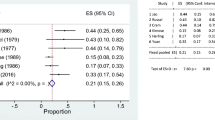
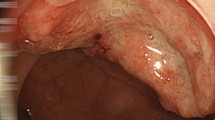
Abstract
Acute radiation proctopathy (ARP) and chronic radiation proctopathy (CRP) are common complications of pelvic radiation therapy. ARP is by definition a self-limited process and is characterized by abdominal symptoms and diarrhea that occur during radiation therapy. Treatment is directed at reduction of symptoms with stool bulking agents and anti-diarrheal medications. CRP occurs at least 3 months after completion of radiation therapy and is associated with significant morbidity. The most common symptom of CRP is rectal bleeding from rupture of mucosal telangiectasias and local mucosal ischemia. Functional symptoms occur from loss of rectal compliance and anal sphincter injury. These symptoms include urgency, tenesmus, increased stool frequency and fecal incontinence. These problems have received less attention in the medical literature. Profound blood loss and fistulization are severe conseq uences of CRP.
Argon plasma coagulation is recommended as optimal treatment for bleeding from telangiectasias. Retinol (retinyl) palmitate has demonstrated efficacy for functional symptoms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang CJ, Leung SW, Chen HC, et al. The correlation of acute toxicity and late rectal injury in radiotherapy for cervical carcinoma: evidence suggestive of consequential late effect (CQLE). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998;40(1):85–91.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Hong JJ, Park W, Ehrenpreis ED. Review article: current therapeutic options for radiation proctopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15(9):1253–62.
Schultheiss TE, Lee WR, Hunt MA, et al. Late GI and GU complications in the treatment of prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:3.
Johnson MJ, Robertson GM, Frizelle FA. Management of late complications of pelvic radiation in the rectum and anus: a review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003;46:247–259.
Ajlouni M. Radiation-induced proctitis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 1999;2:20–26.
Hayne D, Vaizey CJ, Boulos PB. Anorectal injury following pelvic radiotherapy. Br J Surg. 2001;88:1037–1048.
Muthlu E, Brunig K, Morrisey M. Quality of life of patients with radiation proctitis. Gastroenterology. 2002;12:A193–194.
Eifel PJ, Levenback C, Wharton JT, Oswald MJ. Time course and incidence of late complications in patients treated with radiation therapy for FIGO stage IB carcinoma of the uterine cervix. IntRadiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;32:1289–1300.
Moore EM, Magrino TJ, Johnstone PA. Rectal bleeding after radiation therapy for prostate cancer: endoscopic evaluation. Radiology. 2000;217(1):215–8.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). http://www.cdc.gov/ibd/ (2014).
Willett CG, et al. Acute and late toxicity of patients with inflammatory bowel disease undergoing irradiation for abdominal and pelvic neoplasms. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;46:995–8.
Herold DM, Hanlon AL, Hanks GE. Diabetes mellitus: a predictor for late radiation morbidity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;43:475–9.
Ross JG, Hussey DH, Mayr NA, Davis CS. Acute and late reactions to radiation therapy in patients with collagen vascular diseases. Cancer. 1993;71:3744–52.
Eifel PJ, Jhingran A, Bodurka DC, Levenback C, Thames H. Correlation of smoking history and other patient characteristics with major complications of pelvic radiation therapy for cervical cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(17):3651–7.
Lin A, Abu-Isa E, Griffith KA, Ben-Josef E. Toxicity of radiotherapy in patients with collagen vascular disease. Cancer 2008;113:648–53.
Hauer-jensen M, Denham JW, Andreyev HJ. Radiation enteropathy-pathogenesis, treatment and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014
Yeoh EK, Russo A, Botten R, et al. Acute effects of therapeutic irradiation for prostatic carcinoma on anorectal function. Gut. 1998;43(1):123–7.
Chi KD, Ehrenpreis ED, Jani AB. Accuracy and reliability of the endoscopic classification of chronic radiation-induced proctopathy using a novel grading method. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39(1):42–6.
Swaroop VS, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic treatment of chronic radiation proctopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol 1998;27:36–40.
Sharma B, Pandey D, Chiauhan V, et al. Radiation proctitis. J Indian Acad Clin Med. 2005;6:146–51.
Ehrenpreis ED, Jani A, Levitsky J, Ahn J, Hong J. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of retinol palmitate (vitamin A) for symptomatic chronic radiation proctopathy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005;48(1):1–8.
Kountouras J, Zavos C. Recent advances in the management of radiation colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(48):7289–301.
Topkan E, Karaoglu A. Octreotide in the management of chemoradiotherapy-induced diarrhea refractory to loperamide in patients with rectal carcinoma. Oncology. 2006;71(5–6):354–60.
Grdina DJ, Kataoka Y, Murley JS. Amifostine: mechanisms of action underlying cytoprotection and chemoprevention. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2000;16(4):237–79.
Nicolatou-Galitis, O, et al. Systematic review of amifostine for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 2013;21:357–64.
Kochhar, R, et al. Radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis. Prospective, randomized, double-blind controlled trial of oral sulfasalazine plus rectal steroids versus rectal sucralfate. Dig Dis Sci.1991;36:103–7.
Gilinsky NH, Burns DG, Barbezat GO, Levin W, Myers HS, Marks IN. The natural history of radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis: an analysis of 88 patients. Q J Med. 1983;52(205):40–53.
Bondesen S, Rasmussen SN, Rask-madsen J, et al. 5-Aminosalicylic acid in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Med Scand. 1987;221(3):227–42.
Freund U, Schölmerich J, Siems H, Kluge F, Schäfer HE, Wannenmacher M. [Unwanted side-effects in using mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) during radiotherapy]. Strahlenther Onkol. 1987;163(10):678–80.
Baum CA, Biddle WL, Miner PB. Failure of 5-aminosalicylic acid enemas to improve chronic radiation proctitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1989;34(5):758–60.
Sasai T, Hiraishi H, Suzuki Y, Masuyama H, Ishida M, Terano A. Treatment of chronic post-radiation proctopathy with oral administration of sucralfate. Dis Colon Rectum 1999;42(10):1357–1357.
Elson MI. The role of retinoids in wound healing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:S79–81.
Hein R, Mensing H, Muller PK, Muller PK, Braun-Falco O, Krieg T. Effect of vitamin A and it’s derivative on collagen production and chemotactic response of fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol 1984;111:37–44.
Wilson SA, Rex DK. Endoscopic treatment of chronic radiation proctopathy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006;22(5):536–40.
Zincola R, Rutter MD, Falasco G, et al. Hemorrhagic radiation proctitis: endoscopic severity may be useful to guide therapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2003;18:439–44.
Laughter RS, Petrilli ES, Dwyer RM, et al. Nd: YAG laser therapy of rectosigmoid bleeding due to radiation injury. Obstet Gynecol 1982;59(6 suppl):655–75
Johnson MJ, Robertson GM, Frizelle FA. Management of late complications of pelvic radiation in the rectum and anus: a review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003;46:247–59.
Fuentes D, Monserat R, Isern AM, et al. Colitis due to radiation: endoscopic management with heat probe. GEN. 1993;47:165–67.
Luna-Perez P, Rodriguez Ramirez SE. Formalin instillation for refractory radiation-induced hemorrhagic proctitis. J Surg Oncol. 2002;80(1):41–4.
Ginsberg GG, Barkun AN, Bosco JJ, et al. The argon plasma coagulator. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:807–810
Deepak P, Devi R, Sifuentes H, Ehrenpreis ED. Use of polyethylene glycol-based colonoscopy preparations before rectal argon plasma coagulation: lessons still to be learned by practicing gastroenterologists. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46(9):803–4.
Ladas SD, Karamanolis G, Ben-Soussan E. Colonic gas explosion during therapeutic colonoscopy with electrocautery. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(40):5295–8.
Pichon N, Maisonnette F, Cessot F, Sodji M, Sautereau D. Colonic perforations after gas explosion induced by argon plasma coagulation. Endoscopy. 2004;36(6):573.
Villavicencio RT, Rex DK, Rahmani E. Efficacy and complications of argon plasma coagulation for hematochezia related to radiation proctopathy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55:70–4.
Sato Y, Takayama T, Sagawa T, et al. Argon plasma coagulation treatment of hemorrhagic radiation proctopathy: the optimal settings for application and long-term outcome. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(3):543–9.
Chutkan R, Lipp A, Waye J. The argon plasma coagulator: a new and effective modality for treatment of radiation proctitis. Gastrointest Endosc 1997;45:AB27.
Zel G. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in urology. AUA Update Ser 1990;9:114.
Dall’era MA, Hampson NB, Hsi RA, Madsen B, Corman JM. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radiation induced proctopathy in men treated for prostate cancer. J Urol. 2006;176(1):87–90.
Woo TC, Joseph D, Oxer H. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for radiation proctitis. Int Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1997;38(3):619–22.
http://www.hyperbariclink.com/HealthcarePros/HealthcarePros.aspx.
Mackie TR. Radiation therapy treatment optimization. Introduction. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1999;9(1):1–3.
Purdy JA. From new frontiers to new standards of practice: advances inradiotherapy planning and delivery. Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 2007;40:18–39.
Klopp AH, et al. Hematologic toxicity in RTOG 0418: a phase 2 study ofpostoperative IMRT for gynecologic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;86(1):83–90.
Samuelian JM, et al. Reduced acute bowel toxicity in patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(5):1981–7.
Hauer-Jensen M, Wang J, Denham JW. Bowel injury: current and evolvingmanagement strategies. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003;13(3):357–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mazulis, A., Ehrenpreis, E. (2015). Radiation Proctopathy. In: Ehrenpreis, E., Marsh, R., Small Jr., W. (eds) Radiation Therapy for Pelvic Malignancy and its Consequences. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2217-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2217-8_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2216-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2217-8
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)