Abstract
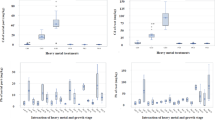
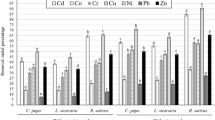
An experiment was conducted under simulated condition to study the influence of vermicompost on growth, yield and heavy metal accumulation by chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), an important essential oil bearing crop grown under simulated condition. Nickel and Cadmium applied at 20 mg kg−1 soil significantly enhanced the dry matter yield of the crop as compared to the control (no heavy metal). The results also revealed that addition of vermicompost (at 2.5 g kg−1 soil) enhanced the heavy metal accumulation by chamomile in metal-treated soil. Although a sizeable amount of metals were being translocated to flowers, the essential oil extracted by hydrodistillation of flowers did not contain any heavy metal. Similarly, chemical constituents of the oil of chamomile were within the range of those obtained from chamomile grown under normal soil condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowes, K., & Zheljazkov, V. (2004). Ocimum sanctum L and Ocimum basillicum L grown in Nova Scotia, Canada show potential as essential oil crops. J Am Soc Sci, 129, 789–794.
Clevenger, J. H. (1928). Apparatus for determination of volatile oil. Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association, 17, 346.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2007). Phytoextraction capacity of the plants growing on tannery sludge dumping sites. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1788–1794.
Jackson, M. L. (1973). Soil chemical analysis. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.
Lai, H. Y., & Chen, Z. S. (2004). Effects of EDTA on solubility of cadmium. Zinc and lead and their uptake by rainbow pink and vetiver grass. Chemosphere, 55, 421–430.
Lasat, M. M. (2002). Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a review of biological mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 109–120.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants. London: Academic Press.
Merritt, K. A., & Enrich, M. S. (2003). Influence of organic matter decomposition on soluble carbon and its copper-binding capacity. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 2122–2131.
Monni, S., Salemma, M., & Miller, N. (2000). The tolerance of Emphetrum nigrum to copper and nickel. Environmental Pollution, 109, 221–229.
Nigam, R., Srivastava, S., Prakash, S., & Srivastava, M. M. (2001). Cadmium mobilization and plant availability—the impact of organic acids commonly exuded from roots. Plant and Soil, 230, 107–113.
Patra, D. D., Anwar, M., Prasad, A., Singh, D., Chand, S., Ram, B., Katiyar, R. S., & Kumar, S. (2002). Performance of three cultivars of lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuous) and chamomile (Matricaria chamomile) under intercropping in sodic soils applied with different levels of gypsum. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33, 1707–1721.
Quartacci, M. F., Argilla, A. J. M., & Navari-lzzo, F. (2006). Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere, 63, 918–925.
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, P. B. A., Kumar, N., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, B. D., Chet, I., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology, 13, 468–474.
Scora, R. W., & Chang, A. C. (1997). Essential oil quality and heavy metal concentrations of peppermint grown on a municipal sludge-amended soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 975–979.
Singh, S., Sinha, S., Saxena, R., Pandey, K., & Bhatt, K. (2004). Translocation of metals and its effects on the tomato plants grown on various amendments of tannery wastes: evidences of involvement of antioxidants. Chemosphere, 57, 91–99.
Sokal, R. R., & Rholf, F. J. (1981). Biometry: the principles and practices of statistics in biological research (2nd ed.). New York: Freeman.
Subbiah, B. V., & Asija, A. L. (1956). A rapid method for determination of available nitrogen is soil. Current Science, 25, 259–260.
Vamerali, T., Bandiera, M., & Mosca, G. (2010). Field crops for phytoremediation of metal contaminated land. A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8, 1–17.
Wang, J. W. C., Lal, K. M., Su, D. S., & Fang, M. (2001). Availability of heavy metals for Brassica chinensei grown in an acidic loamy soil amended with domestic and industrial sewage sludge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 128, 339–353.
Wu, L. H., Luo, Y. M., Christie, P., & Wong, M. H. (2003). Effects of EDTA and low molecular weight organic acids on soil solution properties of heavy metal polluted soil. Chemosphere, 50, 819–822.
Zheljakov, V., & Nielsen, N. E. (1996). Studies on the effect of heavy metal (Cd, Pb. Cu.Mn, Zn and Fe) upon the growth, productivity and quality of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill) production. Journal of Essential Oil Research, 8, 259–274.
Zheljazkov, V. D., Craker, L. E., & Baoshan, X. (2006). Effects of Cd, Pb and Cu on growth and essential oil contents in dill pepper mint, and basil. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 58, 9–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chand, S., Pandey, A. & Patra, D.D. Influence of Vermicompost on Dry Matter Yield and Uptake of Ni and Cd by Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) in Ni- and Cd-Polluted Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 2257–2262 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1020-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1020-5