Abstract
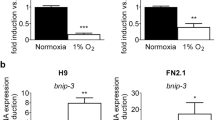
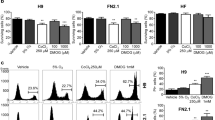
The characteristics of pluripotent cells have great potential for basic and clinical research and application. We describe the effect of normoxia or hypoxia regarding the proliferation and pluripotency of human iPS cells using colony number counting and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). In addition, the function of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) in human iPS cells under hypoxic conditions is evaluated in relation to the expression of pluripotency markers by siRNA and real-time PCR. Furthermore, we introduce the change of HIF-2α expression when signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is suppressed by its inhibitor, Stattic or S31 201, using RT-PCR.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hochedlinger K, Jaenisch R (2003) Nuclear transplantation, embryonic stem cells, and the potential for cell therapy. New Engl J Med 349:275–286
Rideout WM 3rd, Hochedlinger K, Kyba M, Daley GQ, Jaenisch R (2002) Correction of a genetic defect by nuclear transplantation and combined cell and gene therapy. Cell 109:17–27
Maherali N, Sridharan R, Xie W, Utikal J, Eminli S, Arnold K et al (2007) Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell 1:55–70
Meissner A, Wernig M, Jaenisch R (2007) Direct reprogramming of genetically unmodified fibroblasts into pluripotent stem cell. Nat Biotechnol 25:1177–1181
Okita K, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S (2007) Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cell. Nature 448:313–317
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S (2007) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131:861–872
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126:663–676
Wernig M, Meissner A, Foreman R, Brambrink T, Ku M, Hochedlinger K et al (2007) In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature 448:318–324
Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC (2008) The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:967–975
Semenza GL (2000) HIF-1: mediator of physiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 88:1474–1480
Mohyeldin A, Garzon-Muvdi T, Quinones-Hinojosa A (2010) Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell 7:150–161
Wenger RH (2002) Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J 16:1151–1162
Semenza GL, Wang GL (1992) A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 12:721–732
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M et al (2001) HIFα targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292:464–468
Masson N, Willam C, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-α chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation. EMBO J 20:5197–5206
Chen H, Aksoy I, Gonnot F, Osteil P, Aubry M, Hamela C et al (2015) Reinforcement of stat3 activity reprogrammes human embryonic stem cells to naïve-like pluripotency. Nat Commun 6:967–975
Sugimoto K, Matsuura T, Nakazono A, Igawa K, Yamada S, Hayashi Y (2018) Effects of hypoxia inducible factors on pluripotency in human iPS cells. Microsc Res Tech 81:749–754
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan (grant number: 15K20407 to KS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Sugimoto, K., Hayashi, Y. (2020). The Characteristics of Human iPS Cells and siRNA Transfection Under Hypoxia. In: Nagy, A., Turksen, K. (eds) Induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2454. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_299
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_299
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2118-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2119-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols