Abstract
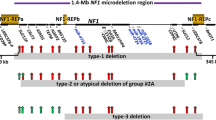
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is a rare, clinically heterogeneous disorder characterized by cognitive impairment and several multiple congenital anomalies. The syndrome is caused by almost private point mutations in the CREBBP (~55 % of cases) and EP300 (~8 %) genes. The CREBBP mutational spectrum is variegated and characterized by point mutations (30–50 %) and deletions (~10 %). The latter are diverse in size and genomic position and remove either the whole CREBBP gene and its flanking regions or only an intragenic portion. Here, we report 14 novel CREBBP deletions ranging from single exons to the whole gene and flanking regions which were identified by applying complementary cytomolecular techniques: fluorescence in situ hybridization, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and array comparative genome hybridization, to a large cohort of RSTS patients. Deletions involving CREBBP account for 23 % of our detected CREBBP mutations, making an important contribution to the mutational spectrum. Genotype–phenotype correlations revealed that patients with CREBBP deletions extending beyond this gene did not always have a more severe phenotype than patients harboring CREBBP point mutations, suggesting that neighboring genes play only a limited role in the etiopathogenesis of CREBBP-centerd contiguous gene syndrome. Accordingly, the extent of the deletion is not predictive of the severity of the clinical phenotype.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho S, Rothenberger K, Tan EM, Ryoo YW, Cho BH, McLean WH, Uitto J (1999) Human periplakin: genomic organization in a clonally unstable region of chromosome 16p with an abundance of repetitive sequence elements. Genomics 56:160–168. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5704
Bartholdi D, Roelfsema JH, Papadia F, Breuning MH, Niedrist D, Hennekam RC, Schinzel A, Peters DJ (2007) Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300. J Med Genet 44:327–333. doi:10.1136/jmg.2006.046698
Bartsch O, Wagner A, Hinkel GK, Krebs P, Stumm M, Schmalenberger B, Böhm S, Balci S, Majewski F (1999) FISH studies in 45 patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: deletions associated with polysplenia, hypoplastic left heart and death in infancy. Eur J Hum Genet 7:748–756
Bartsch O, Locher K, Meinecke P, Kress W, Seemanová E, Wagner A, Ostermann K, Rödel G (2002) Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP. J Med Genet 39:496–501. doi:10.1136/jmg.39.7.496
Bartsch O, Schmidt S, Richter M, Morlot S, Seemanová E, Wiebe G, Rasi S (2005) DNA sequencing of CREBBP demonstrates mutations in 56 % of patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RSTS) and in another patient with incomplete RSTS. Hum Genet 117:485–493. doi:10.1007/s00439-005-1331-y
Bartsch O, Rasi S, Delicado A, Dyack S, Neumann LM, Seemanová E, Volleth M, Haaf T, Kalscheuer VM (2006) Evidence for a new contiguous gene syndrome, the chromosome 16p13.3 deletion syndrome alias severe Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Hum Genet 120:179–186. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0215-0
Beets L, Rodrìguez-Fonseca C, Hennekam R (2014) Growth charts for individuals with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 164:2300–2309. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.36654
Belzen MV, Bartsch O, Lacombe D, Peters DJ, Hennekam RC (2011) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (CREBBP, EP300). Eur J Hum Genet 19:118–120. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.124
Bentivegna A, Milani D, Gervasini C, Castronovo P, Mottadelli F, Manzini S, Colapietro P, Giordano L, Atzeri F, Divizia MT, Uzielli ML, Neri G, Bedeschi MF, Faravelli F, Selicorni A, Larizza L (2006) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Italian patients. BMC Med Genet 7:77. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-7-77
Blough RI, Petrij F, Dauwerse JG, Milatovich-Cherry A, Weiss L, Saal HM, Rubinstein JH (2000) Variation in microdeletions of the cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein gene at chromosome band 16p13.3 in the Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 90:29–34. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000103)90:1
Calì F, Failla P, Chiavetta V, Ragalmuto A, Ruggeri G, Schinocca P, Schepis C, Romano V, Romano C (2013) Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification detection of an unknown large deletion of the CREB-binding protein gene in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Genet Mol Res 12:2809–2815. doi:10.4238/2013
Chan HM, La Thangue NB (2001) p300/CBP proteins: HATs for transcriptional bridges and scaffolds. J Cell Sci 114:2363–2373
Coupry I, Roudaut C, Stef M, Delrue MA, Marche M, Burgelin I, Taine L, Cruaud C, Lacombe D, Arveiler B (2002) Molecular analysis of the CBP gene in 60 patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. J Med Genet 39:415–421. doi:10.1136/jmg.39.6.415
Coupry I, Monnet L, Attia AA, Taine L, Lacombe D, Arveiler B (2004) Analysis of CBP (CREBBP) gene deletions in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome patients using real time quantitative PCR. Hum Mutat 23:278–284. doi:10.1002/humu.20001
Fadly MdA, Ismail A, Keong TM, Yusoff NM, Zakaria Z (2012) Chromosomal 16p microdeletion in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome detected by oligonucleotide-based array comparative genomic hybridization: a case report. J Med Case Rep 6:30. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-6-30
Foley P, Bunyan D, Stratton J, Dillon M, Lynch SA (2009) Further case of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome due to a deletion in EP300. Am J Med Genet 149:997–1000. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32771
Gervasini C, Castronovo P, Bentivegna A, Mottadelli F, Faravelli F, Uzielli GML, Pessagno A, Lucci-Cordisco E, Pinto AM, Salviati L, Selicorni A, Tenconi R, Neri G, Larizza L (2007) High frequency of mosaic CREBBP deletions in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome patients and mapping of somatic and germ-line breakpoints. Genomics 90:567–573. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.07.012
Giles CL, Sun R, Zurada JM (1998) Neural networks and hybrid intelligent models: foundations, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 9:721–723. doi:10.1109/TNN.1998.712147
Giordano A, Avantaggiati ML (1999) p300 and CBP: partners for life and death. J Cell Physiol 181:218–230. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199911)181:2<218
Hennekam RC (2006) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 14:981–985. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201594
Isidor B, Podevin G, Camby C, Mosnier JF, Chauty A, Lyet JM, Fergelot P, Lacombe D, Arveiler B, Pelet A, Amiel J, David A (2010) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome and Hirschsprung disease in a patient harboring an intragenic deletion of the CREBBP gene. Am J Med Genet 152:1847–1848. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33480
Kalkhoven E (2004) CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1145–1155. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2004.03.045
Kim SR, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Kwon JY, Kim JW, Kim SH (2013) Cryptic microdeletion of the CREBBP gene from t(1;16) (p36.2;p13.3) as a novel genetic defect causing Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Ann Clin Lab Sci 43:450–456
Lai AH, Brett MS, Chin WH, Lim EC, Ng JS, Tan EC (2012) A submicroscopic deletion involving part of the CREBBP gene detected by array-CGH in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Gene. 499:182–185. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2012.02.043
Lee JS, Byun CK, Kim H, Lim BC, Hwang H, Choi JE, Hwang YS, Seong M-W, Park SS, Kim KJ, Chae J-H (2015) Clinical and mutational spectrum in Korean patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: the spectrum of brain MRI abnormalities. Brain Dev 37(4):402–408. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2014.07.007
Lichter P, Cremer T (1992) Chromosome analysis by non-isotopic in situ hybridization. In: Rooney DE, Czepulkowski BH (eds) Human cytogenetics. A practical approach. IRL Press at Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 157–192
Lopez-Atalaya JP, Gervasini C, Mottadelli F, Spena S, Piccione M, Scarano G, Selicorni A, Barco A, Larizza L (2012) Histone acetylation deficits in lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. J Med Genet 49:66–74. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100354
Masuno M, Imaizumi K, Ishii T, Kuroki Y, Baba N, Tanaka Y (1998) Pilomatrixomas in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 28:81–82. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980428)77:1<81
Miller RW, Rubinstein JH (1995) Tumors in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 56:112–115
Murata T, Kurokawa R, Krones A, Tatsumi K, Ishii M, Taki T, Masuno M, Ohashi H, Yanagisawa M, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK, Hayashi Y (2001) Defect of histone acetyltransferase activity of the nuclear transcriptional coactivator CBP in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 10:1071–1076. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.10.1071
Negri G, Milani D, Colapietro P, Forzano F, Della Monica M, Rusconi D, Consonni L, Caffi LG, Finelli P, Scarano G, Magnani C, Selicorni A, Spena S, Larizza L, Gervasini C (2014) Clinical and molecular characterization of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome patients carrying distinct novel mutations of the EP300 gene. Clin Genet. doi:10.1111/cge.12348 (Epub ahead of print)
Park E, Kim Y, Ryu H, Kowall NW, Lee J, Ryu H (2014) Epigenetic mechanisms of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Neuromol Med 16:16–24. doi:10.1007/s12017-013-8285-3
Petrij F, Giles RH, Dauwerse HG, Saris JJ, Hennekam RC, Masuno M, Tommerup N, van Ommen GJ, Goodman RH, Peters DJ, Breuning MH (1995) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome caused by mutations in the transcriptional co-activator CBP. Nature 376:348–351. doi:10.1038/376348a0
Petrij F, Dauwerse HG, Blough RI, Giles RH, van der Smagt JJ, Wallerstein R, Maaswinkel-Mooy PD, van Karnebeek CD, van Ommen GJ, van Haeringen A, Rubinstein JH, Saal HM, Hennekam RC, Peters DJ, Breuning MH (2000) Diagnostic analysis of the Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: five cosmids should be used for microdeletion detection and low number of protein truncating mutations. J Med Genet 37:168–176. doi:10.1136/jmg.37.3.168
Roelfsema JH, Peters DJ (2007) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview. Expert Rev Mol Med 9:1–16. doi:10.1017/S1462399407000415
Roelfsema JH, White SJ, Ariyürek Y, Bartholdi D, Niedrist D, Papadia F, Bacino CA, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ, Breuning MH, Hennekam RC, Peters DJ (2005) Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: mutations in both the CBP and EP300 genes cause disease. Am J Hum Genet 76:572–580. doi:10.1086/429130
Rubinstein JH, Taybi H (1963) Broad thumbs and toes and facial abnormalities. A possibile mental retardation syndrome. Am J Dis Child 105:588–608
Schepis C, Greco D, Siragusa M, Batolo D, Romano C (2001) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome with epidermal nevus: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol 18:34–37. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1470.2001.018001034.x
Schorry EK, Keddache M, Lanphear N, Rubinstein JH, Srodulski S, Fletcher D, Blough-Pfau RI, Grabowski GA (2008) Genotype-phenotype correlations in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 146:2512–2519. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32424
Sharma N, Mali AM, Bapat SA (2010) Spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Indian patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. J Biosci 35:187–202. doi:10.1007/s12038-010-0023-5
Spena S, Milani D, Rusconi D, Negri G, Colapietro P, Elcioglu N, Bedeschi F, Pilotta A, Spaccini L, Ficcadenti A, Magnani C, Scarano G, Selicorni A, Larizza L, Gervasini C (2014) Insights into genotype–phenotype correlations from CREBBP point mutation screening in a cohort of 46 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome patients. Clin Genet. doi:10.1111/cge.12537
Stef M, Simon D, Mardirossian B, Delrue MA, Burgelin I, Hubert C, Marche M, Bonnet F, Gorry P, Longy M, Lacombe D, Coupry I, Arveiler B (2007) Spectrum of CREBBP gene dosage anomalies in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome patients. Eur J Hum Genet 15:843–847. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201847
Stevens CA, Hennekam RC, Blackburn BL (1990) Growth in the Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet Suppl 6:51–55
Tsai AC, Dossett CJ, Walton CS, Cramer AE, Eng PA, Nowakowska BA, Pursley AN, Stankiewicz P, Wiszniewska J, Cheung SW (2011) Exon deletions of the EP300 and CREBBP genes in two children with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome detected by aCGH. Eur J Hum Genet 19:43–49. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.121
Udaka T, Samejima H, Kosaki R, Kurosawa K, Okamoto N, Mizuno S, Makita Y, Numabe H, Toral JF, Takahashi T, Kosaki K (2005) Comprehensive screening of CREB-binding protein gene mutations among patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 45:125–131. doi:10.1111/j.1741-4520.2005.00081.x
Wójcik C, Volz K, Ranola M, Kitch K, Karim T, O’Neil J, Smith J, Torres-Martinez W (2010) Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome associated with Chiari type I malformation caused by a large 16p13.3 microdeletion: a contiguous gene syndrome? Am J Med Genet 152:479–483. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33303
Zimmermann N, Acosta AM, Kohlhase J, Bartsch O (2007) Confirmation of EP300 gene mutations as a rare cause of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 15:837–842. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201791
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the patients’ families for participating in this study and to the Italian RSTS Association “Una Vita Speciale” and Associazione Studio Malformazioni (ASM onlus) for supporting this study. We thank Dr. Franca Rossella for her technical support. We thank the Galliera Genetic Bank for establishing lymphoblastoid cell lines through the Italian Telethon project GTF4003. This research was approved by the Ethical Clinical Research Committee of the clinical centers involved in patient recruitment and clinical evaluation. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients’ parents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2015_1542_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Molecular flowchart applied to our RSTS cohort. Molecular flowchart applied to our cohort by combining different techniques. The number of patients tested and identified carriers of CREBB deletions/point mutations or EP300 mutations are provided. (TIFF 1141 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rusconi, D., Negri, G., Colapietro, P. et al. Characterization of 14 novel deletions underlying Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: an update of the CREBBP deletion repertoire. Hum Genet 134, 613–626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1542-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1542-9