Abstract
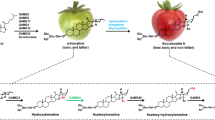
α-Tomatine, i.e. 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl (1→3)]-[β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside of tomatidine, see Fig. 1, is the primary steroid glycoalkaloid present in leaves and immature fruits of common tomato1. This compound is reported to be potentially toxic for animals and human beings2,3. Like other plant glycoalkaloids, it is considered to play a role in plant self-defence against pathogenic organisms and insects4-8.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Friedman, C.E. Levin and G.M. McDonald, a-Tomatidine determination in tomatoes by HPLC using pulsed amperometric detection, J. Agric. Food Chem. 42: 1959 (1994).
M. Friedman, J.R. Rayburn and J.A. Bantle, Structural relationships and developmental toxicity of Solanum alkaloids in the frog embryo teratogenesis assay - Xenopus, J. Agric. Food Chem. 40: 1617 (1993).
H. Ripperger and K. Schreiber, Solanum steroid alkaloids, In: The Alkaloids - Chemistry and Physiology, vol. XIX, R.H.F. Manske and R.G.A. Rodrigo, Eds., Academic Press, New York (1981).
J. Jiratko, Comparison of antifungal activity of tomatine and tomato extract, Ochr. Rostl. 29: 93 (1993).
J.G: Roddick, Antifungal activity of plant steroids, In: Ecology and Metabolism of Plant Lipids, G. Fuller and W.D. Nes, Eds., American Chemical Society, Washington, DC (1987).
F.M. Lu and I.Y. Chu, The antifeeding effects of a-tomatine to the larvae of diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella L.), Chin. J. Entomol. 12: 318 (1992).
M. Weissenberg, J. Klein, J. Meisner and K.R.S. Ascher, Larval growth inhibition of the spiny bollworm, Earias insulana, by some steroidal secondary plant compounds Entomol Exp. Appl. 42: 213 (1986).
C.A. Ellinger, Y. Wong, B.G. Chan and A.C. Waiss, Jr., Growth inhibitors in tomato (Lycopersicon) to tomato fruitworm (Heliothis zea), J. Chem. Ecol. 7: 753 (1981).
E. Heftmann, Biogenesis of steroids in Solanaceae, Phytochemistry 22: 1843 (1983).
S. Osman, Steroidal glycoalkaloid biosynthesis and function in Solanum spp., In: Isopentenoids in Plants. Biochemistry and Function, W.D. Nes, G. Fuller and L-S. Tsai, Eds., Marcel Dekker Inc, New York (1984).
E. Heftmann, Metabolism of cholesterol in plants, In: Isopentenoids in Plants. Biochemistry and Function, W.D. Nes, G. Fuller and L-S. Tsai, Eds., Marcel Dekker Inc, New York (1984).
E. Heftmann, E.R. Lieber and R.D. Bennet, Biosynthesis of tomatidine from cholesterol in Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium, Phytochemistry 6: 225 (1967).
R. Tschesche and M. Spinder, Zur Biogenese des Aza-Oxa-Spiran-System der Steroidalkaloide vom Spirosolan-Typ in Solanaceen, Phytochemistry 17: 251 (1978).
D.R Liljegren, Glucosylation of solasodine by extracts from Solanum lacciniatum, Phytochemistry 10: 3061 (1971).
N. Lavintman, J. Tandecarz and C.E. Cardini, Enzymatic glycosylation of steroid alkaloids in potato tuber, Plant Sci. Lett. 8: 65 (1977).
S.F. Osman, RM. Zacharius and D. Naglak, Solanidine metabolism in potato tuber tissue slices and cell suspension cultures, Phytochemistry 19: 2599 (1980).
A. Stapleton, P.V. Allen, M. Friedman and W.R. Belknap, Purification and characterization of solanidine glucosyltransferase from the potato (Solanum tuberosum), J. Agric. Food Chem. 39: 1187 (1991).
J. Zimowski, The occurrence of a glucosyltransferase specific for solanidine in potato plants, Phytochemistry 27: 2743 (1991).
A. Bergenstrahle, E. Tillberg and L. Jonsson, Characterization of UDP-glucose: solanidine glucosyltransferase and UDP-galactose: solanidine galactosyltransferase from potato tuber, Plant Sci. 84: 35 (1992).
J. Zimowski, Specificity and some other properties of cytosolic and membranous UDPG1c: 3β-hydroxysteroid glucosyltransferases from Solanum tuberosum leaves, Phytochemistry 31:2977 (1992).
A. Stapleton, P.V. Allen, H.P. Tao, W.R. Belknap and M. Friedman, Partial amino acid sequence of potato solanidine UDP-glucose glucosyltransferase purified by new anion-exchange and size exclusion media, Protein Expression and Purification, 3:85 (1992).
C. Pgczkowski and Z.A. Wojciechowski, Glucosylation and galactosylation of diosgenin and solasodine by soluble glycosyltransferase(s) from Solanum melongena leaves, Phytochemistry 35: 1429 (1994).
J. Zimowski, Characterization of UDP-galactose: tomatidine galactosyltransferase from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) leaves. Acta Biochim. Polon. 41: 203 (1994).
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem. 72: 248 (1976).
W. Janiszowska, B. Wilkomirski and Z. Kasprzyk, Synthesis of oleanolic acid 3-O-monoglucoside, Polish J. Chem. 54: 2147 (1980).
C. Pgczkowski, J. Zimowski, D. Krawczyk and Z.A. Wojciechowski, Steroid-specific glucosyltransferases in Asparagus plumosus shoots, Phytochemistry 29: 63 (1990).
Z.A. Wojciechowski, Biochemistry of phytosterol conjugates, In: Physiology and Biochemistry of Sterols, G.W. Patterson and W.D. Nes, Eds., American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, Illinois (1992).
Z.A. Wojciechowski, J. Zimowski, J.G. Zimowski and A. Lyznik, Specificity of sterol-glucosylating enzymes from Sinapis alba and Physarum polycephalum, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 570: 363 (1979).
T. Yoshikawa and T. Furuya, Purification and properties of sterol: UDPG glucosyltransferase in cell culture of Digitalis purpurea, Phytochemistry 18: 239 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zimowski, J. (1996). Enzymatic Glycosylation of Tomatidine in Tomato Plants. In: Waller, G.R., Yamasaki, K. (eds) Saponins Used in Traditional and Modern Medicine. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 404. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1367-8_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1367-8_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4899-1369-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4899-1367-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive