Abstract.
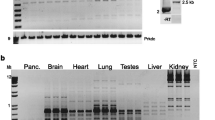
Polycystin-L is a member of the expanding family of polycystins. Mutations in polycystin-1 or -2 cause human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). The mouse ortholog of PKDL, Pkdl, is deleted in a mouse line with renal and retinal defects. We recently have shown that polycystin-L has calcium channel properties. In the current study, we determined the exon/intron organization of the PKDL gene and its alternative splicing. We show that PKDL has 16 exons. All splice acceptor/donor sites for these exons conform to the GT-AG rule. The positions of introns and the sizes of exons in the PKDL gene are very similar to those of PKD2, except for the last two 3′ end exons. RT-PCR demonstrates the existence of at least three polycystin-L splice variants: PKDL(Δ5), PKDL(Δ456), and PKDL(Δ15) that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. In addition, we have localized polymorphic marker D10S603 to intron 4 and exon 5 of PKDL. Elucidation of the gene structure, exact location, and alternative splicing patterns of PKDL will facilitate its evaluation as a candidate gene in cystic or other genetic disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 July 1999 / Accepted: 16 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Chen, M., Basora, N. et al. The human polycystic kidney disease 2-like (PKDL) gene: exon/intron structure and evidence for a novel splicing mechanism. Incorporating Mouse Genome 11, 46–50 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003350010009
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003350010009