Abstract
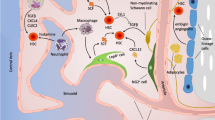
Blood cell production is maintained throughout life by hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), which reside in specific areas of the bone marrow (BM) referred to as niches. These niches regulate the self-renewal, proliferation, and migration of HSC and also integrate signals from the periphery to respond to the hematopoietic demand. In the last decade, several putative cellular components of the HSC niche have been identified. Here, we briefly review current knowledge on different putative niche cells and their regulation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondo M (2009) Principles of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Biology. In: Kondo M (ed) Hematopoietic stem cell biology. Humana Press, New York
Dick JE, Magli MC, Huszar D, Phillips RA, Bernstein A (1985) Introduction of a selectable gene into primitive stem cells capable of long-term reconstitution of the hemopoietic system of W/Wv mice. Cell 42(1):71–79
Keller G, Paige C, Gilboa E, Wagner EF (1985) Expression of a foreign gene in myeloid and lymphoid cells derived from multipotent haematopoietic precursors. Nature 318(6042):149–154
Lemischka IR, Raulet DH, Mulligan RC (1986) Developmental potential and dynamic behavior of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell 45(6):917–927
Soiffer RJ (2008). In: Karp JE (ed) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Humana Press, New York
Magnon C, Frenette PS (2008) Hematopoietic stem cell trafficking. In: StemBook (ed) The stem cell research community. Stembook. http://www.stembook.org, January 2012
Trentin J (1989) Hematopoietic microenviroments. In: Tavassoli M (ed) Handbook of the hematopoietic microenviroment. Humana Press, New York, pp 1–86
Askmyr M, Sims NA, Martin TJ, Purton LE (2009) What is the true nature of the osteoblastic hematopoietic stem cell niche? Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(6):303–309
Kiel MJ, Morrison SJ (2008) Uncertainty in the niches that maintain haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Rev Immunol 8(4):290–301
Lymperi S, Ferraro F, Scadden DT (2010) The HSC niche concept has turned 31. Has our knowledge matured? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1192:12–18
Mendez-Ferrer S, Chow A, Merad M, Frenette PS (2009) Circadian rhythms influence hematopoietic stem cells. Curr Opin Hematol 16(4):235–242
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S, Zhang S, Kobayashi T, Schoonmaker JA et al (2010) Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 464(7290):852–857
Walkley CR, Shea JM, Sims NA, Purton LE, Orkin SH (2007) Rb regulates interactions between hematopoietic stem cells and their bone marrow microenvironment. Cell 129(6):1081–1095
Walkley CR, Olsen GH, Dworkin S, Fabb SA, Swann J, McArthur GA et al (2007) A microenvironment-induced myeloproliferative syndrome caused by retinoic acid receptor gamma deficiency. Cell 129(6):1097–1110
Kim YW, Koo BK, Jeong HW, Yoon MJ, Song R, Shin J et al (2008) Defective Notch activation in microenvironment leads to myeloproliferative disease. Blood 112(12):4628–4638
Lane SW, Scadden DT, Gilliland DG (2009) The leukemic stem cell niche: current concepts and therapeutic opportunities. Blood 114(6):1150–1157
Shiozawa Y, Pedersen EA, Havens AM, Jung Y, Mishra A, Joseph J et al (2011) Human prostate cancer metastases target the hematopoietic stem cell niche to establish footholds in mouse bone marrow. J Clin Invest 121:1298–1312
Schofield R (1978) The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells 4(1–2):7–25
Calvi LM, Adams GB, Weibrecht KW, Weber JM, Olson DP, Knight MC et al (2003) Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature 425(6960):841–846
Zhang J, Niu C, Ye L, Huang H, He X, Tong WG et al (2003) Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature 425(6960):836–841
Till JE, McCulloch EA (1961) A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res 14:213–222
Dexter TM, Allen TD, Lajtha LG, Schofield R, Lord BI (1973) Stimulation of differentiation and proliferation of haemopoietic cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol 82(3):461–473
Dexter TM, Lajtha LG (1974) Proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. Br J Haematol 28(4):525–530
Dexter TM, Wright EG, Krizsa F, Lajtha LG (1977) Regulation of haemopoietic stem cell proliferation in long term bone marrow cultures. Biomedicine 27(9–10):344–349
Friedenstein AJ, Latzinik NW, Grosheva AG, Gorskaya UF (1982) Marrow microenvironment transfer by heterotopic transplantation of freshly isolated and cultured cells in porous sponges. Exp Hematol 10(2):217–227
Fliedner TM, Calvo W, Klinnert V, Nothdurft W, Prummer O, Raghavachar A (1985) Bone marrow structure and its possible significance for hematopoietic cell renewal. Ann N Y Acad Sci 459:73–84
Weiss L (1976) The hematopoietic microenvironment of the bone marrow: an ultrastructural study of the stroma in rats. Anat Rec 186(2):161–184
Westen H, Bainton DF (1979) Association of alkaline-phosphatase-positive reticulum cells in bone marrow with granulocytic precursors. J Exp Med 150(4):919–937
Mayani H, Guilbert LJ, Janowska-Wieczorek A (1992) Biology of the hemopoietic microenvironment. Eur J Haematol 49(5):225–233
Naveiras O, Nardi V, Wenzel PL, Hauschka PV, Fahey F, Daley GQ (2009) Bone-marrow adipocytes as negative regulators of the haematopoietic microenvironment. Nature 460(7252):259–263
Broudy VC, Zuckerman KS, Jetmalani S, Fitchen JH, Bagby GC Jr (1986) Monocytes stimulate fibroblastoid bone marrow stromal cells to produce multilineage hematopoietic growth factors. Blood 68(2):530–534
Sadahira Y, Mori M (1999) Role of the macrophage in erythropoiesis. Pathol Int 49(10):841–848
Fukushima N, Ohkawa H (1995) Hematopoietic stem cells and microenvironment: the proliferation and differentiation of stromal cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 20(3):255–270
Coulombel L, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ (1983) Enzymatic treatment of long-term human marrow cultures reveals the preferential location of primitive hemopoietic progenitors in the adherent layer. Blood 62(2):291–297
Funk PE, Kincade PW, Witte PL (1994) Native associations of early hematopoietic stem cells and stromal cells isolated in bone marrow cell aggregates. Blood 83(2):361–369
Prosper F, Verfaillie CM (2001) Regulation of hematopoiesis through adhesion receptors. J Leukoc Biol 69(3):307–316
Kodama H, Nose M, Niida S, Nishikawa S (1994) Involvement of the c-kit receptor in the adhesion of hematopoietic stem cells to stromal cells. Exp Hematol 22(10):979–984
Simmons PJ, Masinovsky B, Longenecker BM, Berenson R, Torok-Storb B, Gallatin WM (1992) Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expressed by bone marrow stromal cells mediates the binding of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood 80(2):388–395
Miyake K, Weissman IL, Greenberger JS, Kincade PW (1991) Evidence for a role of the integrin VLA-4 in lympho-hemopoiesis. J Exp Med 173(3):599–607
Broxmeyer HE (2001) Regulation of hematopoiesis by chemokine family members. Int J Hematol 74(1):9–17
Williams DA, Rosenblatt MF, Beier DR, Cone RD (1988) Generation of murine stromal cell lines supporting hematopoietic stem cell proliferation by use of recombinant retrovirus vectors encoding simian virus 40 large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol 8(9):3864–3871
Harigaya K, Handa H (1985) Generation of functional clonal cell lines from human bone marrow stroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82(10):3477–3480
Itoh K, Tezuka H, Sakoda H, Konno M, Nagata K, Uchiyama T et al (1989) Reproducible establishment of hemopoietic supportive stromal cell lines from murine bone marrow. Exp Hematol 17(2):145–153
Szilvassy SJ, Weller KP, Lin W, Sharma AK, Ho AS, Tsukamoto A et al (1996) Leukemia inhibitory factor upregulates cytokine expression by a murine stromal cell line enabling the maintenance of highly enriched competitive repopulating stem cells. Blood 87(11):4618–4628
Maekawa TL, Takahashi TA, Fujihara M, Urushibara N, Kadowaki-Kikuchi E, Nishikawa M et al (1997) A novel gene (drad-1) expressed in hematopoiesis-supporting stromal cell lines, ST2, PA6 and A54 preadipocytes: use of mRNA differential display. Stem Cells 15(5):334–339
Otsuka E, Yamaguchi A, Hirose S, Hagiwara H (1999) Characterization of osteoblastic differentiation of stromal cell line ST2 that is induced by ascorbic acid. Am J Physiol 277(1 Pt 1):C132–C138
Castro-Malaspina H, Gay RE, Resnick G, Kapoor N, Meyers P, Chiarieri D et al (1980) Characterization of human bone marrow fibroblast colony-forming cells (CFU-F) and their progeny. Blood 56(2):289–301
Simmons PJ, Torok-Storb B (1991) Identification of stromal cell precursors in human bone marrow by a novel monoclonal antibody, STRO-1. Blood 78(1):55–62
Taichman RS, Emerson SG (1994) Human osteoblasts support hematopoiesis through the production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med 179(5):1677–1682
Taichman RS, Reilly MJ, Emerson SG (1996) Human osteoblasts support human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro bone marrow cultures. Blood 87(2):518–524
Rafii S, Shapiro F, Pettengell R, Ferris B, Nachman RL, Moore MA et al (1995) Human bone marrow microvascular endothelial cells support long-term proliferation and differentiation of myeloid and megakaryocytic progenitors. Blood 86(9):3353–3363
Yin T, Li L (2006) The stem cell niches in bone. J Clin Invest 116(5):1195–1201
Papayannopoulou T, Scadden DT (2008) Stem-cell ecology and stem cells in motion. Blood 111(8):3923–3930
Zhang J, Li L (2008) Stem cell niche: microenvironment and beyond. J Biol Chem 283(15):9499–9503
Lord BI, Testa NG, Hendry JH (1975) The relative spatial distributions of CFUs and CFUc in the normal mouse femur. Blood 46(1):65–72
Gong JK (1978) Endosteal marrow: a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 199(4336):1443–1445
Nilsson SK, Johnston HM, Coverdale JA (2001) Spatial localization of transplanted hemopoietic stem cells: inferences for the localization of stem cell niches. Blood 97(8):2293–2299
Ponomaryov T, Peled A, Petit I, Taichman RS, Habler L, Sandbank J et al (2000) Induction of the chemokine stromal-derived factor-1 following DNA damage improves human stem cell function. J Clin Invest 106(11):1331–1339
Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, Sato H, Matsuoka S, Takubo K et al (2004) Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell 118(2):149–161
Blair HC, Julian BA, Cao X, Jordan SE, Dong SS (1999) Parathyroid hormone-regulated production of stem cell factor in human osteoblasts and osteoblast-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 255(3):778–784
Qian H, Buza-Vidas N, Hyland CD, Jensen CT, Antonchuk J, Mansson R et al (2007) Critical role of thrombopoietin in maintaining adult quiescent hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 1(6):671–684
Yoshihara H, Arai F, Hosokawa K, Hagiwara T, Takubo K, Nakamura Y et al (2007) Thrombopoietin/MPL signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and interaction with the osteoblastic niche. Cell Stem Cell 1(6):685–697
Stier S, Ko Y, Forkert R, Lutz C, Neuhaus T, Grunewald E et al (2005) Osteopontin is a hematopoietic stem cell niche component that negatively regulates stem cell pool size. J Exp Med 201(11):1781–1791
Kiel MJ, Radice GL, Morrison SJ (2007) Lack of evidence that hematopoietic stem cells depend on N-cadherin-mediated adhesion to osteoblasts for their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 1(2):204–217
Lymperi S, Horwood N, Marley S, Gordon MY, Cope AP, Dazzi F (2008) Strontium can increase some osteoblasts without increasing hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 111(3):1173–1181
Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, Terhorst C, Morrison SJ (2005) SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell 121(7):1109–1121
Chute JP, Saini AA, Chute DJ, Wells MR, Clark WB, Harlan DM et al (2002) Ex vivo culture with human brain endothelial cells increases the SCID-repopulating capacity of adult human bone marrow. Blood 100(13):4433–4439
Li W, Johnson SA, Shelley WC, Yoder MC (2004) Hematopoietic stem cell repopulating ability can be maintained in vitro by some primary endothelial cells. Exp Hematol 32(12):1226–1237
Chute JP, Muramoto GG, Salter AB, Meadows SK, Rickman DW, Chen B et al (2007) Transplantation of vascular endothelial cells mediates the hematopoietic recovery and survival of lethally irradiated mice. Blood 109(6):2365–2372
Salter AB, Meadows SK, Muramoto GG, Himburg H, Doan P, Daher P et al (2009) Endothelial progenitor cell infusion induces hematopoietic stem cell reconstitution in vivo. Blood 113(9):2104–2107
Yao L, Yokota T, Xia L, Kincade PW, McEver RP (2005) Bone marrow dysfunction in mice lacking the cytokine receptor gp130 in endothelial cells. Blood 106(13):4093–4101
Kobayashi H, Butler JM, O’Donnell R, Kobayashi M, Ding BS, Bonner B et al (2010) Angiocrine factors from Akt-activated endothelial cells balance self-renewal and differentiation of haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 12(11):1046–1056
Sipkins DA, Wei X, Wu JW, Runnels JM, Cote D, Means TK et al (2005) In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature 435(7044):969–973
Hooper AT, Butler JM, Nolan DJ, Kranz A, Iida K, Kobayashi M et al (2009) Engraftment and reconstitution of hematopoiesis is dependent on VEGFR2-mediated regeneration of sinusoidal endothelial cells. Cell Stem Cell 4(3):263–274
Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Noda M, Nagasawa T (2006) Maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling in bone marrow stromal cell niches. Immunity 25(6):977–988
Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, Di Cesare S, Piersanti S, Saggio I et al (2007) Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell 131(2):324–336
Chan CK, Chen CC, Luppen CA, Kim JB, DeBoer AT, Wei K et al (2009) Endochondral ossification is required for haematopoietic stem-cell niche formation. Nature 457(7228):490–494
Katayama Y, Battista M, Kao WM, Hidalgo A, Peired AJ, Thomas SA et al (2006) Signals from the sympathetic nervous system regulate hematopoietic stem cell egress from bone marrow. Cell 124(2):407–421
Mendez-Ferrer S, Lucas D, Battista M, Frenette PS (2008) Haematopoietic stem cell release is regulated by circadian oscillations. Nature 452(7186):442–447
Mendez-Ferrer S, Michurina TV, Ferraro F, Mazloom AR, Macarthur BD, Lira SA et al (2010) Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche. Nature 466(7308):829–834
Chow A, Lucas D, Hidalgo A, Mendez-Ferrer S, Hashimoto D, Scheiermann S et al (2011) Bone marrow CD169+ macrophages promote the retention of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the mesenchymal stem cell niche. J Exp Med 208(2):261–271
Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Kondoh G, Fujii N, Kohno K et al (2010) The essential functions of adipo-osteogenic progenitors as the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell niche. Immunity 33(3):387–399
Tabarowski Z, Gibson-Berry K, Felten SY (1996) Noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of the mouse femur bone marrow. Acta Histochem 98(4):453–457
Calvo W, Forteza-Vila J (1969) On the development of bone marrow innervation in new-born rats as studied with silver impregnation and electron microscopy. Am J Anat 126(3):355–371
Serre CM, Farlay D, Delmas PD, Chenu C (1999) Evidence for a dense and intimate innervation of the bone tissue, including glutamate-containing fibers. Bone 25(6):623–629
Hohmann EL, Elde RP, Rysavy JA, Einzig S, Gebhard RL (1986) Innervation of periosteum and bone by sympathetic vasoactive intestinal peptide-containing nerve fibers. Science 232(4752):868–871
Maestroni GJ (2000) Neurohormones and catecholamines as functional components of the bone marrow microenvironment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:29–37
Kalinkovich A, Spiegel A, Shivtiel S, Kollet O, Jordaney N, Piacibello W et al (2009) Blood-forming stem cells are nervous: direct and indirect regulation of immature human CD34+ cells by the nervous system. Brain Behav Immun 23(8):1059–1065
Frenette PS, Weiss L (2000) Sulfated glycans induce rapid hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization: evidence for selectin-dependent and independent mechanisms. Blood 96(7):2460–2468
Sweeney EA, Priestley GV, Nakamoto B, Collins RG, Beaudet AL, Papayannopoulou T (2000) Mobilization of stem/progenitor cells by sulfated polysaccharides does not require selectin presence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(12):6544–6549
Bosio A, Binczek E, Stoffel W (1996) Functional breakdown of the lipid bilayer of the myelin membrane in central and peripheral nervous system by disrupted galactocerebroside synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(23):13280–13285
Coetzee T, Fujita N, Dupree J, Shi R, Blight A, Suzuki K et al (1996) Myelination in the absence of galactocerebroside and sulfatide: normal structure with abnormal function and regional instability. Cell 86(2):209–219
Liu F, Poursine-Laurent J, Link DC (2000) Expression of the G-CSF receptor on hematopoietic progenitor cells is not required for their mobilization by G-CSF. Blood 95(10):3025–3031
Winkler IG, Sims NA, Pettit AR, Barbier V, Nowlan B, Helwani F et al (2011) Bone marrow macrophages maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches and their depletion mobilizes HSCs. Blood 116(23):4815–4828
Christopher MJ, Rao M, Liu F, Woloszynek JR, Link DC (2011) Expression of the G-CSF receptor in monocytic cells is sufficient to mediate hematopoietic progenitor mobilization by G-CSF in mice. J Exp Med 208(2):251–260
Burnett SH, Beus BJ, Avdiushko R, Qualls J, Kaplan AM, Cohen DA (2006) Development of peritoneal adhesions in macrophage depleted mice. J Surg Res 131(2):296–301
Van Rooijen N, Sanders A (1994) Liposome mediated depletion of macrophages: mechanism of action, preparation of liposomes and applications. J Immunol Methods 174(1–2):83–93
Chang MK, Raggatt LJ, Alexander KA, Kuliwaba JS, Fazzalari NL, Schroder K et al (2008) Osteal tissue macrophages are intercalated throughout human and mouse bone lining tissues and regulate osteoblast function in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 181(2):1232–1244
Cailhier JF, Partolina M, Vuthoori S, Wu S, Ko K, Watson S et al (2005) Conditional macrophage ablation demonstrates that resident macrophages initiate acute peritoneal inflammation. J Immunol 174(4):2336–2342
Miyake Y, Asano K, Kaise H, Uemura M, Nakayama M, Tanaka M (2007) Critical role of macrophages in the marginal zone in the suppression of immune responses to apoptotic cell-associated antigens. J Clin Invest 117(8):2268–2278
Kollet O, Dar A, Shivtiel S, Kalinkovich A, Lapid K, Sztainberg Y et al (2006) Osteoclasts degrade endosteal components and promote mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Nat Med 12(6):657–664
Lymperi S, Ersek A, Ferraro F, Dazzi F, Horwood NJ (2011) Inhibition of osteoclast function reduces hematopoietic stem cell numbers in vivo. Blood 117(5):1540–1549
Rogers MJ, Gordon S, Benford HL, Coxon FP, Luckman SP, Monkkonen J et al (2000) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Cancer 88(12 Suppl):2961–2978
Kricun ME (1985) Red-yellow marrow conversion: its effect on the location of some solitary bone lesions. Skeletal Radiol 14(1):10–19
Tavassoli M, Maniatis A, Crosby WH (1974) Induction of sustained hemopoiesis in fatty marrow. Blood 43(1):33–38
Touw I, Lowenberg B (1983) No stimulative effect of adipocytes on hematopoiesis in long-term human bone marrow cultures. Blood 61(4):770–774
Yokota T, Oritani K, Takahashi I, Ishikawa J, Matsuyama A, Ouchi N et al (2000) Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages. Blood 96(5):1723–1732
Fialkow PJ, Thomas ED, Bryant JI, Neiman PE (1971) Leukaemic transformation of engrafted human marrow cells in vivo. Lancet 1(7693):251–255
Flynn CM, Kaufman DS (2007) Donor cell leukemia: insight into cancer stem cells and the stem cell niche. Blood 109(7):2688–2692
Hertenstein B, Hambach L, Bacigalupo A, Schmitz N, McCann S, Slavin S et al (2005) Development of leukemia in donor cells after allogeneic stem cell transplantation–a survey of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Haematologica 90(7):969–975
Sala-Torra O, Hanna C, Loken MR, Flowers ME, Maris M, Ladne PA et al (2006) Evidence of donor-derived hematologic malignancies after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 12(5):511–517
Varricchio L, Mancini A, Migliaccio AR (2009) Pathological interactions between hematopoietic stem cells and their niche revealed by mouse models of primary myelofibrosis. Expert Rev Hematol 2(3):315–334
Lataillade JJ, Pierre-Louis O, Hasselbalch HC, Uzan G, Jasmin C, Martyre MC et al (2008) Does primary myelofibrosis involve a defective stem cell niche? From concept to evidence. Blood 112(8):3026–3035
Wei J, Wunderlich M, Fox C, Alvarez S, Cigudosa JC, Wilhelm JS et al (2008) Microenvironment determines lineage fate in a human model of MLL-AF9 leukemia. Cancer Cell 13(6):483–495
Ayala F, Dewar R, Kieran M, Kalluri R (2009) Contribution of bone microenvironment to leukemogenesis and leukemia progression. Leukemia 23(12):2233–2241
Bendall LJ, Kortlepel K, Gottlieb DJ (1993) Human acute myeloid leukemia cells bind to bone marrow stroma via a combination of beta-1 and beta-2 integrin mechanisms. Blood 82(10):3125–3132
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, Wang S, Jablonski E, Sipkins DA (2008) Leukemic cells create bone marrow niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Science 322(5909):1861–1865
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lucas, D., Pinho, S., Frenette, P.S. (2013). MSC Niche for Hematopoiesis. In: Hematti, P., Keating, A. (eds) Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5711-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5711-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-5710-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-5711-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)