Abstract
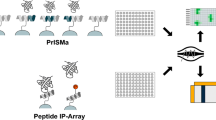
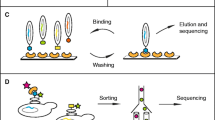
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) play a central role in almost all cellular processes. Recent technological advances have enabled the elucidation of an incredibly complex PPI network within the cell. However, protein interactions driven by posttranslational modifications (PTMs) such as phosphorylation, which comprises a significant part of the PPI network, have proven difficult to decipher systematically. Herein, we describe a reciprocal protein-peptide array strategy to uncover PPIs mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation and the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain. This strategy, namely combining peptide and protein domain arrays for PPI mapping, may be applicable for other peptide-binding modules.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kathiriya JJ, Pathak RR, Clayman E, Xue B, Uversky VN, Dave V (2014) Presence and utility of intrinsically disordered regions in kinases. Mol Biosyst 10(11):2876–2888. doi:10.1039/c4mb00224e
Lamesch P, Li N, Milstein S, Fan C, Hao T, Szabo G, Hu Z, Venkatesan K, Bethel G, Martin P, Rogers J, Lawlor S, McLaren S, Dricot A, Borick H, Cusick ME, Vandenhaute J, Dunham I, Hill DE, Vidal M (2007) hORFeome v3.1: a resource of human open reading frames representing over 10,000 human genes. Genomics 89(3):307–315. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.11.012
Brettner LM, Masel J (2012) Protein stickiness, rather than number of functional protein-protein interactions, predicts expression noise and plasticity in yeast. BMC Syst Biol 6:128. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-6-128
Huang H, Li L, Wu C, Schibli D, Colwill K, Ma S, Li C, Roy P, Ho K, Songyang Z, Pawson T, Gao Y, Li SS (2008) Defining the specificity space of the human SRC homology 2 domain. Mol Cell Proteomics 7(4):768–784. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700312-MCP200
Melton L (2004) Protein arrays: proteomics in multiplex. Nature 429(6987):101–107. doi:10.1038/429101a
Krallinger M, Leitner F, Rodriguez-Penagos C, Valencia A (2008) Overview of the protein-protein interaction annotation extraction task of BioCreative II. Genome Biol 9(Suppl 2):S4. doi:10.1186/gb-2008-9-s2-s4
Tong AHY, Drees B, Nardelli G, Bader GD, Brannetti B, Castagnoli L, Evangelista M, Ferracuti S, Nelson B, Paoluzi S, Quondam M, Zucconi A, Hogue CWV, Fields S, Boone C, Cesareni G (2002) A combined experimental and computational strategy to define protein interaction networks for peptide recognition modules. Science 295(5553):321–324
Xu Z, Hou T, Li N, Xu Y, Wang W (2012) Proteome-wide detection of Abl1 SH3-binding peptides by integrating computational prediction and peptide microarray. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(1):O111.010389. doi:10.1074/mcp.O111.010389
Liu H, Li L, Voss C, Wang F, Liu J, Li SS (2015) A comprehensive immunoreceptor phosphotyrosine-based signaling network revealed by reciprocal protein-peptide array screening. Mol Cell Proteomics 14:1846–1858. doi:10.1074/mcp.M115.047951
Biggar KK, Li SSC (2015) Non-histone protein methylation as a regulator of cellular signalling and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16(1):13
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants (to S.S.C.L.) from the Canadian Cancer Society and the Ontario Research Fund. S.S.C.L. holds the Canada Research Chair in Functional Genomics and Cellular Proteomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Liu, H., Voss, C., Li, S.S.C. (2017). Using Reciprocal Protein-Peptide Array Screening to Unravel Protein Interaction Networks. In: Machida, K., Liu, B. (eds) SH2 Domains. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1555. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6762-9_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-6760-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-6762-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols