Abstract
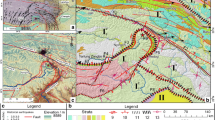
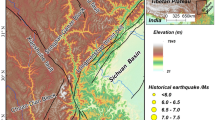
Dongjing reservoir with storage capacity of 955 million m3 and 150 m dam height had been set up in Guizhou province, southeastern China on May in 2005. After filling with water in August 20, 2009, the reservoir-induced earthquake in 20 km took place first in September 2009 at the 440 m water level. When the water level changes, the number of earthquakes is increased rapidly. On January 17, 2010, the largest M 4.4 earthquake with depth of 7 km has happen and month frequency achieved 21 events at the highest water level. M 4.4 earthquake caused rock collapse with the disaster of killed six people and nine injure. After our investigation and study, the reason of higher epicentral intensity of earthquake was the surface effect of near-field elastic wave transmission. The disaster of rock falls certainly depended on the very very shallow earthquake, the height of valley and fault. Comparing as same magnitude of natural earthquake, very shallow earthquake increased 1–2° of epicentral intensity I0, more than twice amplitude of S-wave at 200 m height of valley and the largest displacement on fault. The superposition of three factors has increased the epicentral intensity of earthquake and directly caused rock collapse with the disaster of killed six people and nine injure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K, Richards PG (1980) Quantitative seismology theory and methods [M]. W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco
CENC (2010) Earthquake catalog. http://www.csndmc.ac.cn/newweb/data.htm
Ding Y (1989) The reservoir induced earthquake [M]. Seismological Press (in Chinese), Beijing
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK (1976) Dam and earthquakes [M]. Amsterdam, Elsevier
Hu Y, Zhao M, Hu P, Ma W, Yang Q, Chen X (1995) Estimation of potential risk of reservor-induced earthquake for the proposed hydroelectric project on the yangtze gorges [J]. Earthq Res China 9(4):403–412
Hu Y, Liu Z, Yang Q, Chen X, Hu P, Ma W, Lei J (1996) Induced seismicity at Wujiangdu reservoir. China: a case induced in the Karst Area [J]. PAGEPH 147(2):409–418
Lei X, Ma S, Wen X, Su J, Du F (2008) Integrated analysis of stress and regional seismicity by surface loading—a case study of Zipingpu reservoir [J]. Seismol Geol 30(4):1046–1064 (in Chinese)
Liao W, Zhang L, Yao R (2009) Characteristics of seismicity in the three gorges reservoir area [J]. Seismol Geol 31(4):707–714 (in Chinese)
Ma W, Hu Y, Chen X, Yang Q, Hu P, Zhao M (1995) Surface effects of waves near-field of shallow earthquakes in Sanxia area [J]. Seimol Geol 17(1):63–68 (in Chinese)
Ma W, Xu C, Zhang X, Xu X, Li H, Yuan J (2011) Study on the relationship between the reservoir-induced seismicity at Zipingpu reservoir and the MS Wenchuan Earthquake [J]. Seismol Geol 33(1):175–190 (in Chinese)
PDE (2010) Earthquakes. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqithenews/2010/us2010ryan/
Scholz CH (1990) The mechanics of earthquakes and faulting [M]. Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom
Yang Q (1989) Vibration characteristics on the both sides of valley in Jiaojiping earthquake area of Wujiangdu reservoir [J]. Seimol Geol 11(2):26–32 (in Chinese)
Yang Q, Hu Y, Chen X, Chen L (1994) Catalogue of the reservoir induced seismic events in the world [J]. Seismol Geol 18(4):453–461 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. Lele Zou for the help. This work fund by “Eleventh Five-Year” National Key Science and Technology Support (2008BAC38B04) in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W. Analysis on the disaster mechanism of rock collapse of M4.4 reservoir-induced earthquake on January 17, 2010, at Dongjing reservoir in Guizhou Province, China. Nat Hazards 62, 141–148 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0031-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0031-2