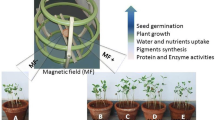
Abstract
This review provides detailed insight on the effects of magnetic fields on germination, growth, development, and yield of plants focusing on ex vitro growth and development and discussing the possible physiological and biochemical responses. The MFs considered in this review range from the nanoTesla (nT) to geomagnetic levels, up to very strong MFs greater than 15 Tesla (T) and also super-weak MFs (near 0 T). The theoretical bases of the action of MFs on plant growth, which are complex, are not discussed here and thus far, there is limited mathematical background about the action of MFs on plant growth. MFs can positively influence the morphogenesis of several plants which allows them to be used in practical situations. MFs have thus far been shown to modify seed germination and affect seedling growth and development in a wide range of plants, including field, fodder, and industrial crops; cereals and pseudo-cereals; grasses; herbs and medicinal plants; horticultural crops (vegetables, fruits, ornamentals); trees; and model crops. This is important since MFs may constitute a non-residual and non-toxic stimulus. In addition to presenting and summarizing the effects of MFs on plant growth and development, we also provide possible physiological and biochemical explanations for these responses including stress-related responses of plants, explanations based on dia-, para-, and ferromagnetism, oriented movements of substances, and cellular and molecular changes.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Alternating current
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- DC:
-
Direct current
- EMF:
-
Electromagnetic field
- G:
-
Gauss
- GMF:
-
Geomagnetic field
- ICR:
-
Ion cyclotron resonance
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MF:
-
Magnetic field
- MW:
-
Magnetized water
- nT:
-
nanoTesla
- POX:
-
Peroxidase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- T:
-
Tesla
- WMF:
-
Weak magnetic field
References
Abdolmaleki P, Ghanati F, Sahebjamei H, Sarvestani AS (2007) Peroxidase activity, lignification and promotion of cell death in tobacco cells exposed to static magnetic field. Environmentalist 27:435–440
Aguilar CH, Dominguez-Pacheco A, Carballo AC, Cruz-Orea A, Ivanov R, Bonilla JLL, Montañez JPV (2009) Alternating magnetic field irradiation effects on the three genotype maize seed field performance. Acta Agrophysica 14(1):7–17
Aksyonov SJ, Bulychev AA, Grunina TY, Goryachev SN, Turovetsky VB (2001) Effects of ELF-EMF treatment on wheat seeds at different stages of germination and possible mechanism of their origin. Electromagn Biol Med 20:231–253
Aksyonov SI, Grunina TY, Goryachev SN (2007) On the mechanism of stimulation and inhibition of wheat seed germination by low-frequency magnetic field. Biophysics 52:233–236
Aladjadjiyan A (2002) Study of the influence of magnetic field on some biological characteristics of Zea mais. J Cent Eur Agric 3(2):89–94
Aladjadjiyan A (2003) Use of physical factors as an alternative to chemical amelioration. J Environ Prot Ecol 4(3):662–667
Aladjadjiyan A (2012) Physical factors for plant growth stimulation improve food quality. In: Aladjadjiyan A (ed) Food production—approaches, challenges and tasks. InTech, Croatia, pp 145–168
Alexander MP, Doijode SD (1995) Electromagnetic field, a novel tool to increase germination and seedling vigour of conserved onion (Allium cepa L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.) seed with low viability. Plant Genet Res Newslett 104:1–5
Ali TB, Khalil SE, Khalil AM (2011) Magnetic treatments of Capsicum annuum L. grown under saline irrigation conditions. J Appl Sci Res 7:1558–1568
Alikamanoglu S, Sen A (2011) Stimulation of growth and some biochemical parameters by magnetic field in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) tissue culture. Afr J Biotechnol 10:10957–10963
Almaghrabi OA, Elbeshehy EKF (2012) Effect of weak electro magnetic field on grain germination and seedling growth of different wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Life Sci J 9:1615–1622
Asemota GNO (2010) Alternating electromagnetic fields in plantains. Afr J Plant Sci Biotechnol 4(Special Issue 1):59–75
Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) (1983) Seed vigor testing handbook. AOSA Handbook 32
Atak Ç, Emiroğlu O, Alikamanoğlu S, Rzakoulieva A (2003) Stimulation of regeneration by magnetic field in soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill) tissue cultures. J Cell Mol Biol 2:113–119
Atak Ç, Çelik O, Olgum A, Alikamanoğlu S, Rzakoulieva A (2007) Effect of magnetic field on peroxidase activities of soybean tissue culture. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 21:166–171
Audus LJ (1960) Magnetotropism: A new plant growth response. Nature 185:132–134
Bathnagar D, Deb A (1977) Some aspects of pregermination exposure of wheat seeds to magnetic field. I. Germination and early growth. Seed Res 5:129–137
Belyavskaya NA (2001) Ultrastructure and calcium balance in meristem cells of pea roots exposed to extremely low magnetic fields. Adv Space Res 28:645–650
Belyavskaya NA (2004) Biological effects due to weak magnetic field on plants. Adv Space Res 34:1566–1574
Berahmand AA, Panahi AG, Sahabi H, Feizi H, Moghaddam PR, Shahtahmassebi N, Fotovat A, Karimpour H, Gallehgir O (2012) Effects silver nanoparticles and magnetic field on growth of fodder maize (Zea mays L.). Biol Trace Elem Res 149:419–424
Bilalis DJ, Katsenios N, Efthimiadou A, Karkanis A, Khah EM, Mitsis T (2013) Magnetic field pre-sowing treatment as an organic friendly technique to promote plant growth and chemical elements accumulation in early stages of cotton. Aust J Crop Sci 7:46–50
Binhi VN (2001) Theoretical concepts in magnetobiology. Electro-Magnetobiol 20:43–58
Blackmore RP (1982) Magnetotactic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 36:217–238
Büyükuslu N, Çelik Ö, Atak Ç (2006) The effect of magnetic field on the activity of superoxide dismutase. J Cell Mol Biol 5:57–62
Cakmak T, Dumlupinar R, Erdal S (2010) Acceleration of germination and early growth of wheat and bean seedlings grown under various magnetic field and osmotic conditions. Bioelectromagnetics 31:120–129
Carbonell MV, Martínez E, Amaya JM (2000) Stimulation of germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by a static magnetic field. Electro-Magnetobiol 19:121–128
Carbonell MV, Martínez E, Flórez M, Maqueda R, Pintor-López A, Amaya JM (2008) Magnetic field treatments improve germination and seedling growth in Festuca arundinaceae Screb. and Lolium perenne L. Seed Sci Technol 36:31–37
Carbonell MV, Flórez M, Martínez E, Maqueda R, Pintor-López A, Amaya JM (2011) Study of stationary magnetic fields on initial growth of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seeds. Seed Sci Technol 39:673–679
Celestino C, Picazo ML, Toribio M, Alvarez-Ude JA, Bardasano JL (1998) Influence of 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on recurrent embryogenesis and germination of cork oak somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 54:65–69
Celestino C, Picazo ML, Toribio M (2000) Influence of chronic exposure to an electromagnetic field on germination and early growth of Quercus suber seeds preliminary study. Electro-Magnetobiol 19:115–120
Çelik O, Atak Ç, Rzakulieva A (2008) Stimulation of rapid regeneration by a magnetic field in Paulownia node cultures. J Cent Eur Agric 9:297–304
Chen Y, Li R, He J (2011) Magnetic field can alleviate toxicological effect induced by cadmium in mungbean seedlings. Ecotoxicology 20:760–769
Commoner B, Heise JJ, Townsend J (1956) Light-induced paramagnetism in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 42(10):710–718
Danilov V, Bas T, Eltez M, Rzakoulieva A (1994) Artificial magnetic field effect on yield and quality of tomatoes. Acta Horticult 366:279–285
Davies MS (1996) Effects of 60 Hz electromagnetic fields on early growth in three plant species and a replication of previous results. Bioelectromagnetics 17:154–161
De Micco V, Aronne G, Joseleau J, Ruel K (2008) Xylem development and cell wall changes of soybean seedlings grown in space. Ann Bot 101:661–669
De Souza A, Garcia D, Sueiro L, Gilart F, Porras E, Licea L (2006) Pre-sowing magnetic treatments of tomato seeds increase the growth and yield of plants. Bioelectromagnetics 27:247–257
Dhawi F, Al-Khayri JM (2009) Magnetic fields induce changes in photosynthetic pigments content in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seedlings. Open Agric J 3:1–5
Efthimiadou A, Katsenios N, Karkanis A, Papastylianou P, Triantafyllidis V, Travlos I, Bilalis DJ (2014) Effects of presowing pulsed electromagnetic treatment of tomato seed on growth, yield, and lycopene content. Sci World J Article ID 369745, 6 pp
Eşitken A (2003) Effect of magnetic fields on yield and growth in strawberry ‘Camarosa’. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 78(2):145–147
Eskov EK, Darkov AV (2003) Consequences of high-intensity magnetic effects on the early growth processes in plant seeds and the development of honeybees. Biol Bull 30:512–516
Faqenabi F, Tajbakhsh M, Bernoosi I, Saber-Rezaii M, Tahri F, Parvizi S, Izadkhah M, Gorttapeh AH, Sedqi H (2009) The effect of magnetic field on growth, development and yield of safflower and its comparison with other treatments. Res J Biol Sci 4(2):174–178
Feizi H, Sahabi H, Moghaddam PR, Shahtahmassebi N, Gallehgir O, Amirmoradi S (2012) Impact of intensity and exposure duration of magnetic field on seed germination of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Not Sci Biol 4(1):116–120
Fischer G, Tausz M, Köck M, Grill D (2004) Effects of weak 16 Hz magnetic fields on growth parameters of young sunflower and wheat seedlings. Bioelectromagnetics 25:638–641
Flórez M, Carbonell MV, Martínez E (2004) Early sprouting and first stages of growth of rice seeds exposed to a magnetic field. Electro Magnetobiol Med 23:167–176
Flórez M, Carbonell MV, Martínez E (2007) Exposure of maize seeds to stationary magnetic fields: effects on germination and early growth. Environ Exp Bot 59:68–75
Flórez M, Martínez E, Carbonell MV, Álvarez J, Campos A (2014) Germination and initial growth of triticale seeds under stationary magnetic treatment. J Adv Agric 2(2):72–79
Galland P, Pazur A (2005) Magnetoreception in plants. J Plant Res 118:371–389
Goldsworthy A (1996) Electrostimulation of cells by weak electric currents. In: Lynch PT, Davey NR (eds) Electrical manipulation of cells. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 249–272
Goldsworthy A (2006) Effects of electrical and electromagnetic fields in plants and related topics. In: Volkov AG (ed) Plant electrophysiology-theory and methods, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 247–267
Goldsworthy A (2007) The biological effects of weak electromagnetic fields. Available online: http://www.radiationresearch.org/pdf/goldsworthy_bio_weak_em_07/pdf. Accessed 5 May 2015
Govoroon RD, Danilov VI, Fomicheva VM, Belyavskaya NA, Zinchenko SY (1992) Effects of fluctuations of a geomagnetic field and its screening on early phases in development of higher plants. Biofizika 37:738–743. (in Russian)
Griffiths DJ (1999) In: Ghosh AK (ed) Introduction to electrodynamics, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, pp 55–507
Gubbels GH (1982) Seedling growth and yield response of flax, buckwheat, sunflower and field pea after preceding magnetic treatment. Can J Plant Sci 62:61–64
Hasan GT, Ali KJ, Ahmed MA (2011) Investigation the influence of magnetic field emitted by high voltage transmission lines on plant growth. Eur J Sci Res 56:272–278
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Teixeira da Silva JA, Fujita M (2012) Plant response and tolerance to abiotic oxidative stress: antioxidant defense is a key factor. In: Bandi V, Shanker AK, Shanker C, Mandapaka M (eds) Crop stress and its management: perspectives and strategies. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 261–315
Hirota N, Nakagawa J, Kitazawa K (1999) Effects of a magnetic field on the germination of plants. J Appl Phys 85(8):5717–5719
Huang HH, Wang SR (2007) The effects of 60 Hz magnetic fields on plant growth. Nat Sci 5(1):60–68
Iqbal M, Haq ZU, Jamil Y, Ahmad MR (2012) Effect of presowing magnetic treatment on properties of pea. Int Agrophys 26:25–31
Jajte JM (2000) Programmed cell death as a biological function of electromagnetic fields at a frequency of (50/60 Hz). Med Pr 51:383–389
Kato R (1988) Effects of a magnetic field on the growth of primary roots of Zea mays. Plant Cell Physiol 29:1215–1219
Kavi PS (1983) The effect of non-homogeneous gradient magnetic field susceptibility values in situ ragi seed material. Mysore J Agric Sci 17:121–123
Kordas L (2002) The effect of magnetic field on growth, development and the yield of spring wheat. Pol J Environ Stud 11(5):527–530
Krawiec M, Komarzynski K, Palonka S, Kaplan M, Baryla P, Kiczorowski P (2013) Does the magnetic field improve the quality of radish seeds? Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus 12(6):93–102
Krystofova O, Sochor J, Zitka O, Babula P, Kudrie V, Adam V, Kizek R (2013) Effect of magnetic nanoparticles on tobacco BY-2 cell suspension culture. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(1):47–71
Lednev VV (1991) Possible mechanism for the influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems. Bioelectromagnetics 12:71–75
Li J, Chang PR, Huang J, Wang Y, Yuan H, Ren H (2013) Physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles towards watermelon. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 13(8):5561–5567
Maffei ME (2014) Magnetic field effects on plant growth, development and evolution. Front Plant Sci 5:445
Mahmood M, Bee OB, Mohamed MTM, Subramaniam S (2013) Effects of electromagnetic field on the nitrogen, protein and chlorophyll content and peroxidase enzyme activity in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) leaves. Emir J Food Agric 25(6):471–482
Manzano AI, Larkin OJ, Dijkstra CE, Anthony P, Davey MR, Eaves L, Hill RJA, Medina FJ (2013) Meristematic cell proliferation and ribosome biogenesis are decoupled in diamagnetically levitated Arabidopsis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol 13:124
Martínez E, Carbonell MV, Flórez M (2002) Magnetic biostimulation of initial growth stages of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Electromagn Biol Med 21(1):43–53
Martínez E, Carbonell MV, Flórez M, Amaya JM (2008) Effect of static magnetic field exposure of salvia seeds on germination characteristics (Salvia officinalis L.). In: Technical and Technological Progress in Agriculture, 13th International Conference, Institute of Agricultural Engineering LUA, Raudondvaris, 25–26 September 2008, pp. 226–232
Martínez E, Carbonell MV, Flórez M, Amaya JM, Maqueda R (2009) Germination of tomato seeds (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) under magnetic field. Int Agrophys 23:45–49
Maus S, Macmillan S, McLean S, Hamilton B, Thomson A, Nair M, Rollins C (2010) The US/UK world magnetic model for 2010–2015. http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/WMM/data/WMM2010/WMM2010_Report.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2015
McClean RG, Schofield MA, Kean WF, Sommer CV, Robertson DP, Toth D, Gajdardziska-Josifovska M (2001) Botanical iron minerals: correlation between nanocrystal structure and modes of biological self-assembly. Eur J Mineral 13:1235–1242
Monselise EB-I, Parola AH, Kost D (2003) Low-frequency electromagnetic fields induce a stress effect upon higher plants, as evident by the universal stress signal, alanine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:427–434
Moon JD, Chung HS (2000) Acceleration of germination of tomato seed by applying AC electric and magnetic fields. J Electrost 48:103–114
Morar R, Munteanu R, Simion E, Muteanu I, Dascalescu L (1999) Electrostatic treatment of bean seeds. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35(1):208–212
Murray LE (1965) Plant growth response in electrostatic field. Nature 207:1177–1178
Naidu MS, Kamaraju V (2007) High voltage engineering, 3rd edn. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., New Delhi, pp 1–366
Namba K, Sasao A, Hibusawa S (1995) Effect of magnetic field on germination and plant growth. Acta Horticult 399:143–148
Neamţu S, Morariu VV (2005) Plant growth in experimental space flight magnetic field conditions. Rom J Biophys 1:41–46
NGDC (National Geophysical Data Center, USA) (2015) http://sec.noaa.gov/Data/index.html#indices. Accessed 5 May 2015
Novitskii YI, Novitskaya GV, Serdyukov YA (2014) Lipid utilization in radish seedlings as affected by weak horizontal extremely low frequency magnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 35(2):91–99
Pang XF, Deng B (2008) Investigation of changes in properties of water under the action of a magnetic field. Sci China Ser G Phys Mech Astro 51:1621–1632
Paul AL, Ferl RJ, Meisel MW (2006) High magnetic field induced changes of gene expression in Arabidopsis. Biomagn Res Technol 4:1–10
Payez A, Ghanati F, Behmanesh M, Abdolmaleki P, Hajnorouzi A, Rajabbeigi E (2013) Increase of seed germination, growth and membrane integrity of wheat seedlings by exposure to static and a 10-KHz electromagnetic field. Electromagn Biol Med 32(4):417–429
Peñuelas J, Llusia J, Martínez B, Fontcuberta J (2004) Diamagnetic susceptibility and root growth response to magnetic fields in Lens culinaris, Glycine soja, and Triticum aestivum. Electromagn Biol Med 23:97–112
Phirke PS, Patil MN, Umbarkar SP, Dudhe YH (1996) The application of magnetic treatment to seeds: methods and responses. Seed Sci Technol 24:365–373
Piacentini MP, Fraternale D, Piatti E (2001) Senescence delay and change of antioxidant enzyme levels in Cucumis sativus L. etiolated seedlings by ELF magnetic fields. Plant Sci 161:45–53
Pietruszewski S (1993) Effects of magnetic seed treatment on yields of wheat. Seed Sci Technol 21:621–626
Piruzyan LA, Kuznetsov AA, Chikov VM (1980) About the magnetic heterogeneity of biological systems. Izv Acad Sci USSR Ser Biol 5:645–653
Pittman UJ (1977) Effects of magnetic seed treatment on yields of barley, wheat and oats on Southern Alberta. Can J Plant Sci 57:37–45
Podleśny J, Pietruszewski S, Podleśna A (2004) Efficiency of the magnetic treatment of broad bean seeds cultivated under experimental plot conditions. Int Agrophys 18:65–71
Poinapen D, Beeharry GK, Bahorun T, Bunwaree M, Préfumo S (2005) Effect of static magnetic fields on the growth and yield of butterhead lettuce seeds (Lactuca sativa var. Salina). MAS 2005 Food and Agricultural Research Council, Proceedings 7th Meeting of Agricultural Scientists. Réduit, Mauritius. Lalouette, JA, Bheenick, K J, Nundalallee, C (Eds), p. 207–216. http://www.gov.mu/portal/sites/ncb/moa/farc/amas2005/pdf/MAS20051stDraft.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2015
Poinapen D, Brown DCW, Beeharry GK (2013) Seed orientation and magnetic field strength have more influence on tomato seed performance than relative humidity and duration of exposure to non-uniform static magnetic fields. J Plant Physiol 170:1251–1258
Qian AR, Yin DC, Yang PF, Lv Y, Tian ZC, Shang P (2013) Application of diamagnetic levitation technology in biological sciences research. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 23(1):3600305
Rãcuciu M, Creangǎ D, Horga I (2008) Plant growth under static magnetic field influence. Rom J Phys 53:353–359
Radhakrishnan R, Kumari BDR (2012) Pulsed magnetic field: a contemporary approach offers to enhance plant growth and yield of soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem 51:139–144
Radhakrishnan R, Kumari BDR (2013a) Influence of pulsed magnetic field on soybean (Glycine max L.) seed germination, seedling growth and soil microbial population. Indian J Biochem Biophys 50:312–317
Radhakrishnan R, Kumari BDR (2013b) Protective role of pulsed magnetic field against salt stress effects in soybean organ culture. Plant Biosyst 147(1):135–140
Rajabbeigi E, Ghanati F, Abdolmaleki P, Payez A (2013) Antioxidant capacity of parsley cells (Petroselium crispum L.) in relation to iron-induced ferritin levels and static magnetic field. Electromagn Biol Med 32(4):430–441
Ramo S, Whinery JR, Van Duzer T (2004) Fields and waves in communication electronics, 3rd edn. Wiley, Kundli, pp 114–299
Rapley BI, Rowland RE, Page WH, Podd JV (1998) Influence of extremely low frequency magnetic fields on chromosomes and mitotic cycle in the broad bean (Vicia faba L.). Bioelectromagnetics 19:152–161
Reina FG, Pascual LA (2001) Influence of a stationary magnetic field on water relations in lettuce seeds. Part 1: theoretical considerations. Bioelectromagnetics 22:589–595
Reina FG, Pascual LA, Fundora IA (2001) Influence of a stationary magnetic field on water relations in lettuce seeds. Part 2: experimental results. Bioelectromagnetics 22:596–602
Rezaiiasl A, Ghasemnezhad A, Shahabi S (2012) Study the response of cucumber plant to different magnetic fields. J Adv Lab Res Biol 3(1):42–46
Ružič R, Jerman I (2002) Weak magnetic field decreases heat stress in cress seedlings. Electromagn Biol Med 21:69–80
Sakhnini L (2007) Influence of Ca2+ in biological stimulating effects of AC magnetic fields on germination of bean seeds. J Magn Magn Mater 310:e1032–e1034
Savostin PW (1930) Magnetic growth relations in plants. Planta 12:327
Scaiano JC, Cozens FL, Mohtat N (1995) Development of a model and application of the radical pair mechanism to radicals in micelles. Photochem Photobiol 62:818–829
Schrödinger E (1935) Probability relations between seperated systems. Camb Phil Soc Proc 31:555–563
Selim AH, El-Nady MF (2011) Physio-anatomical responses of drought stressed tomato plants to magnetic fields. Acta Astronaut 69:387–396
Serdyukov YA, Novitskii YI (2013) Impact of weak permanent magnetic field on antioxydant enzyme activities in radish seedlings. Russ J Plant Physiol 60(1):69–76
Shabrangi A, Majd A (2009) Effect of magnetic fields on growth and antioxidant systems in agricultural plants. PIERS Proceedings, Beijing, China, March 23–27, 2009, pp. 1142–1147
Shine MB, Guruprasad KN (2012) Impact of pre-sowing magnetic field exposure of seeds to stationary magnetic field on growth, reactive oxygen species and photosynthesis of maize under field conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 34:255–265
Shine MB, Guruprasad KN, Anand A (2011) Enhancement of germination, growth, and photosynthesis in soybean by pre-treatment of seeds with magnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 32:474–484
Teixeira da Silva JA, Dobránszki J (2015) How do magnetic fields affect plants in vitro? In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. doi:10.1007/s11627-015-9675-z
Smith SD, McLeod BR, Liboff AR, Cooksey K (1987) Calcium cyclotron resonance and diatom mobility. Bioelectromagnetics 8(3):215–227
Smith SD, McLeod BR, Liboff AR (1993) Effects of CR-tuned 60 Hz magnetic fields on sprouting and early growth of Raphanus sativus. Biochem Bioenerg 32:67–76
Soja G, Kunsch B, Gerzabek M, Relchenauer T, Soja AM, Rippar G, Bolhar-Nordenkampf HR (2003) Growth and yield of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) near a high voltage transmission line. Bioelectromagnetics 24:91–102
Subber ARH, Hail RCA, Jabail WA, Hussein HF (2012) Effects of magnetic field on the growth development of Zea mays seeds. J Nat Prod Plant Resour 2(3):456–459
Tanaka M, Van PT, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ham LH (2010) Novel magnetic field system: application to micropropagation of horticultural plants. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 24(4):2160–2163
Teixeira da Silva JA, Dobránszki J (2013) How timing of sampling can affect the outcome of the quantitative assessment of plant organogenesis. Sci Hortic 159:59–66
Teixeira da Silva JA, Dobránszki J (2014) Impact of magnetic water on plant growth. Environ Exp Biol 12(4):137–142
Teixeira da Silva JA, Singh N, Tanaka M (2006) Priming biotic factors for optimal protocorm-like body and callus induction in hybrid Cymbidium (Orchidaceae), and assessment of cytogenetic stability in regenerated plantlets. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 109:368–378
Theg SM, Sayre RT (1979) Characterization of chloroplast manganese by electron magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plant Sci Lett 16:319–326
Trontelj Z, Thiel G, Jazbinsek V (2006) Magnetic measurements in plant electrophysiology. In: Volkov AG (ed) Plant electrophysiology—theory and methods. Springer, Berlin, pp 187–218
Ursache-Oprisan M, Focanici E, Creanga D, Caltun O (2011) Sunflower chlorophyll levels after magnetic nanoparticles supply. Afr J Biotechnol 10:7092–7098
Vaezzadeh M, Noruzifar E, Faezeh G, Salehkotahi M, Mehdian R (2006) Excitation of plant growth in dormant temperature by steady magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 302:105–108
Van PT, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ham LH, Tanaka M (2011a) Effects of permanent magnetic fields on the proliferation of Phalaenopsis protocorm-like bodies using liquid medium. Sci Hortic 128:479–484
Van PT, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ham LH, Tanaka M (2011b) The effects of permanent magnetic fields on Phalaenopsis plantlet development. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 86(5):473–478
Van PT, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ham LH, Tanaka M (2012) Effects of permanent magnetic fields on growth of Cymbidium and Spathiphyllum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 48(2):225–232
Vashisth A, Nagarajan S (2008) Exposure of seeds to static magnetic field enhances germination and early growth characteristics in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Bioelectromagnetics 29:571–578
Vashisth A, Nagarajan S (2010) Effect on germination and early growth characteristics in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seeds exposed to static magnetic field. J Plant Physiol 167:149–156
Vasilevski G (2003) Perspectives of the application of biophysical methods in sustainable agriculture. Bulgarian J Plant Physiol Special Issue:179–186
Volkov AG (2012) Plant Biosensor and method. Patent US 8,205,502. https://drive.google.com/viewerng/viewer?url=patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/pdfs/US8205502.pdf. Accessed 5 May 2015
Wang BC, Zhou J, Wang YC, Zhu LC, Teixeira da Silva JA (2006) Physical stress and plant growth. In: Teixeira da Silva JA (ed) Floriculture, ornamental and plant biotechnology: advances and topical issues, vol 3, 1st edn. Global Science Books Ltd, Isleworth, pp 68–85
Xi G, Fu ZD, Ling J (1994) Change of peroxidase activity in wheat seedlings induced by magnetic field and its response under dehydration condition. Acta Bot Sin 36:113–118
Xu CX, Yin X, Lv Y, Wu CZ, Zhang YX, Song T (2012) A near-null magnetic field affects cryptochrome-related hypocotyl growth and flowering in Arabidopsis. Adv Space Res 49:834–840
Xu C, Wei S, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Chen C, Song T (2013) Removal of the local geomagnetic field affects reproductive growth in Arabidopsis. Bioelectromagnetics 34(6):437–442
Xu C, Lv Y, Chen C, Zhang Y, Wei S (2014) Blue light-dependent phosphorylations of cryptochromes are affected by magnetic fields in Arabidopsis. Adv Space Res 53:1118–1124
Yamauchi N, Funamoto Y, Shigyo M (2004) Peroxidase-mediated chlorophyll degradation in horticultural crops. Phytochem Rev 3:221–228
Yan D, Guo Y, Zai X, Qin P (2009) Effects of electromagnetic fields exposure on rapid micropropagation of beach plum (Prunus martima). Ecol Eng 35:597–601
Yaycılı O, Alikamanoğlu S (2005) The effect of magnetic field on Paulownia tissue cultures. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 83:109–114
Zaidi S, Khatoon S, Imran M, Zohair S (2013) Effects of electromagnetic fields (created by high tension lines) on some species of family Mimosaceae, Molluginaceae, Nyctaginaceae and Papilionaceae from Pakistan – V. Pak J Bot 45(6):1857–1864
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Pham Thanh Van (Vietnam Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Institute of Agricultural Genetics, Hanoi, Vietnam) for initial feedback on the first version of the draft. The authors also thank Prof. Alexander G. Volkov (Department of Chemistry, Oakwood University, AL, USA), Dr. Marcela Krawiec (Department of Seed Production and Nurseries, University of Life Sciences, Lublin, Poland), and Prof. Elvira Martínez Ramírez (Dpto. Ingeniería Agroforestal, E.T.S.I. Agrónomos (UPM), Madrid, Spain) for constructive comments on the final version of the manuscript in a pre-publication peer review.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Suppl. Fig. 1
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira da Silva, J.A., Dobránszki, J. Magnetic fields: how is plant growth and development impacted?. Protoplasma 253, 231–248 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0820-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0820-7