly explained and it will be helpful for the lung disease identify the system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Human Organs and Organ Systems Homepage. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Book%3A_Human_Biology_(Wakim_and_Grewal)/10%3A_Introduction_to_the_Human_Body/10.4%3A_Human_Organs_and_Organ_Systems
Çetin, G., Akkulak, G., Özdemir, S.: Locate the Internal organs in the human body: a survey in Turkey. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 116, 2819–2824 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.663
Meng, Y.: A machine learning approach to classifying self-reported health status in a cohort of patients with heart disease using activity tracker data. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inf. 24(3), 878–884 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2922178
Hussain, M.A., Hamarneh, G., Garbi, R.: Cascaded regression neural nets for kidney localization and segmentation-free volume estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40(6), 1555–1567 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2021.3060465
Ibragimov, B., Toesca, D.A.S., Yuan, Y., Koong, A.C., Chang, D.T., Xing, L.: Neural networks for deep radiotherapy dose analysis and prediction of liver SBRT outcomes. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 23(5), 1821–1833 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2904078
Alves, S.S.A., de Souza, E., Reboucas, S.A., de Oliveira, F., Braga, A.M., Filho, P.P.R.: Lung diseases classification by analysis of lung tissue densities. IEEE Latin America Trans. 18(09), 1329–1336 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TLA.2020.9381790
Ibrahim, D.M., Elshennawy, N.M., Sarhan, A.M.: Deep-chest: multi-classification deep learning model for diagnosing COVID-19, pneumonia, and lung cancer chest diseases. Comput. Biol. Med. 132, 104348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104348
WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard Homepage. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 27 Dec 2021
How Lungs Work | American Lung Association Homepage. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/how-lungs-work. Accessed 27 Dec 2021
Lung Anatomy, Function, and Homepage. https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/lung. Accessed 10 Dec 2021
Dobric, A., et al.: Novel pharmacological strategies to treat cognitive dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. A., 108017 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHARMTHERA.2021.108017
Tomita, K., et al.: Deep learning facilitates the diagnosis of adult asthma. Allergol. Int. 68(4), 456–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ALIT.2019.04.010
Yu, G., et al.: Identification of pediatric respiratory diseases using a fine-grained diagnosis system. J. Biomed. Inform. 117, 103754 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBI.2021.103754
Jefferson, N., Fitzgerald, K.: Antibiotic stewardship for treatment of acute bronchitis in retail health. J. Nurse Practit. 16(8), 608–611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurpra.2020.05.005
Stokes, K., et al.: A machine learning model for supporting symptom-based referral and diagnosis of bronchitis and pneumonia in limited resource settings. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 41(4), 1288–1302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBE.2021.09.002
Manickam, A., JJiang, Y., Zhou, A., Soundrapandiyan, R., Samuel, D.: Automated pneumonia detection on chest X-ray images: a deep learning approach with different optimizers and transfer learning architectures. Measurement 184, 109953 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109953
Kim, G.H.J., Shi, Y., Yu, W., Wong, W.K.: A study design for statistical learning technique to predict radiological progression with an application of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using chest CT images. Contemp. Clin. Trials 104, 106333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCT.2021.106333
Togo, R., et al.: Cardiac sarcoidosis classification with deep convolutional neural network-based features using polar maps. Comput. Biol. Med. 104, 81–86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPBIOMED.2018.11.008
Tsai, C.H., et al.: Automatic deep learning-based pleural effusion classification in lung ultrasound images for respiratory pathology diagnosis. Phys. Medica 83, 38–45 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJMP.2021.02.023
Piper, A.J.: Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome. In: Modulation of Sleep by Obesity, Diabetes, Age, and Diet, pp. 91–100. Elsevier (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-420168-2.00011-9
Schmuelling, L.: Deep learning-based automated detection of pulmonary embolism on CT pulmonary angiograms: no significant effects on report communication times and patient turnaround in the emergency department nine months after technical implementation. Eur. J. Radiol. 141, 109816 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109816
JWu, J.: Refining diagnostic criteria for paediatric bronchiectasis using low-dose CT scan. Respir. Med. 187, 106547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106547
Crivelli, P.: Role of thoracic imaging in the management of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Respir. Med. 157, 14–20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2019.08.013
Zucker, E.J.: Deep learning to automate Brasfield chest radiographic scoring for cystic fibrosis. J. Cystic Fibrosis 19(1), 131–138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcf.2019.04.016
Agarwala, S.: Deep learning for screening of interstitial lung disease patterns in high-resolution CT images. Clin. Radiol. 75(6), 481.e1-481.e8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2020.01.010
Doppalapudi, S., Qiu, R.G., Badr, Y.: Lung cancer survival period prediction and understanding: deep learning approaches. Int. J. Med. Inf. 148, 104371 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104371
Sathitratanacheewin, S., Sunanta, P., Pongpirul, K.: Deep learning for automated classification of tuberculosis-related chest X-Ray: dataset distribution shift limits diagnostic performance generalizability. Heliyon 6(8), e04614 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04614
Reamaroon, N., Sjoding, M.W., Gryak, J., Athey, B.D., Najarian, K., Derksen, H.: Automated detection of acute respiratory distress syndrome from chest X-Rays using Directionality Measure and deep learning features. Comput. Biol. Med. 134, 104463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104463
Ott, J.: Detecting pulmonary Coccidioidomycosis with deep convolutional neural networks. Mach Learn Appl 5, 100040 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100040
Miller, J.: A structured program maximizes benefit of lung cancer screening in an area of endemic histoplasmosis. Ann. Thoracic Surg. 114(1), 241–247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2021.06.070
Aliboni, L.: Quantitative CT analysis in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a convolutional neural network approach. Acad. Radiol. 29, S31–S40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2020.10.009
Zan, A., et al.: DeepFlu: a deep learning approach for forecasting symptomatic influenza a infection based on pre-exposure gene expression. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 213, 106495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMPB.2021.106495
Galateau Salle, F., et al.: Comprehensive molecular and pathologic evaluation of transitional mesothelioma assisted by deep learning approach: a multi-institutional study of the international mesothelioma panel from the MESOPATH reference center. J. Thorac. Oncol. 15(6), 1037–1053 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JTHO.2020.01.025
Sharan, R.V., Berkovsky, S., Navarro, D.F., Xiong, H., Jaffe, A.: Detecting pertussis in the pediatric population using respiratory sound events and CNN. Biomed Sig Process Control 68, 102722 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102722
Jimenez-del-Toro, O.: A lung graph model for the radiological assessment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in CT. Comput. Biol. Med. 125, 103962 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103962
Long, K.: Probability-based Mask R-CNN for pulmonary embolism detection. Neurocomputing 422, 345–353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2020.10.022
Sharma, A., Tiwari, S., Deb, M.K., Marty, J.L.: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): a global pandemic and treatment strategies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 56(2), 106054 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106054
Li, X.: Deep learning-enabled system for rapid pneumothorax screening on chest CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 120, 108692 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108692
Jiang, J., et al.: Multiple resolution residually connected feature streams for automatic lung tumor segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(1), 134–144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2857800
Surendar, P.: Diagnosis of lung cancer using hybrid deep neural network with adaptive sine cosine crow search algorithm, Elsevier. Accessed Dec 06 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877750321000636
Guo, Y.: Histological subtypes classification of lung cancers on CT images using 3D Deep learning and radiomics. Acad. Radiol. 28(9), e258–e266 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACRA.2020.06.010
Tortora, M.: Deep reinforcement learning for fractionated radiotherapy in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Artif. Intell. Med. 119, p. 102137 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARTMED.2021.102137
Su, Y.: Lung nodule detection based on faster R-CNN framework. Elsevier. Accessed 6 Dec 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169260720316990
Singh, A., Lall, B., Panigrahi, B.: Deep LF-Net: Semantic lung segmentation from Indian chest radiographs including severely unhealthy images. Elsevier. Accessed 6 Dec 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1746809421002639
Trajanovski, S.: Towards radiologist-level cancer risk assessment in CT lung screening using deep learning. Elsevier (2019). Accessed 06 Dec 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895611121000318
Xu, X.: A deep learning system to screen novel coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Engineering 6(10), 1122–1129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2020.04.010
Jiang, H., Tang, S., Liu, W., Zhang, Y.: Deep learning for COVID-19 chest CT (computed tomography) image analysis: a lesson from lung cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 19, 1391–1399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSBJ.2021.02.016
Hassantabar, S., Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A.: Diagnosis and detection of infected tissue of COVID-19 patients based on lung x-ray image using convolutional neural network approaches. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHAOS.2020.110170
Tuncer, S.A., Ayyıldız, H., Kalaycı, M., Tuncer, T.: Scat-NET: COVID-19 diagnosis with a CNN model using scattergram images. Comput. Biol. Med. 135, 104579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPBIOMED.2021.104579
Shibly, K.H., Dey, S.K., Islam, M.T.U., Rahman, M.M.: COVID faster R–CNN: a novel framework to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-Ray images. Inf. Med. Unlocked 20, 100405 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IMU.2020.100405
Islam, M.Z., Islam, M.M., Asraf, A.: A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inf. Med. Unlocked 20, 100412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IMU.2020.100412
Manickam, A., Jiang, J., Zhou, Y., Sagar, A., Soundrapandiyan, R., Dinesh Jackson Samuel, R.: Automated pneumonia detection on chest X-ray images: a deep learning approach with different optimizers and transfer learning architectures. Measurement 184, 109953 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2021.109953
Liz, H., Sánchez-Montañés, M., Tagarro, A., Domínguez-Rodríguez, S., Dagan, R., Camacho, D.: Ensembles of Convolutional Neural Network models for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 122, 220–233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUTURE.2021.04.007
Altan, G., Kutlu, Y., Allahverdi, N.: Deep learning on computerized analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inf. 24(5), 1344–1350 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2019.2931395
Du, R.: Identification of COPD from multi-view snapshots of 3D Lung Airway Tree via Deep CNN. IEEE Access 8, 38907–38919 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974617
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumaran, N.V., Preethi, D.M.D. (2022). Impact of Chronic Lung Disease Using Deep Learning: A Survey. In: Neuhold, E.J., Fernando, X., Lu, J., Piramuthu, S., Chandrabose, A. (eds) Computer, Communication, and Signal Processing. ICCCSP 2022. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 651. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-11633-9_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-11633-9_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-11632-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-11633-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)