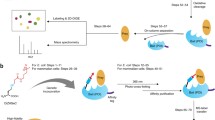
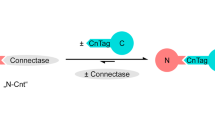
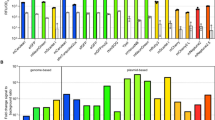
Abstract
Fundamental to all living organisms is the ability of proteins to interact with other biological molecules at the right time and location, with the proper affinity, and to do so reversibly. One well-established technique to study protein interactions is chemical cross-linking, a process in which proteins in close spatial proximity are covalently tethered together. An emerging technology that overcomes many limitations of traditional cross-linking methods is one in which photoactivatable cross-linking noncanonical amino acids are genetically encoded into a protein of interest using the cell’s native translational machinery. These proteins can then be used to trap interacting biomolecules upon UV illumination. Here, we describe a method for the site-specific incorporation of photoactivatable cross-linking amino acids into fluorescently tagged proteins of interest in E. coli. Photo-cross-linking and analysis by SDS-PAGE using in-gel fluorescence detection, which provides rapid, highly sensitive, and specific detection of cross-linked adducts even in impure systems, are also described. An example expression and cross-linking experiment involving transmembrane signaling of a bacterial second messenger receptor system that controls biofilm formation is shown. All reagents needed to carry out these experiments are commercially available, and do not require special or unique technology to perform, making this method tractable to a broad community studying protein structure and function.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melcher K, Chen HT (2007) Identification and analysis of multiprotein complexes through chemical crosslinking. Curr Protoc Cell Biol Chapter 17:Unit 17 10
Lowder MA, Appelbaum JS, Hobert EM, Schepartz A (2011) Visualizing protein partnerships in living cells and organisms. Curr Opin Chem Biol 15(6):781–788
Tanaka Y, Bond MR, Kohler JJ (2008) Photocrosslinkers illuminate interactions in living cells. Mol BioSyst 4(6):473–480
Mohibullah N, Hahn S (2008) Site-specific cross-linking of TBP in vivo and in vitro reveals a direct functional interaction with the SAGA subunit Spt3. Genes Dev 22(21):2994–3006
Rannversson H, Andersen J, Sorensen L, Bang-Andersen B, Park M, Huber T, Sakmar TP, Stromgaard K (2016) Genetically encoded photocrosslinkers locate the high-affinity binding site of antidepressant drugs in the human serotonin transporter. Nat Commun 7:11261
Wang L, Brock A, Herberich B, Schultz PG (2001) Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science 292(5516):498–500
Dumas A, Lercher L, Spicer CD, Davis BG (2015) Designing logical codon reassignment–expanding the chemistry in biology. Chem Sci 6(1):50–69
Chin JW, Santoro SW, Martin AB, King DS, Wang L, Schultz PG (2002) Addition of p-azido-L-phenylalanine to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. J Am Chem Soc 124(31):9026–9027
Young DD, Young TS, Jahnz M, Ahmad I, Spraggon G, Schultz PG (2011) An evolved aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with atypical polysubstrate specificity. Biochemistry 50(11):1894–1900
Miyake-Stoner SJ, Miller AM, Hammill JT, Peeler JC, Hess KR, Mehl RA, Brewer SH (2009) Probing protein folding using site-specifically encoded unnatural amino acids as FRET donors with tryptophan. Biochemistry 48(25):5953–5962
Chin JW, Martin AB, King DS, Wang L, Schultz PG (2002) Addition of a photocrosslinking amino acid to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(17):11020–11024
Chatterjee D, Cooley RB, Boyd CD, Mehl RA, O'Toole GA, Sondermann H (2014) Mechanistic insight into the conserved allosteric regulation of periplasmic proteolysis by the signaling molecule cyclic-di-GMP. eLlife 3:e03650
Peeler JC, Mehl RA (2012) Site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids as probes for protein conformational changes. Methods Mol Biol 794:125–134
Cooley RB, Smith TJ, Leung W, Tierney V, Borlee BR, O'Toole GA, Sondermann H (2016) Cyclic di-GMP-regulated Periplasmic proteolysis of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa type Vb secretion system substrate. J Bacteriol 198(1):66–76
Navarro MV, Newell PD, Krasteva PV, Chatterjee D, Madden DR, O'Toole GA, Sondermann H (2011) Structural basis for c-di-GMP-mediated inside-out signaling controlling periplasmic proteolysis. PLoS Biol 9(2):e1000588
Newell PD, Boyd CD, Sondermann H, O'Toole GA (2011) A c-di-GMP effector system controls cell adhesion by inside-out signaling and surface protein cleavage. PLoS Biol 9(2):e1000587
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):207–234
Boyd CD, Chatterjee D, Sondermann H, O'Toole GA (2012) LapG, required for modulating biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf0-1, is a calcium-dependent protease. J Bacteriol 194(16):4406–4414
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NIH under grants R01-AI097307 (H.S.) and F32-GM108440 (R.B.C.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Cooley, R.B., Sondermann, H. (2017). Probing Protein–Protein Interactions with Genetically Encoded Photoactivatable Cross-Linkers. In: Sauer, K. (eds) c-di-GMP Signaling. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1657. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7240-1_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7240-1_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7239-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7240-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols