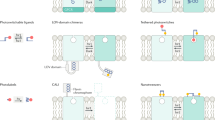
Abstract
The metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptor family plays a diverse role in cellular function. However, differentiation of the specific contributions of individual mGlu subtypes has traditionally relied on pharmacological approaches, which have proven difficult due to many factors including inadequate selectivity for specific receptor subtypes, a lack of discernment in receptor modulation across different cell types, and a lack of spatial and temporal precision over control of receptor activation or inactivation. In this chapter, we review three newly developed approaches that have attempted to circumvent these issues. These approaches include the use of selective photoactivatable mGlu ligands, optogenetic activation of light-sensitive chimeric rhodopsin/mGlu receptors (OptoXRs), and optogenetic modulation of mGlu membrane expression. We hypothesize that these novel methods for targeting mGlu receptors will provide new insight into the roles of individual receptor subtypes in specific cell functions in both normal and disease states.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
Ferraguti F, Shigemoto R (2006) Metabotropic glutamate receptors. Cell Tissue Res 326:483–504
Rondard P, Pin J (2015) Dynamics and modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 20C:95–101
Doherty AJ, Palmer MJ, Henley JM et al (1997) (RS)-2-chloro-5-hydroxyphenylglycine (CHPG) activates mGlu5, but not mGlu1, receptors expressed in CHO cells and potentiates NMDA responses in the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 36:265–267
Kammermeier PJ (2012) The orthosteric agonist 2-chloro-5-hydroxyphenylglycine activates mGluR5 and mGluR1 with similar efficacy and potency. BMC Pharmacol 12:6
Leach K, Gregory KJ (2017) Molecular insights into allosteric modulation of class C G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol Res 116:105–118
Lindsley CW, Emmitte KA, Hopkins CR et al (2016) Practical strategies and concepts in GPCR allosteric modulator discovery: recent advances with metabotropic glutamate receptors. Chem Rev 116:6707–6741
Rook JM, Noetzel MJ, Pouliot WA et al (2013) Unique signaling profiles of positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 determine differences in in vivo activity. Biol Psychiatry 73:501–509
O’Leary DM, Movsesyan V, Vicini S et al (2000) Selective mGluR5 antagonists MPEP and SIB-1893 decrease NMDA or glutamate-mediated neuronal toxicity through actions that reflect NMDA receptor antagonism. Br J Pharmacol 131:1429–1437
Gasparini F, Lingenhohl K, Stoehr N et al (1999) 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP), a potent, selective and systemically active mGlu5 receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 38:1493–1503
Salt TE, Binns KE, Turner JP et al (1999) Antagonism of the mGlu5 agonist 2-chloro-5-hydroxyphenylglycine by the novel selective mGlu5 antagonist 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP) in the thalamus. Br J Pharmacol 127:1057–1059
Mathiesen JM, Svendsen N, Brauner-Osborne H et al (2003) Positive allosteric modulation of the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 (hmGluR4) by SIB-1893 and MPEP. Br J Pharmacol 138:1026–1030
Heidbreder CA, Bianchi M, Lacroix LP et al (2003) Evidence that the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 antagonist MPEP may act as an inhibitor of the norepinephrine transporter in vitro and in vivo. Synapse 50:269–276
Kramer RH, Fortin DL, Trauner D (2009) New photochemical tools for controlling neuronal activity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19:544–552
Canepari M, Nelson L, Papageorgiou G et al (2001) Photochemical and pharmacological evaluation of 7-nitroindolinyl-and 4-methoxy-7-nitroindolinyl-amino acids as novel, fast caged neurotransmitters. J Neurosci Methods 112:29–42
Durand-de Cuttoli R, Chauhan PS, Petriz Reyes A et al (2020) Optofluidic control of rodent learning using cloaked caged glutamate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:6831–6835
Melchiorri D, Cappuccio I, Ciceroni C et al (2007) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in stem/progenitor cells. Neuropharmacology 53:473–480
Julio-Pieper M, Flor PJ, Dinan TG et al (2011) Exciting times beyond the brain: metabotropic glutamate receptors in peripheral and non-neural tissues. Pharmacol Rev 63:35–58
Ferrigno A, Berardo C, Di Pasqua LG et al (2017) Localization and role of metabotropic glutamate receptors subtype 5 in the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 23:4500–4507
Mudo G, Trovato-Salinaro A, Caniglia G et al (2007) Cellular localization of mGluR3 and mGluR5 mRNAs in normal and injured rat brain. Brain Res 1149:1–13
Panatier A, Robitaille R (2016) Astrocytic mGluR5 and the tripartite synapse. Neuroscience 323:29–34
Spampinato SF, Copani A, Nicoletti F et al (2018) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in glial cells: a new potential target for neuroprotection? Front Mol Neurosci 11:414
D’Antoni S, Berretta A, Bonaccorso CM et al (2008) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in glial cells. Neurochem Res 33:2436–2443
Romano C, van den Pol AN, O’Malley KL (1996) Enhanced early developmental expression of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 in rat brain: protein, mRNA splice variants, and regional distribution. J Comp Neurol 367:403–412
McQuail JA, Davis KN, Miller F et al (2013) Hippocampal Gaq/11 but not Gao-coupled receptors are altered in aging. Neuropharmacology 70:63–73
Noda M (2016) Dysfunction of glutamate receptors in microglia may cause neurodegeneration. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:381–386
Teh JL, Chen S (2012) Glutamatergic signaling in cellular transformation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 25:331–342
Holmes SE, Girgenti MJ, Davis MT et al (2017) Altered metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 markers in PTSD: in vivo and postmortem evidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:8390–8395
Kramer RH, Mourot A, Adesnik H (2013) Optogenetic pharmacology for control of native neuronal signaling proteins. Nat Neurosci 16:816–823
Lopez-Cano M, Font J, Llebaria A et al (2019) Optical modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 in vivo using a photoactive drug. Methods Mol Biol 1947:351–359
Dong M, Babalhavaeji A, Samanta S et al (2015) Red-shifting azobenzene photoswitches for in vivo use. Acc Chem Res 48:2662–2670
Pittolo S, Gomez-Santacana X, Eckelt K et al (2014) An allosteric modulator to control endogenous G protein-coupled receptors with light. Nat Chem Biol 10:813–815
Rovira X, Trapero A, Pittolo S et al (2016) OptoGluNAM4.1, a photoswitchable allosteric antagonist for real-time control of mGlu4 receptor activity. Cell Chem Biol 23:929–934
Reiner A, Isacoff EY (2014) Photoswitching of cell surface receptors using tethered ligands. Methods Mol Biol 1148:45–68
Reiner A, Levitz J, Isacoff EY (2015) Controlling ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors with light: principles and potential. Curr Opin Pharmacol 20:135–143
Levitz J, Pantoja C, Gaub B et al (2013) Optical control of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat Neurosci 16:507–516
Levitz J, Broichhagen J, Leippe P et al (2017) Dual optical control and mechanistic insights into photoswitchable group II and III metabotropic glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E3546–E3E54
Broichhagen J, Damijonaitis A, Levitz J et al (2015) Orthogonal optical control of a G protein-coupled receptor with a SNAP-tethered photochromic ligand. ACS Cent Sci 1:383–393
Acosta-Ruiz A, Gutzeit VA, Skelly MJ et al (2020) Branched photoswitchable tethered ligands enable ultra-efficient optical control and detection of G protein-coupled receptors in vivo. Neuron 105:446–463
Levitz J, Popescu AT, Reiner A et al (2016) A toolkit for orthogonal and in vivo optical manipulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Front Mol Neurosci 9:2
Britt JP, Bonci A (2013) Optogenetic interrogations of the neural circuits underlying addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23:539–545
Stuber GD, Britt JP, Bonci A (2012) Optogenetic modulation of neural circuits that underlie reward seeking. Biol Psychiatry 71:1061–1067
Cao ZFH, Burdakov D, Sarnyai Z (2011) Optogenetics: potentials for addiction research. Addict Biol 16:519–531
Kim JM, Hwa J, Garriga P et al (2005) Light-driven activation of beta 2-adrenergic receptor signaling by a chimeric rhodopsin containing the beta 2-adrenergic receptor cytoplasmic loops. Biochemistry 44:2284–2292
Airan RD, Thompson KR, Fenno LE et al (2009) Temporally precise in vivo control of intracellular signalling. Nature 458:1025–1029
Oh E, Maejima T, Liu C et al (2010) Substitution of 5-HT1A receptor signaling by a light-activated G protein-coupled receptor. J Biol Chem 285:30825–30836
Barish PA, Xu Y, Li J et al (2013) Design and functional evaluation of an optically active mu-opioid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 705:42–48
Bailes HJ, Zhuang LY, Lucas RJ (2012) Reproducible and sustained regulation of Gas signalling using a metazoan opsin as an optogenetic tool. PLoS One 7:e30774
Dhami GK, Ferguson SS (2006) Regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling, desensitization and endocytosis. Pharmacol Ther 111:260–271
Mahato PK, Ramsakha N, Ojha P et al (2018) Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs): ins and outs. Adv Exp Med Biol 1112:163–175
Suh YH, Chang K, Roche KW (2018) Metabotropic glutamate receptor trafficking. Mol Cell Neurosci 91:10–24
Wend S, Wagner HJ, Muller K et al (2014) Optogenetic control of protein kinase activity in mammalian cells. ACS Synth Biol 3:280–285
Kim N, Kim JM, Lee M et al (2014) Spatiotemporal control of fibroblast growth factor receptor signals by blue light. Chem Biol 21:903–912
Tischer D, Weiner OD (2014) Illuminating cell signalling with optogenetic tools. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:551–558
Beyer HM, Naumann S, Weber W et al (2015) Optogenetic control of signaling in mammalian cells. Biotechnol J 10:273–283
Takenouchi O, Yoshimura H, Ozawa T (2018) Unique roles of b-arrestin in GPCR trafficking revealed by photoinducible dimerizers. Sci Rep 8:677
Wang H, Westin L, Nong Y et al (2009) Norbin is an endogenous regulator of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling. Science 326:1554–1557
Calebiro D, Nikolaev VO, Persani L et al (2010) Signaling by internalized G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31:221–228
Gobeil F, Fortier A, Zhu T et al (2006) G-protein-coupled receptors signalling at the cell nucleus: an emerging paradigm. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 84:287–297
Jalink K, Moolenaar WH (2010) G protein-coupled receptors: the inside story. BioEssays 32:13–16
Jong YJ, Sergin I, Purgert CA et al (2014) Location-dependent signaling of the group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu5. Mol Pharmacol 86:774–785
Boivin B, Vaniotis G, Allen BG et al (2008) G protein-coupled receptors in and on the cell nucleus: a new signaling paradigm? J Recept Signal Transduct Res 28:15–28
Lester HA, Miwa JM, Srinivasan R (2012) Psychiatric drugs bind to classical targets within early exocytotic pathways: therapeutic effects. Biol Psychiatry 72:907–915
O’Malley KL, Jong YJ, Gonchar Y et al (2003) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu5 on nuclear membranes mediates intranuclear Ca2+ changes in heterologous cell types and neurons. J Biol Chem 278:28210–28219
Shigemoto R, Mizuno N (2000) Metabotropic glutamate receptors—immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization analysis. In: Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J (eds) Handbook of chemical Neuroanatomy: metabotropic glutamate receptors: immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization analyses. Elsevier, London, pp 63–98
Mitrano DA, Arnold C, Smith Y (2008) Subcellular and subsynaptic localization of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens of cocaine-treated rats. Neuroscience 154:653–666
Kell DB (2015) What would be the observable consequences if phospholipid bilayer diffusion of drugs into cells is negligible? Trends Pharmacol Sci 36:15–21
Buchwald P, Bodor N (1998) Octanol-water partition: searching for predictive models. Curr Med Chem 5:353–380
Dahan A, Miller JM (2012) The solubility-permeability interplay and its implications in formulation design and development for poorly soluble drugs. AAPS J 14:244–251
Jong YJ, Kumar V, O’Malley KL (2009) Intracellular metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) activates signaling cascades distinct from cell surface counterparts. J Biol Chem 284:35827–35838
Kingston AE, Griffey K, Johnson MP et al (2002) Inhibition of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor responses in vivo in rats by a new generation of carboxyphenylglycine-like amino acid antagonists. Neurosci Lett 330:127–130
Cosford ND, Tehrani L, Roppe J et al (2003) 3-[(2-Methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)ethynyl]-pyridine: a potent and highly selective metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptor antagonist with anxiolytic activity. J Med Chem 46:204–206
Zou MF, Cao J, Rodriguez AL et al (2011) Design and synthesis of substituted N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)benzamides as positive allosteric modulators of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:2650–2654
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Jong YJ, Kumar V, Kingston AE et al (2005) Functional metabotropic glutamate receptors on nuclei from brain and primary cultured striatal neurons: role of transporters in delivering ligand. J Biol Chem 280:30469–30480
Jong YJ, Schwetye KE, O’Malley KL (2007) Nuclear localization of functional metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu1 in HEK293 cells and cortical neurons: role in nuclear calcium mobilization and development. J Neurochem 101:458–469
Purgert CA, Izumi Y, Jong YJ et al (2014) Intracellular mGluR5 can mediate synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 34:4589–4598
Kumar V, Fahey PG, Jong YJ et al (2012) Activation of intracellular metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in striatal neurons leads to up-regulation of genes associated with sustained synaptic transmission including arc/Arg3.1 protein. J Biol Chem 287:5412–5425
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants R01 DA043172, R21 DA037741, and R01 AA025590 (MFO) and F32 AA027962 (JMLJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Hood, L.E., Leyrer-Jackson, J.M., Olive, M.F. (2021). Optical Approaches for Modulating mGlu Receptor Activity. In: Olive, M.F., Burrows, B.T., Leyrer-Jackson, J.M. (eds) Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Technologies. Neuromethods, vol 164. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1107-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1107-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1106-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1107-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols