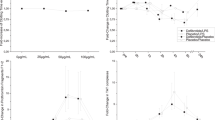
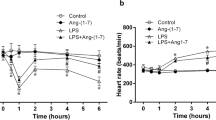
Abstract
Increased concentrations of tumor necrosis factor concentrations, activated neutrophils, and inadequate oxygen delivery to tissue are associated with free radical generation and also with endotoxic shock. Pentoxifylline suppresses the synthesis of tumor necrosis factor in endotoxin stimulated macrophages1 and when administered in vivo significantly attenuates circulating tumor necrosis factor and survival in mice challenged with endotoxin.2 Pentoxifylline also inhibits neutrophil activation induced by tumor necrosis factor.3 Additionally, pentoxifylline possesses antithrombotic activity and induces synthesis of endothelial cell prostacyclin, both of which should promote tissue perfusion during endotoxin-induced low flow conditions. This study was designed to determine the effect of pentoxifylline on the development of cardiovascular, metabolic, and pathologic responses to endotoxin.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.M. Stieter, D.G. Remick, P.A. Ward, R.N. Spengler, J.P. Lynch, J. Larrick, and S.L. Kuhkel, Cellular and molecular regulation of TNF-alpha production by pentoxifylline, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 155: 1230 (1988).
U.F. Schade, Pentoxifylline increases survival in murine endotoxin shock and decreases formation of tumor necrosis factor, Circ. Shock 31: 171 (1990).
H. Zheng, J.J. Crowley, J.C. Chan, H. Hoffmann, J.R. Hatherill, A. Ishizaka, and T.A. Raffin, Attenuation of TNF-induced endothelial cell cytotoxicity and neutrophil chemiluminescence, Am. Rev.Respir. Dis. 42:1073 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lerner, M.R., Balla, A.K., Wilson, M.F., Brackett, D.J. (1994). Pentoxifylline Interferes with Potental Sources of Free Radical Generation during Endotoxemia. In: Armstrong, D. (eds) Free Radicals in Diagnostic Medicine. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 366. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1833-4_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1833-4_50
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5742-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1833-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive