Abstract
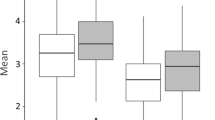
The purpose of the study was to investigate the influence of weight bias and demographic characteristics on the assessment of pediatric chronic pain. Weight status, race, and sex were manipulated in a series of virtual human (VH) digital images of children. Using a web-based platform, 96 undergraduate students with health care-related majors (e.g., Health Science, Nursing, Biology, and Pre-Medicine) read a clinical vignette and provided five ratings targeting the assessment of each VH child’s pain. Students also answered a weight bias questionnaire. Group-based analyses were conducted to determine the influence of the VH child’s weight and demographic cues, as well as greater weight bias on assessment ratings. Male and VH children with obesity were rated as more likely to avoid non-preferred activities due to pain compared to female and healthy weight children, respectively (both p < .001). The pain of VH children with obesity was rated as more likely to be influenced by psychological/behavioral issues compared to the pain of healthy weight VH children (p = .022). African American VH children were rated as experiencing significantly greater pain than Caucasian VH children (p = .037). As child weight increased, low weight bias participants felt more sympathy, while high weight bias participants felt less sympathy (p = .002). Also, low weight bias participants showed increased motivation to help, while high weight bias participants showed less motivation to help, as VH patient weight increased (p = .008). Child weight and evaluator weight bias may be influential in the assessment of pediatric pain. If supported by future research, results highlight the importance of training in evidence-based practice and education on weight bias for students majoring in health-care fields.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; American Pain Society, Task Force on Pain in Infants, Children, and Adolescents. (2001). The assessment and management of acute pain in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics, 108, 793–797.
Andrade, A. D., Ruiz, J. G., Mintzer, M. J., Cifuentes, P., Anam, R., Diem, J., … Roos, B. A. (2012). Medical students’ attitudes toward obese patient avatars of different skin color. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 173, 23–29.
Bacon, J. G., Scheltema, K. E., & Robinson, B. E. (2001). Fat phobia scale revisited: The short form. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 25, 252–257.
Bell, L. M., Curran, J. A., Byrne, S., Roby, H., Suriano, K., Jones, T. W., & Davis, E. A. (2011). High incidence of obesity co-morbidities in young children: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 47, 911–917
Bertakis, K. D., & Azari, R. (2005). The impact of obesity on primary care visits. Obesity Research, 13, 1615–1623.
Beyer, J. E., DeGood, D. E., Ashley, L. C., & Russell, G. A. (1983). Patterns of postoperative analgesic use with adults and children following cardiac surgery. Pain, 17, 71–81.
Bongers, I. L., Koot, H. M., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2004). Developmental trajectories of externalizing behaviors in childhood and adolescence. Child Development, 75, 1523–1537.
Crandall, C. S. (1994). Prejudice against fat people: Ideology and self-interest. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 66, 882–894.
Crandall, C. S., & Reser, A. H. (2005). Attributions and anti-fat bias. In K. D. Brownell, R. M. Puhl, & M. B. Schwartz (Eds.), Weight bias: Nature, consequences and remedies (pp. 83–96). New York: Guilford.
Csabi, G., Tenyi, T., & Molnar, D. (2000). Depressive symptoms among obese children. Eating and Weight Disorders- Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity, 5, 43–45.
Dovidio, J. F., & Fiske, S. T. (2012). Under the radar: How unexamined biases in decision-making processes in clinical interactions can contribute to health care disparities. American Journal of Public Health, 102, 945–952.
Dovidio, J. F., & Gaertner, S. L. (2004). Averisve racism. In M. P. Zanna (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 36, pp. 1–51). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Dovidio, J. F., & Gaertner, S. L. (2010). Intergroup bias. In S. T. Fiske, D. T. Gilbert & G. Lindzey (Eds.), Handbook of social psychology (Vol. 2, 5th ed., pp. 1084–1121). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Edmunds, L. D. (2005). Parents’ perceptions of health professionals’ responses when seeking help for their overweight children. Family Practice, 22, 287–292.
Fazio, R. H., & Olson, M. A. (2003). Implicit measures in social cognition research: Their meaning and uses. Annual Review of Psychology, 54, 297–327.
Geiger, H. J. (2003). Racial and ethnic disparities in diagnosis and treatment: A review of the evidence and a consideration of causes. In B. D. Smedley, A. Y. Stith, & A. E. Nelson (Eds.), Unequal treatment: Confronting racial and ethnic disparities in health care (pp. 417–454). Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Gray, W. N., Janicke, D. M., Ingerski, L. M., & Silverstein, J. H. (2008). The impact of peer victimization, parent distress and child depression on barrier formation and physical activity in overweight youth. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 29, 26–33.
Griffin, R. A., Polit, D. F., & Byrne, M. W. (2007). Stereotyping and nurses’ recommendations for treating pain in hospitalized children. Research in Nursing & Health, 30, 655–666
Gudzune, K. A., Beach, M. C., Roter, D. L., & Cooper, L. A. (2012). Physicians build less rapport with obese patients. Obesity (Silver Spring), 21, 2146–2152.
Hambrook, J., Kimball, T., Khoury, P., & Cnota, J. (2010). Disparities exist in the emergency department evaluation of pediatric chest pain. Congenital Heart Disease, 5, 285–291.
Hershey, A. D., Powers, S. W., Nelson, T. D., Kabbouche, M. A., Winner, P., Yonker, M., … McClintock, W. (2009). Obesity in the pediatric headache population: A multicenter study. Headache, 49, 170–177.
Hirsh, A. T., Alqudah, A., Stutts, L. A., & Robinson, M. E. (2008). Virtual human technology: Capturing sex, race, and age influences in individual pain decision policies. Pain, 140, 231–238.
Hirsh, A. T., George, S. Z., & Robinson, M. E. (2009). Pain assessment and treatment disparities: A virtual human technology investigation. Pain, 143, 106–113.
Hunfeld, J. A., Perquin, C. W., Duivenvoorden, H. J., Hazebroek-Kampschreur, A. A., Passchier, J., van Suijlekom-Smit, L. W., … van der Wouden, J. C. (2001). Chronic pain and its impact on quality of life in adolescents and their families. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 26, 145–153.
Konijnenberg, A. Y., Uiterwaal, C. S., Kimpen, J. L., van der Hoeven, J., Buitelaar, J. K., & de Graeff-Meeder, E. R. (2005). Children with unexplained chronic pain: Substantial impairment in everyday life. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 90, 680–686.
Kroner-Herwig, B., Heinrich, M., & Morris, L. (2007). Headache in German children and adolescents: A population-based epidemiological study. Cephalalgia, 27, 519–527.
LaFond, C. M., Van Hulle Vincent, C., Corte, C., Hershberger, P. E., Johnson, A., Park, C. G., … Wilkie, D. J. (2015). PICU nurses’ pain assessments and intervention choices for virtual human and written vignettes. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 30, 580–590.
LaFond, C. M., Van Hulle Vincent, C., Lee, S., Corte, C., Hershberger, P. E., Johnson, A., … Wilkie, D. J. (2015). Development and validation of a virtual human vignette to compare nurses’ assessment and intervention choices for pain in critically ill children. Simulation in Healthcare, 10, 14–20.
Lim, C. S., Mayer-Brown, S. J., Clifford, L. M., & Janicke, D. M. (2014). Pain is associated with physical activity and health-related quality of life in overweight and obese children. Children’s Health Care, 43, 186–202.
Lippa, N. C., & Sanderson, S. C. (2012). Impact of information about obesity genomics on the stigmatization of overweight individuals: An experimental study. Obesity (Silver Spring), 20, 2367–2376.
Magliocca, K. R., Jabero, M. F., Alto, D. L., & Magliocca, J. F. (2005). Knowledge, beliefs, and attitudes of dental and dental hygiene students toward obesity. Journal of Dental Education, 69, 1332–1339.
Major, B., Mendes, W. B., & Dovidio, J. F. (2013). Intergroup relations and heal disparities: A social psychological perspective. Health Psychology, 32(5), 514–524.
Mikhailovich, K., & Morrison, P. (2007). Discussing childhood overweight and obesity with parents: A health communication dilemma. Journal of Child Health Care, 11, 311–322.
Miller, M. M., Allison, A., Trost, Z., De Ruddere, L., Wheelis, T., Goubert, L., … Hirsh, A. T. (2018). Differential effect of patient weight on pain-related judgements about male and female chronic low back pain patients. Journal of Pain, 19(1), 57–66.
O’Brien, K. S., Hunter, J. A., & Banks, M. (2007). Implicit anti-fat bias in physical educators: Physical attributes, ideology and socialization. International Journal of Obesity, 31, 308–314.
Penner, L. A., Albrecht, T. L., Orom, H., Coleman, D., & Underwood, W. (2010). Health and health care disparities. In J. F. Dovidio, M. Hewstone, P. Glick, & V. M. Esses (Eds.), The Sage handbook of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Persky, S., & Eccleston, C. P. (2011). Medical student bias and care recommendations for an obese versus non-obese virtual patient. International Journal of Obesity (London), 35(5), 728–735.
Podeszwa, D. A., Stanko, K. J., Mooney, J. F., Cramer, K. E., & Mendelow, M. J. (2006). An analysis of the functional health of obese children and adolescents utilizing the PODC instrument. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 26, 140–143.
Poustchi, Y., Saks, N. S., Piasecki, A., Hahn, K., & Ferrante, J. M. (2013). Brief intervention effective in reducing weight bias in medical students. Family Medicine, 45, 345–348.
Puhl, R., Wharton, C., & Heuer, C. (2009). Weight bias among dietetics students: Implications for treatment practices. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109, 438–444.
Puhl, R. M., & Heuer, C. A. (2009). The stigma of obesity: A review and update. Obesity (Silver Spring), 17, 941–964.
Puhl, R. M., Latner, J. D., O’Brien, K., Luedicke, J., Danielsdottir, S., & Forhan, M. (2015). A multinational examination of weight bias: Predictors of anti-fat attitudes across four countries. International Journal of Obesity, 39, 1166–1173.
Puhl, R. M., Peterson, J. L., & Luedicke, J. (2011). Parental perceptions of weight terminology that providers use with youth. Pediatrics, 128, e786–e793.
Roth-Isigkeit, A., Thyen, U., Stoven, H., Schwarzenberger, J., & Schmucker, P. (2005). Pain among children and adolescents: Restrictions in daily living and triggering factors. Pediatrics, 115, e152–e162.
Sabin, J. A., & Greenwald, A. G. (2012). The influence of implicit bias on treatment recommendations for 4 common pediatric conditions: Pain, urinary tract infection, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and asthma. American Journal of Public Health, 102, 988–995.
Schwimmer, J., Burwinkle, T., & Varni, J. (2003). Health-related quality of life of obese children and adolescents. Journal of the American Medical Association, 289, 1813–1819.
Smedley, B. D., Stith, A. Y., & Nelson, A. R. (Eds.). (2003). Unequal treatment: Confronting racial and ethnic disparities in health care. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Strauss, R. S., & Pollack, H. A. (2003). Social marginalization of overweight children. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, 157, 746–752.
Swift, J. A., Tischler, V., Markham, S., Gunning, I., Glazebrook, C., Beer, C., … Puhl, R. (2013). Are anti-stigma films a useful strategy for reducing weight bias among trainee healthcare professionals? Results of a pilot randomized trial. Obesity Facts, 6, 91–102.
Teal, C. R., Shada, R. E., Gill, A. C., Thompson, B. M., Frugé, E., Villarreal, G. B., & Haidet, P. (2010). When best intentions aren’t enough: Helping medical students develop strategies for managing bias about patients. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 25, 115–118.
Wandner, L. D., Stutts, L. A., Alqudah, A. F., Craggs, J. G., Scipio, C. D., Hirsh, A. T., & Robinson, M. E. (2010). Virtual human technology: Patient demographics and healthcare training factors in pain observation and treatment recommendations. Journal of Pain Research, 3, 241–247.
Washington, R. L. (2011). Childhood obesity: Issues of weight bias. Preventing Chronic Disease, 8, A94.
Yen, K., Kim, M., Stremski, E. S., & Gorelick, M. H. (2003). Effect of ethnicity and race on the use of pain medications in children with long bone fractures in the emergency department. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 42, 41–47.
Funding
This study was supported by National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial Research (Grant No. R01DE013208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Shana L. Boyle, David M. Janicke, Michael E. Robinson, and Laura D. Wandner declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from every participant before engaging in the study procedures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyle, S.L., Janicke, D.M., Robinson, M.E. et al. Using Virtual Human Technology to Examine Weight Bias and the Role of Patient Weight on Student Assessment of Pediatric Pain. J Clin Psychol Med Settings 26, 106–115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-018-9569-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-018-9569-4