Abstract
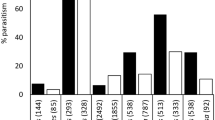
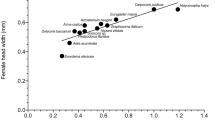
Despite numerous interceptions at the border, the brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB), Halyomorpha halys Stål (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), is not yet established in New Zealand. Nevertheless, a classical biocontrol programme using the egg parasitoid Trissolcus japonicus Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) has been initiated in anticipation of its likely arrival. The potential host range of the parasitoid in New Zealand was investigated by importing parasitised BMSB eggs into quarantine from Newark, DE, USA. Egg masses of seven species of Pentatomidae, including one sub-species, were individually exposed to naïve mated female T. japonicus in no-choice laboratory experiments. The results showed that predatory Cermatulus nasalis nasalis, C. nasalis hudsoni and Oechalia schellenbergii, and the phytophagous Monteithiella humeralis, Dictyotus caenosus, Glaucias amyoti, and Cuspicona simplex are all within the physiological host range of T. japonicus, although not all appeared to be equally susceptible to parasitism. No development or emergence of T. japonicus from eggs of the cosmopolitan pentatomid plant pest Nezara viridula were observed. The likely ecological consequences of releasing T. japonicus in New Zealand are discussed, as is the subsequent decision of New Zealand’s Environmental Protection Authority to approve release of the parasitoid once BMSB arrives in New Zealand.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram PK, Hoelmer KA, Acebes-Doria A, Andrews H, Beers EH, Bergh JC, Bessin R, Biddinger D, Botch P, Buffington ML, Cornelius ML, Costi E, Delfosse ES, Dieckhoff C, Dobson R, Donais Z, Grieshop M, Hamilton G, Haye T, Hedstrom C, Herlihy MV, Hoddle MS, Hooks CRR, Jentsch P, Joshi NK, Kuhar TP, Lara J, Lee JC, Legrand A, Leskey TC, Lowenstein D, Maistrello L, Mathews CR, Milnes JM, Morrison WR, Nielsen AL, Ogburn EC, Pickett CH, Poley K, Pote J, Radl J, Shrewsbury PM, Talamas E, Tavella L, Walgenbach JF, Waterworth R, Weber DC, Welty C, Wiman NG (2017) Indigenous arthropod natural enemies of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe. J Pest Sci 90:1009–1020
Abram PK, Talamas EJ, Acheampong S, Mason PG, Gariepy TD (2019) First detection of the samurai wasp, Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), in Canada. J Hymenopt Res 68:29–36
Avila GA, Charles JG (2018) Modelling the potential geographic distribution of Trissolcus japonicus: a biological control agent of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. BioControl 63:505–518
Avila GA, Withers TM, Holwell GI (2016) Laboratory odour-specificity testing of Cotesia urabae to assess potential risks to non-target species. BioControl 61:365–377
Barratt BIP, Evans AA, Ferguson CM, Barker GM, McNeill MR, Phillips CB (1997) Laboratory nontarget host range of the introduced parasitoids Microctonus aethiopoides and M. hyperodae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) compared with field parasitism in New Zealand. Entomol Soc Am 26:694–702
Barratt BIP, Berndt LA, Dodd SL, Ferguson CM, Hill RL, Kean JM, Teulon DAJ, Withers TM (2007) BIREA—Biocontrol Information Resource for EPA applicants. http://www.b3nz.org/birea/. Accessed 2 Oct 2017
Buffington M, Talamas EJ, Hoelmer KA (2018) Team Trissolcus: integrating taxonomy and biological control to combat the brown marmorated stink bug. Am Entomol 64:224–232
Conti E, Salerno G, Bin F, Vinson SB (2004) The role of host semiochemicals in parasitoid specificity: a case study with Trissolcus brochymenae and Trissolcus simoni on pentatomid bugs. Biol Control 29:435–444
Dieckhoff C, Tatman K, Hoelmer KA (2017) Natural biological control of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) by native egg parasitoids—a multi-year survey in northern Delaware. J Pest Sci 90:1143–1158
Duthie C (2012) Risk analysis of Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stinkbug) on all pathways. Ministry for primary industries. https://mpi.govt.nz/dmsdocument/2909-halyomorpha-halys-brown-marmorated-stink-bug-riskanalysis-november-2012. Accessed 02 Feb 2017
EPA (2018) Application and approval to release Trissolcus japonicus into New Zealand. https://www.epa.govt.nz/search/SearchForm?Search=Trissolcus+japonicus. Accessed March 2019
Faúndez EI, Rider DA (2017) The brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål 1885) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile. Arquivos Entomol 17:305–330
Ferro J (2017) Stink bug killers: Scientists to release Samurai wasps. Discovery of wasps in Ulster County is likely to speed process across New York. http://www.stopbmsb.org/more-resources/bmsb-in-the-news/stink-bug-killers-scientists-to-release-samurai-wasps/. Accessed 10 May 2017
Gapon D (2016) First records of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål, 1855) (Heteroptera, Pentatomidae) in Russia, Abkhazia, and Georgia. Entomol Rev 96:1086–1088
Haye T, Goulet H, Mason P, Kuhlmann U (2005) Does fundamental host range match ecological host range? A retrospective case study of a Lygus plant bug parasitoid. Biol Control 35:55–67
Haye T, Gariepy T, Hoelmer K, Rossi J-P, Streito J-C, Tassus X, Desneux N (2015a) Range expansion of the invasive brown marmorated stinkbug, Halyomorpha halys: an increasing threat to field, fruit and vegetable crops worldwide. J Pest Sci 88:665–673
Haye T, Fischer S, Zhang J, Gariepy T (2015b) Can native egg parasitoids adopt the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), in Europe. J Pest Sci 88:693–705
Haye T, Moraglio ST, Stahl J, Visentin S, Grogorio T, Tavella L (2019) Fundamental host range of Trissolcus japonicus in Europe. J Pest Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-019-01127-3
Hedstrom C, Lowenstein D, Andrews H, Bai B, Wiman N (2017) Pentatomid host suitability and the discovery of introduced populations of Trissolcus japonicus in Oregon. J Pest Sci 90:1169–1179
Jentsch P (2016) BMSB News: The invasive parasitic wasp, Trissolcus japonicus, recently found in New York State. https://blogs.cornell.edu/jentsch/2016/09/19/bmsb-news-the-invasive-parasitic-wasp-trissolcus-japonicus-recently-found-in-new-york-state/. Accessed 26 April 2017
Kim KY, Choi D-S, Choi J-Y, Hong K-J (2017) Host records of Trissolcus (Hymenoptera: Platygasteridae: Telenominae) parasitizing eggs of stink bugs in Korea. Korean J Appl Entomol 56:87–92
Kriticos DJ, Kean JM, Phillips CB, Senay SD, Acosta H, Haye T (2017) The potential global distribution of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys, a critical threat to plant biosecurity. J Pest Sci 90:1033–1043
Lara J, Pickett C, Ingels C, Haviland D, Grafton-Cardwell E, Doll D, Bethke J, Dara S, Hoddle M (2016) Biological control program is being developed for brown marmorated stink bug. Calif Agric 70:15–23
Larivière M-C (1995) Cydnidae, Acanthosomatidae, and Pentatomidae (Insecta: Heteroptera): systematics, geographical distribution, and bioecology. Fauna of New Zealand 35. Whenua Press, Lincoln
Lee D-H (2015) Current status of research progress on the biology and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) as an invasive species. Appl Entomol Zool 50:277–290
Lee D-H, Short BD, Leskey TC, Joseph SV, Bergh JC (2013) Review of the biology, ecology, and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Environ Entomol 42:627–641
Leskey TC, Nielsen AL (2018) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe: history, biology, ecology, and management. Ann Rev Entomol 63:599–618
Liebhold AM, Berec L, Brockerhoff EG, Epanchin-Niell RS, Hastings A, Herms DA, Kean JM, McCullough DG, Suckling DM, Tobin PC, Yamanaka T (2016) Eradication of invading insect populations: from concepts to applications. Annu Rev Entomol 61:335–352
Medal J, Smith T, Fox A, Santa Cruz A, Poplin A, Hodges A (2012) Rearing the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys. Flo Entomol 95:800–802
Milnes JN, Wiman NG, Talamas EJ, Brunner JF, Hoelmer KA, Buffington ML, Beers EH (2016) Discovery of an exotic egg parasitoid of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) in the Pacific Northwest. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 118:466–470
Morrison WR III, Blaauw BR, Nielsen AL, Talamas E, Leskey TC (2018) Predation and parasitism by native and exotic natural enemies of Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) eggs augmented with semiochemicals and differing host stimuli. Biol Control 121:140–150
Nystrom Santacruz E, Venette R, Dieckhoff C, Hoelmer K, Koch RL (2017) Cold tolerance of Trissolcus japonicus and T. cultratus, potential biological control agents of Halyomorpha halys, the brown marmorated stink bug. Biol Control 107:11–20
Ogburn E, Bessin R, Dieckhoff C, Dobson R, Grieshop M, Hoelmer K, Mathews C, Moore J, Nielsen A, Poley K, Pote J, Rogers M, Welty C, Walgenbach J (2016) Natural enemy impact on eggs of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), in organic agroecosystems: a regional assessment. Biol Control 101:39–51
Quinn NF, Talamas EJ, Acebes-Doria AL, Leskey TC, Bergh JC (2019) Vertical sampling in tree canopies for Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) life stages and its egg parasitoid, Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Environ Entomol 48:173–180
Rice K, Bergh C, Bergmann E, Biddinger D, Dieckhoff C, Dively G, Fraser H, Gariepy T, Hamilton G, Haye T, Herbert A, Hoelmer K, Hooks C, Jones A, Krawczyk G, Kuhar T, Martinson H, Mitchell W, Nielson A, Pfeiffer D, Raupp M, Rodriguez-Saona C, Shearer P, Shrewsbury P, Venugopal P, Whalen J, Wiman N, Leskey T, Tooker J (2014) Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Integr Pest Manag 5:1–13
Rider D (2015) Pentatomoidea home page. North Dakota State University. https://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~rider/Pentatomoidea/. Accessed 2 Oct 2017
Sabbatini Peverieri G, Talamas E, Bon MC, Marianelli L, Bernardinelli I, Malossini G, Benvenuto L, Roversi PF, Hoelmer K (2018) Two asian egg parasitoids emerge in Italy on Halyomorpha halys: Trissolcus mitsukurii (Ashmead) and Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). J Hym Res 67:37–53
Stahl J, Tortorici F, Pontini M, Bon MC, Hoelmer K, Marazzi C, Tavella L, Haye T (2019) First discovery of adventive populations of Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) in Europe. J Pest Sci 92:371–379
Taekul C, Valerio A, Austin A, Klompen H, Johnson N (2014) Molecular phylogeny of telenomine egg parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae s.l.: Telenominae): evolution of host shifts and implications for classification. Syst Entomol 39:24–35
Talamas EJ, Buffington M, Hoelmer K (2013) New synonymy of Trissolcus halyomorphae (Yang). J Hymenopt Res 33:113–117
Talamas E, Johnson N, Buffington M (2015a) Key to Nearctic species of Trissolcus Ashmead (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), natural enemies of native and invasive stink bugs (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae). J Hymenopt Res 43:45–110
Talamas EJ, Herlihy MV, Dieckhoff C, Hoelmer K, Buffington M, Bon M-C, Weber DC (2015b) Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae) emerges in North America. J Hymenopt Res 43:119–128
Tobin PC, Kean JM, Suckling DM, McCullough DG, Herms DA, Stringer LD (2014) Determinants of successful arthropod eradication programs. Biol Invasions 16:401–414
van Driesche RG, Murray TJ (2004) Overview of testing schemes and designs used to estimate host ranges. In: van Driesche RG, Reardon R (eds) Assessing host ranges for parasitoids and predators used for classical biological control: a guide to best practice. Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team (FHTET), Morgantown, pp 68–89
Williams DA (1982) Extra-binomial variation in logistic linear models. J R Stat Soc 31:144–148
Yang Z-Q, Yao Y-X, Qiu L-F, Li Z-X (2009) A new species of Trissolcus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) parasitizing eggs of Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in China with comments on its biology. Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:39–47
Zhang J, Zhang F, Gariepy T, Mason P, Gillespie D, Talamas E, Haye T (2017) Seasonal parasitism and host specificity of Trissolcus japonicus in northern China. J Pest Sci 90:1127–1141
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr Barbara Barratt (AgResearch), Dr Mark Hoddle (University of California, Riverside), Dr Cathy McKenna (Plant and Food Research), Dr David Teulon (Plant and Food Research), Graham Walker (Plant and Food Research) and Libby Burgess (Plant and Food Research) for their useful comments on draft versions of this manuscript. We thank Mark Wohlers (Plant and Food Research) for assistance in statistical analysis, and Dr N. A. Martin for collecting Pentatomidae from which laboratory cultures were initiated. We also thank Brian Patrick (Wildlands Consultants Ltd), and the AgResearch Invermay team for their efforts in support of this work. This work was funded by New Zealand’s Ministry of Science and Innovation, the Better Border Biosecurity (B3) (http://www.b3nz.org) research collaboration and The New Zealand Institute for Plant & Food Research Limited Strategic Science Investment Fund. Support for maintenance of T. japonicus cultures in the USA was provided to K. Hoelmer by USDA NIFA SCRI Grant 2011-51181-30937.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Research involving human and/or animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals (vertebrates) performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stefano Colazza
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charles, J.G., Avila, G.A., Hoelmer, K.A. et al. Experimental assessment of the biosafety of Trissolcus japonicus in New Zealand, prior to the anticipated arrival of the invasive pest Halyomorpha halys. BioControl 64, 367–379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-019-09949-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-019-09949-x