Abstract
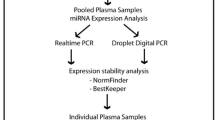
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are promising biomarkers for many diseases. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) is a gold standard for miRNA expression profiling that requires proper data normalization. Since there is no universal normalizer, it is recommended to evaluate normalizers under every experimental condition. This study describes the identification of suitable endogenous normalizer(s) (ENs) for plasma miRNA expression in essential hypertension. Expression levels of 5 candidate ENs and 2 plasma quality markers were determined by qRT-PCR in plasma samples from 18 hypertensive patients and 10 healthy controls. NormFinder, GeNorm, and DataAssist software programs were used to select the best EN(s). Expression levels of the 5 candidate ENs were also analyzed in urine samples from hypertensive patients and compared to the plasma samples of the hypertensive patients. Among the analyzed candidates, hsa-miR-92a-3p was identified as the best EN, and hsa-miR-21-5p and hsa-miR-16-5p as the next best. Moreover, hsa-miR-92a-3p showed the most consistent expression between plasma and urine. In conclusion, this study showed that hsa-miR-92a-3p, hsa-miR-21-5p, and hsa-miR-16-5p may be used as normalizers for plasma miRNA expression data in essential hypertension studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. (2002). The World Health report: Reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Carretero, O. A., & Oparil, S. (2000). Essential hypertension. Part I: Definition and etiology. Circulation, 101(3), 329–335.
Hamet, P., Pausova, Z., Adarichev, V., Adaricheva, K., & Tremblay, J. (1998). Hypertension: Genes and environment. Journal of Hypertension, 16(4), 397–418.
Synetos, A., Toutouzas, K., Stathogiannis, K., Latsios, G., Tsiamis, E., Tousoulis, D., & Stefanadis, C. (2013). MicroRNAs in arterial hypertension. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 13(13), 1527–1532.
Lewis, B. P., Burge, C. B., & Bartel, D. P. (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell, 120(1), 15–20.
Lagos-Quintana, M., Rauhut, R., Lendeckel, W., & Tuschl, T. (2001). Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science, 294(5543), 853–858.
Ambros, V. (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature, 431(7006), 350–355.
Calin, G. A., Dumitru, C. D., Shimizu, M., Bichi, R., Zupo, S., Noch, E., et al. (2002). Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 99(24), 15524–15529.
van Rooij, E., Sutherland, L. B., Liu, N., Williams, A. H., McAnally, J., Gerard, R. D., et al. (2006). A signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103(48), 18255–18260.
Weber, J. A., Baxter, D. H., Zhang, S., Huang, D. Y., Huang, K. H., Lee, M. J., et al. (2010). The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clinical Chemistry, 56(11), 1733–1741.
Li, S., Zhu, J., Zhang, W., Chen, Y., Zhang, K., Popescu, L. M., et al. (2011). Signature microRNA expression profile of essential hypertension and its novel link to human cytomegalovirus infection. Circulation, 124(2), 175–184.
Heid, C. A., Stevens, J., Livak, K. J., & Williams, P. M. (1996). Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Research, 6(10), 986–994.
Roberts, T. C., Coenen-Stass, A. M., & Wood, M. J. (2014). Assessment of RT-qPCR normalization strategies for accurate quantification of extracellular microRNAs in murine serum. PLoS One, 9(2), e89237.
McDermott, A. M., Kerin, M. J., & Miller, N. (2013). Identification and validation of miRNAs as endogenous controls for RQ-PCR in blood specimens for breast cancer studies. PLoS One, 8(12), e83718.
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., & Speleman, F. (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biology, 3(7), RESEARCH0034.
Pfaffl, M. W. (2001). A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(9), e45.
Bas, A., Forsberg, G., Hammarström, S., & Hammarström, M. L. (2004). Utility of the housekeeping genes 18S rRNA, beta-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase for normalization in real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of gene expression in human T lymphocytes. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 59(6), 566–573.
Schmittgen, T. D., & Zakrajsek, B. A. (2000). Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 46(1–2), 69–81.
Andersen, C. L., Jensen, J. L., & Ørntoft, T. F. (2004). Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Research, 64(15), 5245–5250.
Xia, M., Sherlock, J., Hegerich, P., You, X., Lee, K.,Walworth, C., and Spier, E. (2010). DataAssist™—Data analysis software for TaqMan® real-time PCR data. In Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2010, IMECS 2010 (Vol I) March 17–19, 2010, Hong Kong.
Johnson, J. A., Boerwinkle, E., Zineh, I., Chapman, A. B., Bailey, K., Cooper-DeHoff, R. M., et al. (2009). Pharmacogenomics of antihypertensive drugs: Rationale and design of the pharmacogenomic evaluation of antihypertensive responses (PEAR) study. American Heart Journal, 157(3), 442–449.
Welder, G. J., Wessel, T. R., Arant, C. B., Schofield, R. S., & Zineh, I. (2006). Complementary and alternative medicine use among individuals participating in research: implications for research and practice. Pharmacotherapy, 26(12), 1794–1801.
Zineh, I., Welder, G. J., DeBella, A. E., Arant, C. B., Wessel, T. R., & Schofield, R. S. (2006). Atorvastatin effect on circulating and leukocyte-produced CD40 ligand concentrations in people with normal cholesterol levels: A pilot study. Pharmacotherapy, 26(11), 1572–1577.
Shaffer, J., Schlumpberger, M., & Lader, E. (2012) miRNA profiling from blood—challenges and recommendations. SABiosciences Technical White Papers. Retrieved from http://www.sabiosciences.com/support_whitepapers.php.
Meyer, S. U., Pfaffl, M. W., & Ulbrich, S. E. (2010). Normalization strategies for microRNA profiling experiments: A ‘normal’ way to a hidden layer of complexity? Biotechnology Letters, 32(12), 1777–1788.
Kan, C. W., Hahn, M. A., Gard, G. B., Maidens, J., Huh, J. Y., Marsh, D. J., & Howell, V. M. (2012). Elevated levels of circulating microRNA-200 family members correlate with serous epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer, 12, 627.
Viprey, V. F., Corrias, M. V., & Burchill, S. A. (2012). Identification of reference microRNAs and suitability of archived hemopoietic samples for robust microRNA expression profiling. Analytical Biochemistry, 421(2), 566–572.
Benson, E. A., & Skaar, T. C. (2013). Incubation of whole blood at room temperature does not alter the plasma concentrations of microRNA-16 and -223. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 41(10), 1778–1781.
Kroh, E. M., Parkin, R. K., Mitchell, P. S., & Tewari, M. (2010). Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods, 50(4), 298–301.
Guo, L. J., & Zhang, Q. Y. (2012). Decreased serum miR-181a is a potential new tool for breast cancer screening. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 30(3), 680–686.
Bergkvist, A., Forootan, A., Zoric, N., Strombom, L., Sjoback, R., & Kubista, M. (2008). Choosing a normalization strategy for RT-PCR: GenEx system aids in the selection of reference genes for standardizing mRNA measurements. Genetic Engineering Biotechnology News, 28, 13.
Davoren, P. A., McNeill, R. E., Lowery, A. J., Kerin, M. J., & Miller, N. (2008). Identification of suitable endogenous control genes for microRNA gene expression analysis in human breast cancer. BMC Molecular Biology, 9, 76.
Song, J., Bai, Z., Han, W., Zhang, J., Meng, H., Bi, J., et al. (2012). Identification of suitable reference genes for qPCR analysis of serum microRNA in gastric cancer patients. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 57(4), 897–904.
Mestdagh, P., Van Vlierberghe, P., De Weer, A., Muth, D., Westermann, F., Speleman, F., & Vandesompele, J. (2009). A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biology, 10(6), R64.
Zhu, H. T., Dong, Q. Z., Wang, G., Zhou, H. J., Ren, N., Jia, H. L., et al. (2012). Identification of suitable reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis of circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Molecular Biotechnology, 50(1), 49–56.
Semmelmann, K., Lewis, M., Shaffer, J., & Lader, E. miRNA biomarker discovery—overcoming limiting sample material. SABiosciences Technical White Papers. Retrieved from http://www.sabiosciences.com/support_whitepapers.php.
Ramachandran, K., Saikumar, J., Bijol, V., Koyner, J. L., Qian, J., Betensky, R. A., et al. (2013). Human miRNome profiling identifies microRNAs differentially present in the urine after kidney injury. Clinical Chemistry, 59(12), 1742–1752.
Acknowledgments
This study was ancillary to the PEAR study that was funded by the National Institutes of Health (U01 GM074492). Mohamed Hassan M. Solayman was funded by the Embassy of the Arab Republic of Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the corresponding institutional review boards and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solayman, M.H.M., Langaee, T., Patel, A. et al. Identification of Suitable Endogenous Normalizers for qRT-PCR Analysis of Plasma microRNA Expression in Essential Hypertension. Mol Biotechnol 58, 179–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-015-9912-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-015-9912-z