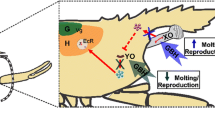
Abstract
As compared to other groups of aquatic gastropods, documented examples of endocrine disruption in pulmonates are rather limited. This is quite surprising because the endocrine control of physiological functions has been extensively studied in these animals. In the model-species Lymnaea stagnalis, the neurohormonal regulation of reproduction has been thoroughly investigated, and the primary structure of several peptides and receptors involved in endocrine processes has been established. However, the use of this knowledge has been fairly limited in the context of ecotoxicology, to investigate the effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. The present review summarizes the main and more recent findings on the neuroendocrine control of reproduction in aquatic pulmonate snails (Basommatophora). It then comprehensively describes selected in vivo laboratory and semi-field studies which provide evidence for possible endocrine disrupting effects of estrogenic and androgenic test compounds [e.g., ethynylestradiol, methyltestosterone (MT)], and of environmental contaminants [e.g., cadmium (Cd), tributyltin (TBT), and nonylphenol (NP), pesticides]. Finally, challenging perspectives for future research are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacchetta R, Mantecca P, Vailati G (2002) Oocyte degeneration and altered ovipository activity induced by paraquat in the freshwater snail Physa fontinalis (Gastropoda : Pulmonata). J Moll Stud 68:181–186
Baturo W (1995) Etude des effets écotoxicologiques de l’atrazine et de l’hexachlorobenzène sur Lymnaea palustris (Müller) (Gastropoda, Pulmonata) maintenue en mésocosmes: identification et validation expérimentale de biomarqueurs. Thesis report. University of Paris-Sud, Orsay, France
Baturo W, Lagadic L (1996) Benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylase and glutathione S-transferase activities as biomarkers in Lymnaea palustris (Mollusca, Gastropoda) exposed to atrazine and hexachlorobenzene in freshwater mesocosms. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:771–781
Baturo W, Lagadic L, Caquet T (1995) Growth, fecundity and glycogen utilization in Lymnaea palustris exposed to atrazine and hexachlorobenzene in freshwater mesocosms. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:503–511
Bayley M, Larsen PF, Baekgaard H, Baatrup E (2003) The effects of vinclozolin, an anti-androgenic fungicide, on male guppy secondary sex characters and reproductive success. Biol Reprod 69:1951–1956
Bohlken S, Joosse J, van Elk R, Geraerts WPM (1986) Interaction of photoperiod and nutritive state in female reproduction of Lymnaea stagnalis. Int J Invert Reprod Dev 10:151–157
Boss KJ (1982) Mollusca. In: Parker SP (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms, vol 1. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 945–1166
Bottke W, Burschyk M, Volmer J (1988) On the origin of the yolk protein ferritin in snails. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 197:377–382
Brown D (1994) Freshwater snails of Africa and their medical importance. 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, London, p. 609
Brown DS (1978) Pulmonate molluscs as intermediate hosts for digenetic trematodes. In: Fretter V, Peake J (eds) Pulmonates : systematics, evolution and ecology, vol. 2A. Academic Press, New York, pp 287–333
Brown KM (1991) Mollusca: Gastropoda. In: Thorp JH, Covich AP (eds) Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 285–314
Bulloch AG, Diep CQ, Logan CC, Bulloch ES, Robbins SM, Hislop J, Sossin WS (2005) Ltrk is differentially expressed in developing and adult neurons of the Lymnaea central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 487:240–254
Calow P (1983) Life-cycle patterns and evolution. In: Russell-Hunter WD (ed) The mollusca: ecology, vol 6. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 649–680
Casey D, Pascoe D, Tattersfield L, Hutchinson TH (2005) A comparison of freshwater pulmonate and prosobranch mollusc responses to steroidal oestrogens. In: Abstracts of the SETAC Europe 15th annual meeting, Lille, France, 22–26 May 2005, pp 105–106
Charbonnel N, Rasatavonjizay R, Sellin E, Brémond P, Jarne P (2005) The influence of genetic factors and population dynamics on the mating system of the hermaphroditic freshwater snail Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Oikos 108:283–296
Coeurdassier M, de Vaufleury A, Badot PM (2003) Bioconcentration of cadmium and toxic effects on life-history traits of pond snails (Lymnaea palustris and Lymnaea stagnalis) in laboratory bioassays. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:102–109
Coutellec M-A, Lagadic L (2006) Effects of self-fertilization, environmental stress and exposure to xenobiotics on fitness related traits of the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Ecotoxicology 15:199–213
Coutellec-Vreto M-A, Madec L, Guiller A (1997) Selfing and biparental inbreeding: a mating system analysis in Lymnaea peregra (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae). Heredity 79:277–285
Coutellec-Vreto M-A, Jarne P, Guiller A, Madec L, Daguzan J (1998) Inbreeding and fitness in the freshwater snail Lymnaea peregra: an evaluation over two generations of self-fertilization. Evolution 52:1635–1647
Cox KJ, Tensen CP, van der Schors RC, Li KW, van Heerikhuizen H, Vreugdenhil E, Geraerts WPM, Burke JF (1997) Cloning, characterization, and expression of a G-protein-coupled receptor from Lymnaea stagnalis and identification of a leucokinin-like peptide, PSFHSWSamide, and its endogenous ligand. J Neurosci 17:1197–1205
Croll RP, van Minnen J, Kits KS, Smit AB (1991) APGWamide: molecular, histological and physiological examination of a novel neuropeptide involved with reproduction in the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. In: Kits KS, Boer HH, Joosse J (eds) Molluscan neurobiology. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 248–254
Crossland NO, Wolff CJM (1985) Fate and biological effects of pentachlorophenol in outdoor ponds. Environ Toxicol Chem 4:73–86
Czech P, Weber K, Dietrich DR (2001) Effects of modulating substances on reproduction in the hermaphroditic snail Lymnaea stagnalis L. Aquat Toxicol 53:103–114
de Boer PACM, Jansen RF, Koene JM, ter Maat A (1997) Nervous control of male sexual drive in the hermaphroditic snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Biol 200:941–951
de Fur PL, Crane M, Ingersoll C, Tattersfield L (eds) (1999). Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: endocrinology, testing and assessment. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Pensacola, p 303
de Jong-Brink M, Geraerts WPM (1982) Oogenesis in gastropods. Malacologia 22:145–149
de Jong-Brink M, Schot LPC, Schoenmakers HJN, Bergamin-Sasser MJM (1981) A biochemical and quantitative electron microscope study on steroidogenesis in ovotestis and digestive gland of the pulmonate snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 45:30–38
de Lange RPJ, van Minnen J (1997) Localization of the neuropeptide APGWamide in gastropod molluscs by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Gen Comp Endocrinol 109:166–174
Dictus WJAG, de Jong-Brink M, Boer HH (1987) A neuropeptide (calfluxin) is involved in the influx of calcium into mitochondria of the albumen gland of the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 65:439–450
Dillon RT Jr (2005) Freshwater gastropods. In: Sturm CS, Pearce T, Valdès A (eds) The mollusks: a guide to their study, collection, and preservation. The American Malacological Society, Arlington, pp 130–138
Dogterom GE, Thijseen R, van Loenhout H (1985) Environmental and hormonal control of the seasonal egg laying period in field specimens of Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 57:37–42
Doums C, Jarne P (1996) The evolution of phally polymorphism in Bulinus truncatus (Gastropoda, Planorbidae): the cost of male function analyzed through life-history traits and sex allocation. Oecologia 106:464–469
Doums C, Perdieu M-A, Jarne P (1998) Resource allocation and stressful conditions in the aphallic snail Bulinus truncatus. Ecology 79:720–733
Doums C, Viard F, Pernot AF, Delay B, Jarne P (1996) Inbreeding depression, neutral polymorphism and copulatory behavior in freshwater snails: a self-fertilization syndrom. Evolution 50:1908–1918
Fent K (1996) Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 26:1–117
Ferguson GP, Pieneman AW, Jansen RF, ter Maat A (1993) Neuronal feedback in egg-laying behaviour of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Biol 178:251–259
Fries E, Puttmann W (2003) Occurrence and behaviour of 4-nonylphenol in river water of Germany. J Environ Monitor 5:598–603
Garcia M, Griffond B, Lafont R (1995) What are the origins of ecdysteroids in gastropods? Gen Comp Endocrinol 97:76–85
Geraerts WPM (1992) Neurohormonal control of growth and carbohydrate metabolism by the light green cells in Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 86:433–444
Geraerts WPM, Joosse J (1984) Freshwater snails (Basommatophora). In: Tompa AS, Verdonk NH, van den Biggelar JAM (eds) The mollusca, reproduction, vol 7. London, Academic Press, London, pp 141–207
Geraerts WPM, ter Maat A, Vreugdenhil E (1988) The peptidergic neurodendocrine control of egg-laying behaviour in Aplysia and Lymnaea. In: Laufer H, Downer R (eds) Endocrinology of selected invertebrate types, invertebrate endocrinology, vol 2. Alan R. Liss, New Yok, pp 144–231
Geraerts WPM, Smit AB, Li KW, Vreugdenhil E, van Heerikhuizen H (1991) Neuropeptide gene families that control reproductive behaviour and growth in molluscs. In: Osborne NN (ed) Current aspects of the neurosciences. MacMillan, London, pp 255–304
Gerhardt CC, Leysen JE, Planta RJ, Vreugdenhil E, van Heerikhuizen H (1996) Functional characterization of a 5-HT2 receptor cDNA cloned from Lymnaea stagnalis. Eur J Pharmacol 311:249–258
Gerhardt CC, Bakker RA, Peik GJ, Planta RJ, Vreugdenhil E, Leysen JE, van Heerikhuizen H (1997) Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of a molluscan octopamine receptor. Mol Pharmacol 51:293–300
Goldberg JI, Garofalo R, Price CJ, Chang JP (1993) Presence and biological activity of a GnRH-like factor in the nervous system of Helisoma trivolvis. J Comp Neurol 336:571–582
Gomot A (1998) Toxic effects of cadmium on reproduction, development, and hatching in freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis for water quality monitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 41:288–297
Gottfried H, Dorfman RI (1970) Steroids of invertebrates V. The in vitro biosynthesis of steroids by the male-phase ovotestis of the slug (Ariolimax californicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 15:120–138
Habdija I, Latjner J, Belinic I (1995) The contribution of gastropod biomass in macrobenthic communities of a karstic river. Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 80:103–110
Harvey RJ, Vreugdenhil E, Zaman SH, Bhandal NS, Usherwood PNR, Barnard EA, Darlison MG (1991) Sequence of a functional invertebrate GABAA receptor subunit, which can form a chimeric receptor with a vertebrate α subunit. EMBO J 10:3239–3245
Hermann PM, de Lange RPJ, Pieneman AW, ter Maat A, Jansen RF (1997) Role of neuropeptides encoded on CDCH-1 gene in the organization of egg-laying behavior in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurophysiol 78:2859–2869
Hermann PM, van Kesteren RE, Wildering WC, Painter SD, Reno JM, Sith J.S., Kumar SB, Geraerts WPM, Ericsson LH, Smit AB, Bulloch AGM, Nagle GT (2000) Neurotrophic action of a novel molluscan epidermal growth factor. J Neurosci 20:6355–6364
Hoek RM, van Kesteren RE, Smit AB, de Jong-Brink M, Geraerts WPM (1997) Altered gene expression in the host brain caused by a trematode parasite: Neuropeptide genes are preferentially affected during parasitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14072–14076
Holmes P, Harrison P, Bergman A, Brandt I, Brouwer B, Keiding N, Randall G, Sharpe R, Skakkebaek N, Ashby J, Barlow S, Dikkerson R, Humfrey C, Smith LM (1997) In: Proceedings of the European workshop on the impact of endocrine disruptors on human health and wildlife. MRC Institute for Environment and Health, Weibridge, UK
Hubendick B (1978) Systematics and comparative morphology of the Basommatophora. In: Fretter V, Peake J (eds) Pulmonates: systematics, evolution and ecology, vol 2A. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–47
Hunter RD (1980) Effects of grazing on the quantity and quality of freshwater aufwuchs. Hydrobiologia 69:251–259
Ibrahim MM (2006) Energy allocation patterns in Biomphalaria alexandrina snails in response to cadmium exposure and Schistosoma mansoni infection. Exp Parasitol 112:31–36
Ingersoll CG, Hutchinson T, Crane M, Dodson S, DeWitt T, Gies A, Huet M-C, McKenney CL Jr, Oberdörster E, Pascoe D, Versteeg DJ, Warwick O (1999) Laboratory toxicity tests for evaluating potential effects of endocrine-disrupting compounds. In: deFur PL, Crane M, Ingersoll C, Tattersfield L (eds) Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: endocrinology, testing, and assessment. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Pensacola, pp 107–197
Jarne P, Charlesworth D (1993) The evolution of the selfing rate in functionally hermaphrodite plants and animals. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 24:441–466
Jarne P, Städler T (1995) Population genetic structure and mating system evolution in freshwater pulmonates. Experientia 51:482–497
Jarne P, Vianey-Liaud M, Delay B (1993) Selfing and outcrossing in hermaphrodite freshwater gastropods (Basommatophora) : where, when and why. Biol J Linn Soc 49:99–125
Jarne P, Perdieu MA, Pernot AF, Delay B, David P (2000) The influence of self-fertilization and grouping on fitness attributes in the freshwater snail Physa acuta: population and individual inbreeding depression. J Evol Biol 13:645–655
Jeffery P (2001) Suprageneric classification of class Gastropoda. The Natural History Museum, London
Joosse J (1988) The hormones of molluscs. In: Laufer H, Downer RGH (eds) Endocrinology of selected invertebrate types, invertibrate endocrinolgy, vol 2. Alan R. Liss, New York, pp 89–140
Jumel A (2002) Effets du fomésafène (diphényl éther herbicide) seul et en mélange avec un adjuvant à base de nonylphénols polyéthoxylés chez Lymnaea stagnalis (Mollusque Gastéropode): relations entre biomarqueurs et performances reproductrices. Thesis Report, University of Rennes 1, France
Jumel A, Coutellec M-A, Cravedi J-P, Lagadic L (2002) Nonylphenol polyethoxylate adjuvant mitigates the reproductive toxicity of fomesafen on the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis in outdoor experimental ponds. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1876–1888
Kannan K, Keith TL, Naylor CG, Staples CA, Snyder SA, Giesy JP (2003) Nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates in fish, sediment, and water from the Kalamazoo River, Michigan. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:77–82
Kelce W, Monosson E, Gamsik M, Laws S, Gray LE Jr (1994) Environmental hormone disruptors: Evidence that vinclozolin developmental toxicity is mediated by antiandrogenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 126:276–285
Kellet E, Perry SJ, Santama N, Worster BM, Benjamin PR, Burke JF (1996) Myomodulin gene of Lymnaea: structure, expression, and analysis of neuropeptides. J Neurosci 16:4949–4957
Knott E, Puurtinen M, Kaitala V (2003) Primers for nine microsatellite loci in the hermaphroditic snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Mol Ecol Notes 3:333–335
Koene J, ter Maat A (2005) Sex role alternation in the simultaneous hermaphroditic pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis is determined by the availability of seminal fluid. Anim Behav 69:845–850
Koene J, Montagne-Wajer K, ter Maat A (2006) Effects of frequent mating on sex allocation in the simultaneously hermaphroditic great pond snail (Lymnaea stagnalis). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 60:332–338
Kojima H, Katsura E, Takeuchi S, Niiyama K, Kobayashi K (2004) Screening for estrogen and androgen receptor activities in 200 pesticides by in vitro reporter gene assays using chinese hamster ovary cells. Environ Health Persp 112:524–531
Lafont R (2000) The endocrinology of invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 9:41–57
Lagadic L, Bursztyka J, Baradat M, Lorber S, Heydorff M, Azam D, Quemeneur A, Cravedi J-P (2005) Influence of the complexity of aquatic test systems on the fate of vinclozolin and its reprotoxic effects in Lymnaea stagnalis. In: Abstracts of the SETAC Europe 15th annual meeting, Lille, France, 22–26 May 2005, p 105
Lal H, Misra V, Viswanathan PN, Krishna Murti CR (1983) Comparative studies on ecotoxicology of synthetic detergents. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 7:538–545
Landmeyer JE, Tanner TL, Watt BE (2004) Biotransformation of tributyltin to tin in freshwater river-bed sediments contaminated by an organotin release. Environ Sci Technol 38:4106–4112
Lanzer R, Pfister G, Schramm K-W, Kettrup A (1999) Evaluation of the toxicity of nonylphenol in the embryonic development of Lymnaea stagnalis (Linne). In: SECOTOX 99, fifth european conference on ecotoxicology and environmental safety, Neuherberg/Munich, Germany, March 15–17, 1999
LeBlanc GA, Campbell PM, Den Besten P, Brown RP, Chang ES, Coats JR, deFur PL, Dhadialla T, Edwards J, Riddiford LM, Simpson MG, Snell TW, Thorndyke M, Matsumura F (1999) The endocrinology of invertebrates. In: deFur PL, Crane M, Ingersoll C, Tattersfield L (eds) Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: endocrinology, testing, and assessment. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Pensacola, pp 23–106
Leung KMY, Morley NJ, Grist EPM, Morritt D, Crane M (2004) Chronic toxicity of tributyltin on development and reproduction of the hermaphroditic snail Physa fontinalis: Influence of population density. Mar Environ Res 58:157–162
Li KW, Geraerts WPM (1992) Isolation and chemical characterization of a novel insulin-related neuropeptide from the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Eur J Biochem 205:675–678
Li KW, Jimenez CR, van Veelen PA, Geraerts WPM (1994) Processing and targeting of a molluscan egg-laying peptide prohormone as revealed by mass spectrometric fingerprinting and peptide sequencing. Endocrinology 134:1812–1819
Li KW, van der Schors RC, Jeffery D, Jorgenson JW (1999) Detection of released egg-laying hormones from single cerebral ganglia of pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis by means of capillary column liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. In: Roubos EW, Wendelaar Bonga SE, de Vaudry E, Loof A (eds) Recent developments in comparative endocrinology and neurobiology. Shaker Publishing B.V, Maastricht, pp 363–366
Linacre A, Kellet E, Saunders SE, Bright K, Benjamin PR, Burke JF (1990) Cardioactive neuropeptide Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMRFamide) and novel related peptides are encoded in multiple copies by a single gene in the snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurosci 10:412–419
Lydeard C, Bogan A, Bouchet P, Cowie RH, Cummings KS, Frest TJ, Herbert D, Hershler R, Perez KE, Ponder WF, Roth B, Seddon M, Strong E, Thompson F (2004) The global decline of non-marine mollusks. Bioscience 54:321–330
Mahendru VK, Agarwal RA (1981) Changes in carbohydrate metabolism in various organs of the snail, Lymnaea acuminata following exposure to trichlorfon. Acta Pharmacol 48:377–381
Mandaville SM (1999) Bioassessment of freshwaters using benthic macroinvertebrates-a primer. Soil and Water Conservation Society of Metro Halifax, Halifax, p 244
Meunier C, Hurtrez-Boussès S, Jabbour-Zahab R, Durand P, Rondelaud D, Renaud F (2004) Field and experimental evidence of preferential selfing in the freshwater mollusc Lymnaea truncatula (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Heredity 92:312–322
Miksys S, Saleuddin ASM (1986) Ferritin as an exogenously derived yolk protein in Helisoma duryi (Mollusca: Pulmonata). Can J Zool 64:2678–2682
Minchella DJ, Leathers BK, Brown KM, McNair JK (1985) Host and parasite counter-adaptations: An example from a freshwater snail. Am Nat 126:843–854
Misra V, Lal H, Viswanathan PN, Krishna Murti CR (1984) 45Ca uptake from water by snails (Lymnaea vulgaris) in control and detergent-polluted samples. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 8:97–99
Molnar G, Salanki J, Kiss T (2004) Cadmium inhibits GABA-activated ion currents by increasing intracellular calcium level in snail neurons. Brain Res 1008:205–211
Mukai ST, Kiehn L, Saleuddin ASM (2004) Dopamine stimulates snail albumen gland glycoprotein secretion through the activation of a D1-like receptor. J Exp Biol 207:2507–2518
Nagle GT, de Jong-Brink M, Painter SD, Li KW (2001) Structure, localization and potential role of a novel molluscan trypsin inhibitor in Lymnaea. Eur J Biochem 268:1213–1221
Nolte A, Koolman J, Dorlöchter M, Straub H (1986) Ecdysteroids in the dorsal bodies of pulmonates (Gastropoda): synthesis and release of ecdysone. Comp Biochem Physiol A 84:777–782
Oehlmann J, di Benedetto P, Tillmann M, Duft M, Oetken M, Schulte-Oehlmann U (2007) Endocrine disruption in prosobranch molluscs: evidence and ecological relevance. Ecotoxicology, DOI: 10.1007/s10646-006-0109-x
Oetken M, Bachmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Oehlmann J (2004) Evidence for endocrine disruption in invertebrates. Int Rev Cytol 236:1–44
OSPAR (2005) 2005 assessment of data collected under the co-ordinated environmental monitoring programe. OSPAR Commission, London, p 115
Ostrowski MF, Jarne P, David P (2000) Quantitative genetics of sexual plasticity: the environmental threshold model and genotype-by-environment interaction for phallus development in the snail Bulinus truncatus. Evolution 54:1614–1625
Ravera O (1991) Influence of heavy metals on the reproduction and embryonic development of freshwater pulmonates (Gastropoda, Mollusca) and cladocerans (Crustacea, Arthropoda). Comp Biochem Physiol 100C:215–219
Roovers E, Vincent ME, van Kesteren E, Geraerts WPM, Planta RJ, Vreugdenhil E, van Heerikhuizen H (1995) Characterization of a putative molluscan insulin-related peptide receptor. Gene 162:181–188
Rotchell JM, Ostrander GK (2003) Molecular markers of endocrine disruption in aquatic organisms. J Toxicol Environ Health B 6:453–495
Roubos EW, van de Ven MH (1987) Morphology of neurosecretory cells in basommatophoran snails homologous with egg-laying and growth hormone-producing cells of Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 67:7–23
Roubos EW, van Winkoop A, van der Haar C, van Minnen J (1988) Postembryonic development of endocrine dorsal bodies and neuroendocrine egg laying and growth hormone producing neurones of Lymnaea stagnalis. Int J Invert Reprod Dev 13:119–145
Russell-Hunter WD (1983) Overview: Planetary distribution of and ecological constraints upon the mollusca. In: Russell-Hunter WD (ed) The mollusca: ecology, vol 6. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 1–28
Russell-Hunter WD, Buckley DE (1983) Actuarial bioenergetics of non-marine molluscan productivity. In: Russell-Hunter WD (ed) The mollusca ecology, vol 6. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 463–503
Saleuddin ASM, Ashton ML, Khan HR (1989) Mating-induced release of granules by the endocrine dorsal body cells of the snail Helisoma duryi (Mollusca). J Exp Zool 250:206–213
Saleuddin ASM, Mukai ST, Khan HR (1994) Molluscan endocrine structures associated with the central nervous system. In: Davey KG, Peter RE, Tobe SS (eds) Perspectives in comparative endocrinology. Ottawa: National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, pp 257–263
Saunders SE, Kellett E, Bright K, Benjamin PR, Burke JF (1992) Cell-specific alternative RNA splicing of an FMRFamide gene transcript in the brain. J Neurosci 12:1033–1039
Schrag SJ, Ndifon GT, Read AF (1994) Temperature-determined outcrossing ability in wild populations of a simultaneous hermaphrodite snail. Ecology 75:2066–2077
Schrag SJ, Read AF (1992) Temperature determination of male outcrossing ability in a simultaneous hermaphrodite gastropod. Evolution 46:1698–1707
Segner H, Caroll K, Fenske M, Janssen CR, Maack G, Pascoe D, Schäfers C, Vandenbergh GF, Watts M, Wenzel A (2003) Identification of endocrine-disrupting effects in aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates: report from the European IDEA project. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 54:302–314
Smit AB, Jiménez CR, Dirks RW, Croll RP, Geraerts WPM (1992) Characterization of a cDNA clone encoding multiple copies of the neuropeptide APGWamide in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurosci 12:1709–1715
Smit AB, van Marle A, van Elk R, Bogerd J, van Heerikhuizen H, Geraerts WPM (1993) Evolutionary conservation of the insulin gene structure in invertebrates: cloning of the gene encoding molluscan insulin-related peptide III from Lymnaea stagnalis. J Mol Endocrinol 11:103–113
Smit AB, de Jong-Brink M, Li KW, Sassen MMJ, Spijker S, van Elk R, Buijs S, van Minnen J, van Kesteren RE (2004) Granularin, a novel molluscan opsonin comprising a single vWF type C domain is up-regulated during parasitation. FASEB J 18:845–847
Städler T, Weisner S, Streit B (1995) Outcrossing rates and correlated matings in a predominantly selfing frehswater snail. Proc R Soc Lond B 262:119–125
Szücs A, Salánki J, Rózsa KS (1994) Effects of chronic exposure to cadmium- or lead-enriched environments on ionic currents of identified neurons in Lymnaea stagnalis L. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14:769–780
Takeda N (1979) Induction of egg-laying by steroid hormones in slugs. Comp Biochem Physiol 62:273–278
Takeda N (2000) Mollusca. In: Dorn A (ed) Reproductive biology of invertebrates, part A, progress in developmental endocrinology, vol 10. Wiley, New York, pp 93–147
Tensen CP, Cox KJ, Smit AB, van der Schors RC, Meyerhof W, Richter D, Planta RJ, Hermann PM, van Minnen J, Geraerts WPM, Knol JC, Burke JF, Vreugdenhil E, van Heerikhuizen H (1998) The Lymnaea cardioexcitatory peptide (LyCEP) receptor: a G-protein-coupled receptor for a novel member of the RFamide neuropeptide family. J Neurosci 18:9812–9821
ter Maat A, Pieneman AW, Goldschmeding JT, Smelik WFE, Ferguson GP (1989) Spontaneous and induced egg-laying behavior of the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Comp Physiol A 164:673–683
Teunissen Y, Geraerts WPM, van Heerikhuzen H, Planta RJ (1992) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a member of a novel cytochrome P-450 family in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. J Biochem 112:249–252
Thibaut R, Jumel A, Debrauwer L, Rathahao E, Lagadic L, Cravedi J-P (2000) Identification of 4-n-nonylphenol metabolic pathways and residues in aquatic organisms by HPLC and LC-MS analyses. Analusis 28:793–801
Thornton JW, Need E, Crews D (2003) Resurrecting the ancestral steroid receptor: ancient origin of estrogen signalling. Science 301:1714–1717
Tillman M, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Duft M, Markert B, Oehlmann J (2001) Effects of endocrine disruptors on prosobranch snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) in the laboratory. Part III: Cyproterone acetate and vinclozolin as antioandrogens. Ecotoxicology 10:373–388
Tsitrone A, Jarne P, David P (2003) Delayed selfing and resource reallocations in relation to mate availability in the frehswater snail Physa acuta. Am Nat 162:474–488
Uyenoyama MK, Holsinger KE, Waller DM (1993) Ecological and genetic factors directing the evolution of self-fertilization. Oxford Surv Evol Biol 9:327–381
van den Berg M, Sanderson JT, Kurihara N, Katayama A (2003) The role of metabolism in the endocrine disrupting effects of chemicals in aquatic and terrestrial systems. Pure Appl Chem 75:1917–1932
van Golen FA, Li KW, de Lange RPJ, van Kesteren RE, van der Schors RC, Geraerts WPM (1995) Co-localized neuropeptides conopressin and Ala-Pro-Gly-Trp-NH2 have antagonistic effects on the vas deferens of Lymnaea. Neuroscience 69:1275–1287
van Kesteren RE, Smit AB, de Lange RPJ, Kits KS, van Golen FA, van der Schors RC, de With ND, Burke JF, Geraerts WPM (1995) Structural and functional evolution of the vasopressin/oxytocin superfamily: vasopressin-related conopressin is the only member present in Lymnaea, and is involved in the control of sexual behavior. J Neurosci 15:5989–5998
van Kesteren RE, Tensen CP, Smit AB, van Minnen J, Kolakowski LF, Meyerhof W, Richter D, van Heerikhuizen H, Vreugdenhil E, Geraerts WPM (1996) Co-evolution of ligand-receptor pairs in the vasopressin/oxytocin superfamily of bioactive peptides. J Biol Chem 271:3619–3626
van Kesteren RE, Fainzilber M, Hauser G, van Minnen J, Vreugdenhil E, Smit AB, Ibáñez CF, Geraerts WPM, Bulloch AGM (1998) Early evolutionary origin of the neurotrophin receptor family. EMBO J 17:2534–2542
van Nierop P, Bertrand S, Munno DW, Gouwenberg Y, van Minnen J, Spafford JD (2006) Identification and functional expression of a family of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in the central nervous system of the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. J Biol Chem 281:1680–1691
Viard F, Doums C, Jarne P (1997) Selfing, sexual polymorphism and microsatellites in the hermaphroditic freshwater snail Bulinus truncatus. Proc R Soc Lond B 264:39–44
Vreugdenhil E, Jackson JF, Bouwmeester T, Smit AB, van Minnen J, van Heerikhuizen H, Klootwijk J, Joosse J (1988) Isolation, characterization, and evolutionary aspects of a cDNA clone encoding multiple neuropeptides involved in the stereotyped egg-laying behavior of the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurosci 8:4184–4191
Weltje L, Scholz C, van Doornmalen J, Markert B, Oehlmann J (2003) Endocrine disruption in the hermaphroditic pondsnail Lymnaea stagnalis. In: Abstracts of the SETAC Europe 13th annual meeting, Hamburg, Germany, 27 April-1 May 2005, p189
Wethington AR, Dillon RT Jr (1997) Selfing, outcrossing, and mixed mating in the freshwater snail Physa heterostropha: lifetime fitness and inbreeding depression. Invest Biol 116:192–199
Wijdenes J, van Elk E, Joosse J (1983) Effects of two gonadotropic hormones on polysaccharides synthesis in the albumen gland of Lymnaea stagnalis, studied with the organ culture technique. Gen Comp Endocrinol 51:263–271
Young KG, Chang JP, Goldberg JI (1999) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal system of the freshwater snails Helisoma trivolvis and Lymnaea stagnalis: Possible involvement in reproduction. J Comp Neurol 404:427–437
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lagadic, L., Coutellec, MA. & Caquet, T. Endocrine disruption in aquatic pulmonate molluscs: few evidences, many challenges. Ecotoxicology 16, 45–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0114-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0114-0