Abstract
Objectives
Polymorphism of the gene for matrix GLA protein (MGP), a calcification inhibitor, is associated with nephrolithiasis. However, experimental investigations of MGP role in stone pathogenesis are limited. We determined the effect of renal epithelial exposure to oxalate (Ox), calcium oxalate (CaOx) monohydrate (COM) or hydroxyapatite (HA) crystal on the expression of MGP.
Methods
MDCK cells in culture were exposed to 0.3, 0.5 or 1 mM Ox and 33, 66 or 133–150 μg/cm2 of COM/HA for 3–72 h. MGP expression and production were determined by Western blotting and densitometric analysis. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was performed to determine MGP release into the medium. Hyperoxaluria was induced in male Sprague–Dawley rats by feeding hydroxyl-l-proline. Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect renal MGP expression.
Results
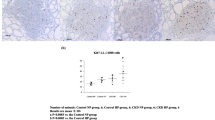
Exposure to Ox and crystals led to time- and concentration-dependent increase in expression of MGP in MDCK cells. Cellular response was quicker to crystal exposure than to the Ox, expression being significantly higher after 3-h exposure to COM or HA crystals and more than 6 h of exposure to Ox. MGP expression was increased in kidneys of hyperoxaluric rats particularly in renal peritubular vessels.
Conclusion
We demonstrate increased expression of MGP in renal tubular epithelial cells exposed to Ox or CaOx crystals as well as the HA crystals. The most significant finding of this study is the increased staining seen in renal peritubular vessels of the hyperoxaluric rats, indicating involvement of renal endothelial cells in the synthesis of MGP.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coe FL, Keck J, Norton ER (1977) The natural history of calcium urolithiasis. JAMA 238:1519–1523
Khan SR, Kok DJ (2004) Modulators of urinary stone formation. Front Biosci 9:1450–1482
Ryall RL (2008) The future of stone research: rummagings in the attic, Randall’s plaque, nanobacteria, and lessons from phylogeny. Urol Res 36:77–97
Schurgers LJ, Cranenburg EC, Vermeer C (2008) Matrix Gla-protein: the calcification inhibitor in need of vitamin K. Thromb Haemost 100:593–603
Price PA, Urist MR, Otawara Y (1983) Matrix Gla protein, a new gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein which is associated with the organic matrix of bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 117:765–771
Fraser J, Price P (1988) Lung, heart, and kidney express high levels of mRNA for the vitamin K-dependent matrix Gla protein. Implications for the possible functions of matrix Gla protein and for the tissue distribution of the gamma-carboxylase. J Biol Chem 263:11033–11036
Herrmann SM, Whatling C, Brand E et al (2000) Polymorphisms of the human matrix gla protein (MGP) gene, vascular calcification, and myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2386–2393
Gao B, Yasui T, Itoh Y, Tozawa K, Hayashi Y, Kohri K (2007) A polymorphism of matrix Gla protein gene is associated with kidney stones. J Urol 177:2361–2365
Yasui T, Fujita K, Sasaki S et al (1999) Expression of bone matrix proteins in urolithiasis model rats. Urol Res 27:255–261
Gao B, Yasui T, Lu X et al (2010) Matrix Gla protein expression in NRK-52E cells exposed to oxalate and calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals. Urol Int 85:237–241
Khan SR, Glenton PA, Byer KJ (2006) Modeling of hyperoxaluric calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis: experimental induction of hyperoxaluria by hydroxy-l-proline. Kidney Int 70:914–923
Murshed M, McKee MD (2010) Molecular determinants of extracellular matrix mineralization in bone and blood vessels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:359–365
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD et al (1997) Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature 386:78–81
Meier M, Weng LP, Alexandrakis E, Ruschoff J, Goeckenjan G (2001) Tracheobronchial stenosis in Keutel syndrome. The European respiratory journal: official journal of the European society for clinical respiratory physiology 17:566–569
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee M et al (1997) Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature 386:78–81
Murshed M, Schinke T, McKee M, Karsenty G (2004) Extracellular matrix mineralization is regulated locally; different roles of two gla-containing proteins. J Cell Biol 165:625–630
Farzaneh-Far A, Davies JD, Braam LA et al (2001) A polymorphism of the human matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein promoter alters binding of an activating protein-1 complex and is associated with altered transcription and serum levels. J Biol Chem 276:32466–32473
Lu X, Gao B, Liu Z et al (2012) A polymorphism of matrix Gla protein gene is associated with kidney stone in the Chinese Han population. Gene 511:127–130
Cancela ML, Hu B, Price PA (1997) Effect of cell density and growth factors on matrix GLA protein expression by normal rat kidney cells. J Cell Physiol 171:125–134
Wang L, Raikwar N, Deng L et al (2000) Altered gene expression in kidneys of mice with 2,8-dihydroxyadenine nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 58:528–536
Khan SR (2010) Nephrocalcinosis in animal models with and without stones. Urol Res 38:429–438
Khan SR, Glenton PA (2010) Experimental induction of calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis in mice. J Urol 184:1189–1196
Evan A, Lingeman J, Coe FL, Worcester E (2006) Randall’s plaque: pathogenesis and role in calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 69:1313–1318
Khan SR, Rodriguez DE, Gower LB, Monga M (2012) Association of Randall plaque with collagen fibers and membrane vesicles. J Urol 187:1094–1100
Khan SR, Finlayson B, Hackett R (1984) Renal papillary changes in patient with calcium oxalate lithiasis. Urology 23:194–199
Roy ME, Nishimoto SK (2002) Matrix Gla protein binding to hydroxyapatite is dependent on the ionic environment: calcium enhances binding affinity but phosphate and magnesium decrease affinity. Bone 31:296–302
Lian JB, Prien EL Jr, Glimcher MJ, Gallop PM (1977) The presence of protein-bound gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in calcium-containing renal calculi. J Clin Invest 59:1151–1157
Joshi S, Saylor BT, Wang W, Peck AB, Khan SR (2012) Apocynin-treatment reverses hyperoxaluria induced changes in NADPH oxidase system expression in rat kidneys: a transcriptional study. PLoS ONE 7:e47738
Spronk HM, Soute BA, Schurgers LJ et al (2001) Matrix Gla protein accumulates at the border of regions of calcification and normal tissue in the media of the arterial vessel wall. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:485–490
Fraser JD, Price PA (1988) Lung, heart, and kidney express high levels of mRNA for the vitamin K-dependent matrix Gla protein. Implications for the possible functions of matrix Gla protein and for the tissue distribution of the gamma-carboxylase. J Biol Chem 263:11033–11036
Cola C, Almeida M, Li D, Romeo F, Mehta JL (2004) Regulatory role of endothelium in the expression of genes affecting arterial calcification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:424–427
Price PA, Thomas GR, Pardini AW, Figueira WF, Caputo JM, Williamson MK (2002) Discovery of a high molecular weight complex of calcium, phosphate, fetuin, and matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein in the serum of etidronate-treated rats. J Biol Chem 277:3926–3934
Proudfoot D, Shanahan CM (2006) Molecular mechanisms mediating vascular calcification: role of matrix Gla protein. Nephrology (Carlton) 11:455–461
Randall A (1937) The origin and growth of renal calculi. Ann Surg 105:1009–1027
Stoller ML, Meng MV, Abrahams HM, Kane JP (2004) The primary stone event: a new hypothesis involving a vascular etiology. J Urol 171:1920–1924
O’Connor PM, Cowley AW Jr (2010) Modulation of pressure-natriuresis by renal medullary reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. Curr Hypertens Rep 12:86–92
Sarica K, Aydin H, Yencilek F, Telci D, Yilmaz B (2012) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells accelerate oxalate-induced apoptosis of human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells in co-culture system which is prevented by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate. Urol Res 40:461–466
Rule AD, Roger VL, Melton LJ 3rd et al (2010) Kidney stones associate with increased risk for myocardial infarction. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1641–1644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Wang, W. & Khan, S.R. Calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis and expression of matrix GLA protein in the kidneys. World J Urol 32, 123–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1050-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1050-2