Abstract
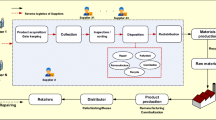
Depending on the significant increase in the consumption and as a result in the production has caused some problems besides its utilities. One of the biggest concerns at this point is the adverse environmental effects of this growth. Hence, most of the companies take into account the environmental considerations during the design and implementation of their business facilities within their supply chains. As a result of these developments, the attempt to design supply chains greener has increased both practically and theoretically. Various studies have been performed dealing with green supply chains. However, in this study, it is focused on the greenness assessment of supply chains under four stages including inbound logistics, in-plant logistics, outbound logistics and reverse logistics. Different from the few studies in the literature, intuitionistic fuzzy (IF) approach which enables to handle fuzziness and hesitancy is used within DEMATEL and ANP techniques to measure supply chain greenness. The related steps are explicitly provided within the proposed methodology. In general, firstly the main dimensions of greenness are determined with the related indicators. Then, regarding the dependency between the dimensions, the relation network is obtained via IF-DEMATEL by taking the evaluations of supply chain experts. Afterwards, based on the network diagram and expert judgments, the importance weights of dimensions are provided with IF-ANP and used in the developed greenness scoring system. An application in a firm’s supply chain is performed to demonstrate the validation of the proposed methodology and consequently, the greenness score is obtained.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarkis, J.: A strategic decision framework for green supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 11(4), 397–409 (2003)
Barnes Jr., J.H.: Recycling: a problem in reverse logistics. J. Macromark. 2(2), 31–37 (1982)
Bloom, G.F., Morton, M.S.S.: Hazardous waste is every manager’s problem. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 32(4), 75 (1991)
Drumwright, M.E.: Socially responsible organizational buying: environmental concern as a noneconomic buying criterion. J. Mark. 58(3), 1–19 (1994)
Sarkis, J.: Manufacturing strategy and environmental consciousness. Technovation 15(2), 79–97 (1995)
Wilkerson, T.: Can one green deliver another? Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation. Retrieved January, 10, 2012 (2005)
Topgul, M.H., Kilic, H.S., Tuzkaya, G.: Assessment of supply chain greenness: a literature review. In: Green Production Strategies for Sustainability (pp. 27–53). IGI Global (2018)
Sarkis, J., Weinrach, J.: Using data envelopment analysis to evaluate environmentally conscious waste treatment technology. J. Clean. Prod. 9(5), 417–427 (2001)
Lakhal, S.Y., H’Mida, S., Béland, M., Kassogue, C.O.: Green supply chain parameters for companies in the lumber industry. In: Supply Chain discussion paper (2004)
Zhu, Q., Sarkis, J., Geng, Y.: Green supply chain management in China: pressures, practices and performance. Int. J. Oper. & Prod. Manag. 25(5), 449–468 (2005)
Hervani, A.A., Helms, M. M., Sarkis, J.: Performance measurement for green supply chain management. Benchmarking: Int. J. 12(4), 330–353 (2005)
Büyüközkan, G., Çifçi, G.: A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(3), 3000–3011 (2012)
Sangaiah, A.K., Ramachandran, M., Goa, X.Z., Zheng, X.: A fuzzy DEMATEL approach based on intuitionistic fuzzy information for evaluating knowledge transfer effectiveness in GSD projects. Int. J. Innovative Comput. Appl. 6(3–4) (2015)
Büyüközkan, G., Güleryüz, S., Karpak, B.: A new combined IF-DEMATEL and IF-ANP approach for CRM partner evaluation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 191, 194–206 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Topgul, M.H., Kilic, H.S., Tuzkaya, G. (2020). Supply Chain Greenness Assessment Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Approaches. In: Kahraman, C., Cebi, S., Cevik Onar, S., Oztaysi, B., Tolga, A., Sari, I. (eds) Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques in Big Data Analytics and Decision Making. INFUS 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1029. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23756-1_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23756-1_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23755-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23756-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)