Abstract
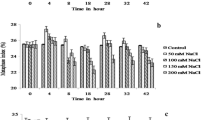
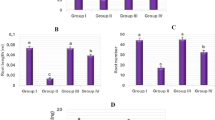
Salt-induced growth reduction of plants is a well-known phenomenon which poses major problem in crop productivity in places where vast majority of land plants are affected by salt. In this report, studies were carried out to reveal the effect of salt injury on the cell division pattern in roots and the role of myo-inositol in preventing the salt-induced ion disequilibrium on the chromosome and DNA degradation in roots. Present study revealed induction of various chromosomal abnormalities on the root tip mitotic cells of Allium cepa by treatment with different concentrations of NaCl (0–500 mM) for 24 h as also the amelioration of such effect by prior treatment of the roots with different concentration of myo-inositol (0–300 mM). Results showed that a narrow albeit definite range of extracellular myo-inositol (100–150 mM) is effective in preventing internucleosomal fragmentation which is the early response in roots under salt stress. Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing Oryza (OsINO1) as well as Porteresia (PcINO1) cytosolic l-myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase coding genes can withstand and retain their chromosomal and DNA integrity in 100 mM NaCl solution and can subsequently prevent DNA fragmentation, caused by intracellular endonuclease activity at this salt concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams P, Thomas JC, Vernon DM, Bohnert HJ, Jensen RG (1992) Distinct cellular and organismic responses to salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 33:1215–1223
Affenzeller MJ, Darehshouri A, Andosch A, Lütz C, Lütz-Meindl U (2009) Salt stress-induced cell death in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias denticulate. J Exp Bot 60:939–954
Biffen M, Hanke DE (1990) Reduction in the level of intracellular myo-inositol in cultured soybean (Glycine max) cells inhibits cell division. Biochem J 265:809–814
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptations to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7:1099–1111
Das-Chatterjee A, Goswami L, Maitra S, Ghosh Dastidar K, Ray S, Majumder AL (2006) Introgression of a novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol l-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka (PcINOl) confers salt tolerance to evolutionary diverse organisms. FEBS Letts 580:3980–3988
DeWald DB, Torabinejad J, Jones CA, Shope J, Cangelosi AR, Thompson JE, Prestwich GD, Hama H (2001) Rapid accumulation of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate and inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate correlates with calcium mobilization in salt stressed Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:759–769
Hanke DE, Biffen M, Davies H (1990) Phosphoinositides and plant growth substance action. Symp Soc Exp Biol 44:193–205
Huh GH, Damaz B, Matsumoto TK, Reddy MP, Rus AM, Ibeas JI (2002) Salt causes ion disequilibrium-induced programmed cell death in yeast and plants. Plant J 29:649–659
Katsuhara M (1997) Apoptosis-like cell death in barley roots under salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 38:1091–1093
Katsuhara M, Kawasaki T (1996) Salt stress induced nuclear and DNA degradation in meristematic cells of barley root. Plant Cell Physiol 37:169–173
Li JY, Jiang AL, Zhang W (2007) Salt stress induced programmed cell death in rice root tip cells. J Integr Plant Biol 49:481–486
Liljeroth E, Bryngelsson T (2001) DNA fragmentation in cereal roots indicative of programmed root cortical cell death. Physiol Plant 111:363–372
Lin J, Wang Y, Wang G (2006) Salt stress-induced programmed cell death in tobacco protoplasts is mediated by reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial permeability transition pore status. J Plant Physiol 163:731–739
Lodhi MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grape-vine cultivars, Vitis sp. and ampelopsis. Plant Mol Biol Report 12:6–13
Loewus FA, Dickinson DB (1982) Cyclitols. In: Loewus FA, Tanner W (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology, new series, vol. 13A, plant carbohydrates. Springer, Berlin, pp 94–216
Maehara Y, Anai H, Kusumoto T, Sakaguchi Y, Sugimachi K (1989) Nick translation detection in situ of cellular DNA strand break induced by radiation. Am J Pathol 134:7–10
Majee M, Maitra S, Dastidar KG, Pattnaik S, Chatterjee A, Hait NC, Das KP, Majumder AL (2004) A novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka, a halophytic wild rice, molecular cloning, bacterial overexpression, characterization, and functional introgression into tobacco conferring salt tolerance phenotype. J Biol Chem 279:28539–28552
Nelson DE, Rammesmayer G, Bohnert HJ (1998) Regulation of cell-specific inositol metabolism and transport in plant salinity tolerance. Plant Cell 10:753–764
Ning SB, Wang L, Song YC (2002) Identification of programmed cell death in situ in individual plant cells in vivo using a chromosome preparation technique. J Exp Bot 53:651–658
Ryerson DE, Heath MC (1996) Cleavage of nuclear DNA into oligonucleosomal fragments during cell death induced by fungal infection or by abiotic treatments. Plant Cell 8:393–402
Serano R, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2001) Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants. Cur Opin Cell Biol 13:399–404
Shabala S (2009) Salinity and programmed cell death: unraveling mechanisms for ion specific signaling. J Exp Bot 60:709–712
Stein JC, Hansen G (1999) Mannose induces an endonuclease responsible in plant cells. Plant Physiol 121:71–79
Wertz IE, Hanley MR (1996) Diverse molecular provocation of programmed cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 21:359–364
Acknowledgments
The work has been supported by research grants (to ALM) from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bhumi Nath Tripathi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, J., Majumder, A.L. Salt-induced abnormalities on root tip mitotic cells of Allium cepa: prevention by inositol pretreatment. Protoplasma 245, 165–172 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0170-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0170-4