Abstract
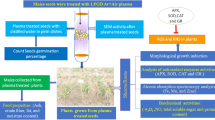
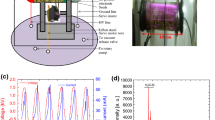
Atmospheric pressure plasma fit great in agricultural applications due to their reduced complexity and to their chemical reactivity, being produced in air. In this work we present some of our results regarding agricultural applications of plasmas, obtained with seeds and soil exposed in atmospheric pressure plasmas conditions. The treatment of seeds shown a non-linear behavior with the exposure time and voltage for seed germination and development. The effects are strongly dependent on the type of seeds. Radish seeds were stimulated with lower voltages plasma and shorter exposures as compared to broccoli. In some conditions plasma exposure inhibited the growth, with lower germination rates than un-exposed samples and smaller size of the sprouts. For soil treatment we found the possibility to increase the nitrogen content of soil when tuning plasma treatment conditions, and we believe it is due to the reaction between reactive nitrogen species produced in plasma and organic components in soil.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitazaki S, Sarinont T, Koga K, Hayashi N, Shiratani M (2014) Plasma induced long-therm growth enhancement of Raphanus sativus L. using combinatorial atmospheric air dielectric barrier discharge plasmas. Curr Appl Phys 14:S149–S153
Dhayal M, Lee SY, Park S-U (2006) Using low-pressure plasma for Carthamus tinctorium L. seed surface modification. Vacuum 80:499–506
Zahoranova Z, Henselova M, Hudecova D, Kalinakova B, Kovacik D, Medvecka V, Cernak M (2016) Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma on the wheat seedlings vigor and on the inactivation of microorganisms on the seed surface. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36:397–414
Ito, M., Ohta, T., Hori, M.: Plasma agriculture. J Korean Phys Soc 60, 937–943 (2012)
Iseki, S., Ohta, T., Aomatsu, A., Ito, M., Kano, H., Higashijima, Y., Hori, M.: Rapid inactivation of Penicillium digitatum spores using high-density nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl Phys Lett 96, 153704 (2010)
Koga K, Thapanut S, Amano T, Seo H, Itagaki N, Hayashi N, Shiratani M (2016) Simple method of improving harvest by nonthermal air plasma irradiation of seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.). Appl Phys Express 9:016201
Jiafeng, J., Xin, H., Ling, L., Jiangang, L., Hanliang, S., Qilai, X., Renhong, Y., Yuanhua, D.: Effect of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and growth of wheat. Plasma Sci Technol 16, 54 (2014)
Jiang, J., Lu, Y., Li, J., He, X., Shao, H., Dong, Y.: Effect of seed treatment by cold plasma on the resistance of tomato to Ralstonia solanacearum (Bacterial Wilt). PLoS ONE 9, e97753 (2014)
Ling, L., Jiangang, L., Minchong, S., Chunlei, Z., Yuanhua, D.: Cold plasma treatment enhances oilseed rape seed germination under drought stress. Sci Rep 5, 13033 (2015)
Bormashenko, E., Grynyov, R., Bormashenko, Y., Drori, E.: Cold radiofrequency plasma treatment modifies wettability and germination speed of plant seeds. Sci Rep 2, 741 (2012)
Donkor, O.N., Stojanovksa, L., Ginn, P., Ashton, J., Vasiljevic, T.: Germinated grains—sources of bioactive compounds. Food Chem 135(3), 950–959 (2012)
Gan, R.Y., Lui, W.Y., Wu, K., Chan, C.L., Dai, S.H., Sui, Z.Q., Corke, H.: Bioactive compounds and biactivities of germinated edible seeds and sprouts: an updated review. Trends Food Sci Technol 59, 1–14 (2017)
Nestle, M.: Broccoli sprouts in cancer prevention. Nutr Rev 56(4), 127–130 (1998)
Eto, H., Ono, Y., Ogino, A., Nagatsu, M.: Low-temperature sterilization of wrapped materials using flexible sheet-type dielectric barrier discharge. Appl Phys Lett 93, 221502 (2008)
Jayasena, D.D., Kim, H.J., Yong, H.I., Park, S., Kim, K., Choe, W., Jo, C.: Flexible thin-layer dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment of pork butt and beef loin: effects on pathogen inactivation and meat-quality attributes. Food Microbiol 46, 51–57 (2015)
Patil, B.S., Wang, Q., Hessel, V., Lang, J.: Plasma N2-fixation: 1900–2014. Catal Today 256, 49–66 (2015)
Stryczewska, H.D., Ebihara, K., Takayama, M., Gyoutoku, Y., Tachibana, M.: Non-thermal plasma-based technology for soil treatment. Plasma Process Polym 2, 238–245 (2005)
Lichtenthaler, H.K., Wellburn, A.R.: Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biol Soc Trans 11, 591–592 (1985)
Gomez-Ramirez, A., Lopez-Santos, C., Cantos, M., Garcia, J.L., Molina, R., Cotrino, J., Espinos, J.P., Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.: Surface chemistry and germination improvement of Quinoa seeds subjected to plasma activation. Sci Rep 7, 5924 (2017)
Bafoil, M., Jemmat, A., Martinez, Y., Merbahi, N., Eichwald, O., Dunand, C., Mohammed, Y.: Effects of low temperature plasmas and plasma activated waters on Arabidopsis thaliana germination and growth. PLoS ONE 13(4), e0195512 (2017)
Guo, Q., Meng, Y., Qu, G., Wang, T., Yang, F., Liang, D., Hu, S.: Improvement of wheat seed vitality by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Bioelectromagnetics 39(2), 120–131 (2017)
Tounekti, T., Mujahid, Z.I., Khemira, H.: Non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma affects germination of coffee and grape seeds. AIP Conf Proc 1976, 020029 (2018)
Sidaway, G.H.: influence of electrostatic fields on seed germination. Nature 211, 303 (1966)
Pietruszewski S (2014) Electromagnetic fields, impact on seed germination and plant growth. Encycl Agrophys Encycl Earth Sci Ser 267–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Motrescu, I., Filip, M., Herciu, F.P., Jitareanu, G. (2020). Utilization of Atmospheric Plasmas for Agricultural Applications. In: Várkonyi-Kóczy, A. (eds) Engineering for Sustainable Future. INTER-ACADEMIA 2019. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 101. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36841-8_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36841-8_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36840-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36841-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)