Abstract
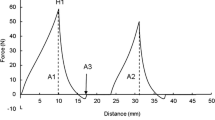
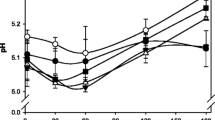
Reduction of dietary fat by Americans has led to the introduction of various low-fat dairy products. Consumption of Mozzarella cheese in the U.S. has reached 3.5 kg per person per year (USDA, 1993), making this variety an appropriate target for fat reduction. Our laboratory has developed a “light” Mozzarella containing <10% fat (Tunick et al., 1991, 1993a, 1993b) which is currently being tested for use in the National School Lunch Program. The effects of cooking temperature, moisture level, and storage time were examined to determine which combination produces the best product. Meltability studies were of particular interest since three-fourths of the Mozzarella cheese produced in the U.S. is used in pizza (Kindstedt, 1993). Homogenization of cheesemilk was also investigated as a possible means of enhancing textural properties and because homogenization is required when recombined milks are used for cheesemaking. In this study, texture profile analysis, small amplitude dynamic oscillatory shear measurements, and meltability measurements were used to compare the rheological properties of low-fat and full-fat Mozzarella cheeses.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC, 1990, “Official Methods of Analysis”, 15th edn., Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC.
Dean, M.R., Berridge, N.J., and Mabbit, L.A., 1959, Microscopical observations on Cheddar cheese and curd, J. Dairy Res. 26:77.
Kiely, L.J., Hendricks, G.M., Levis, J.E., Kindstedt, P.S., Yun, J.J., Rasmussen, R.R., and Barbano, D.M., 1992, Age related changes in the microstructure of Mozzarella cheese manufactured with different rod:coccus starter ratios, J. Dairy Sci. 75(Suppl. 1): 101.
Kindstedt, P.S., 1993, Effect of manufacturing parameters, composition, and proteolysis on the functional characteristics of Mozzarella cheese, Crit. Revs. Food Sci. Nutr. 33:167.
Kosikowski, F.V., 1982, “Cheese and Fermented Milk Foods”, 3rd edn., Edwards Bros., Ann Arbor.
Lelievre, J.R., Shaker, R., and Taylor, M.W., 1990, The role of homogenization in the manufacture of halloumi and mozzarella cheese from recombined milk, J. Soc. Dairy Technol. 43:21.
Malin, E.L., Tunick, M.H., Smith, P.W., Shieh, J.J., Sullivan, B.C., and Holsinger, V.H., 1993, Effect of homogenization on properties of low-fat Mozzarella cheese, Proc. Int. Dairy Fed. Seminar on Cheese Ripening ,in press.
McPherson, A.V., Dash, M.C., and Kitchen, B.J., 1984, Isolation and composition of milk fat globule membrane material. II. From homogenized and ultra heat treated milks, J. Dairy Res. 51:289.
Olson, N.F. and Johnson, M.E., 1990, Light cheese products: characteristics and economics, Food Technol. 44:93.
Park, J., Rosenau, J.R., and Peleg, M., 1984, Comparison of four procedures of cheese meltability evaluation, J. Food Sci. 49:1158.
Tunick, M.H., Mackey, K.L., Smith, P.W., and Holsinger, V.H., 1991, Effects of composition and storage on the texture of Mozzarella cheese, Neth. Milk Dairy J. 45:117.
Tunick, M.H., Mackey, K.L., Shieh, J.J., Smith, P.W., Cooke, P., and Malin, E.L., 1993a, Rheology and microstructure of low-fat Mozzarella cheese, Int. Dairy J. 3:649.
Tunick, M.H., Malin, E.L., Smith, P.W., Shieh, J.J., Sullivan, B.C., Mackey, K.L., and Holsinger, V.H., 1993b, Proteolysis and rheology of low fat and full fat Mozzarella cheeses prepared from homogenized milk, J. Dairy Sci. 76:3621.
USDA, 1993, “Dairy Situation and Outlook Yearbook”, US Govt. Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tunick, M.H., Shieh, J.J. (1995). Rheology of Reduced-Fat Mozzarella Cheese. In: Malin, E.L., Tunick, M.H. (eds) Chemistry of Structure-Function Relationships in Cheese. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 367. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1913-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1913-3_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5782-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1913-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive