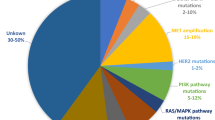
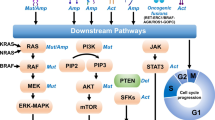
Abstract
Oncogenic mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are identified in a subset of non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC). These alterations lead to constitutive EGFR activation and upregulation of pathways promoting cell survival and proliferation. The development of small molecule inhibitors of EGFR has transformed the care of patients with advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC. We review here the clinical development and activity of the third-generation EGFR inhibitor osimertinib in the advanced and adjuvant settings. As with other targeted therapies, resistance to osimertinib is common and limits the efficacy of this agent. Here we present an overview of reported acquired resistance mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance. The heterogeneity of resistance mechanisms (including secondary EGFR mutations and diverse EGFR-independent alterations) presents a major therapeutic challenge in EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Midha A, Dearden S, McCormack R (2015) EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: a systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am J Cancer Res 5:2892–2911
Dearden S, Stevens J, Wu YL et al (2013) Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann Oncol 24:2371–2376
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S et al (2014) A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol 9:154–162
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M et al (2004) EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13306–13311
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:169–181
Janne PA, Neal JW, Camidge DR et al (2019) Antitumor activity of TAK-788 in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Clin Oncol 37:9007–9007
Heymach J, Negrao M, Robichaux J et al (2018) OA02.06 A phase II trial of Poziotinib in EGFR and HER2 exon 20 mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J Thorac Oncol 13:S323–S324
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S et al (2014) AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov 4:1046–1061
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS et al (2011) Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res 17:1616–1622
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N et al (2013) Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19:2240–2247
Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV et al (2008) The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2070–2075
Sos ML, Rode HB, Heynck S et al (2010) Chemogenomic profiling provides insights into the limited activity of irreversible EGFR inhibitors in tumor cells expressing the T790M EGFR resistance mutation. Cancer Res 70:868–874
Ballard P, Yates JW, Yang Z et al (2016) Preclinical comparison of Osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin Cancer Res 22:5130–5140
Janne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW et al (2015) AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372:1689–1699
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ et al (2017) Osimertinib or platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376:629–640
Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, Lee CK et al (2018) Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36:841–849
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J et al (2018) Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:113–125
Nanjo S, Ebi H, Arai S et al (2016) High efficacy of third generation EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 in a leptomeningeal carcinomatosis model with EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:3847–3856
Nanjo S, Hata A, Okuda C et al (2018) Standard-dose osimertinib for refractory leptomeningeal metastases in T790M-positive EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 118:32–37
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC et al (2018) CNS response to Osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol:JCO2018783118
Wu YL, Tsuboi M, He J et al (2020) Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 383:1711–1723
Piotrowska Z, Isozaki H, Lennerz JK et al (2018) Landscape of acquired resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-mutant NSCLC and clinical validation of combined EGFR and RET inhibition with Osimertinib and BLU-667 for acquired RET fusion. Cancer Discov 8:1529–1539
Bordi P, Del Re M, Minari R et al (2019) From the beginning to resistance: study of plasma monitoring and resistance mechanisms in a cohort of patients treated with osimertinib for advanced T790M-positive NSCLC. Lung Cancer 131:78–85
Ercan D, Choi HG, Yun CH et al (2015) EGFR mutations and resistance to irreversible pyrimidine-based EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 21:3913–3923
Schmid S, Klingbiel D, Aeppli S et al (2019) Patterns of progression on osimertinib in EGFR T790M positive NSCLC: a Swiss cohort study. Lung Cancer 130:149–155
Brown BP, Zhang YK, Westover D et al (2019) On-target resistance to the mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor Osimertinib can develop in an allele-specific manner dependent on the original EGFR-activating mutation. Clin Cancer Res 25:3341–3351
Uchibori K, Inase N, Araki M et al (2017) Brigatinib combined with anti-EGFR antibody overcomes osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 8:14768
Niederst MJ, Hu H, Mulvey HE et al (2015) The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies. Clin Cancer Res 21:3924–3933
Jia Y, Yun CH, Park E et al (2016) Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 534:129–132
Oztan A, Fischer S, Schrock AB et al (2017) Emergence of EGFR G724S mutation in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma post progression on osimertinib. Lung Cancer 111:84–87
Zhang Q, Zhang XC, Yang JJ et al (2018) EGFR L792H and G796R: two novel mutations mediating resistance to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor Osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol 13:1415–1421
Ma L, Chen R, Wang F et al (2019) EGFR L718Q mutation occurs without T790M mutation in a lung adenocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to osimertinib. Ann Transl Med 7:207
Starrett JH, Guernet AA, Cuomo ME et al (2020) Drug sensitivity and allele specificity of first-line Osimertinib resistance EGFR mutations. Cancer Res 80:2017–2030
Nakatani K, Yamaoka T, Ohba M et al (2019) KRAS and EGFR amplifications mediate resistance to Rociletinib and Osimertinib in acquired Afatinib-resistant NSCLC harboring exon 19 deletion/T790M in EGFR. Mol Cancer Ther 18:112–126
Knebel FH, Bettoni F, Shimada AK et al (2017) Sequential liquid biopsies reveal dynamic alterations of EGFR driver mutations and indicate EGFR amplification as a new mechanism of resistance to osimertinib in NSCLC. Lung Cancer 108:238–241
Planchard D, Loriot Y, Andre F et al (2015) EGFR-independent mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC patients. Ann Oncol 26:2073–2078
Ortiz-Cuaran S, Scheffler M, Plenker D et al (2016) Heterogeneous mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 22:4837–4847
Sequist LV, Han JY, Ahn MJ et al (2020) Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol 21:373–386
Vojnic M, Kubota D, Kurzatkowski C et al (2019) Acquired BRAF rearrangements induce secondary resistance to EGFR therapy in EGFR-mutated lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol 14:802–815
Weng CH, Chen LY, Lin YC et al (2019) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI. Oncogene 38:455–468
Taniguchi H, Yamada T, Wang R et al (2019) AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat Commun 10:259
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D et al (2011) Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med 3:75ra26
Marcoux N, Gettinger SN, O’Kane G et al (2019) EGFR-mutant adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung Cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinomas: clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol 37:278–285
Ferrer L, Giaj Levra M, Brevet M et al (2019) A brief report of transformation from NSCLC to SCLC: molecular and therapeutic characteristics. J Thorac Oncol 14:130–134
Antony J, Huang RY (2017) AXL-driven EMT state as a targetable conduit in cancer. Cancer Res 77:3725–3732
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Talsania, A., Zhang, J., Wilson, F.H. (2021). Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Clinical Activity and Mechanisms of Resistance. In: Chiang, A.C., Herbst, R.S. (eds) Lung Cancer. Current Cancer Research. Humana, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74028-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-74028-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-74027-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-74028-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)