Abstract
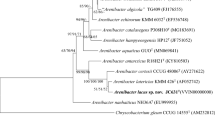
A Gram-stain-negative, yellow-pigmented, rod-shaped, strictly aerobic, non-motile bacterium, designated BDHS18T, was isolated from the sediment of the Hasuhai Lake, China. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that this strain belongs to the genus Moheibacter in the family Flavobacteriaceae and its closest relative was Moheibacter sediminis JCM 19634T (96.0%), followed by Moheibacter stercoris DSM 29388T (95.3%). Cells of strain BDHS18T were catalase-positive and oxidase-negative. Strain BDHS18T was found to grow optimally at 28–33 ℃, pH 7.5–8.0, and in the presence of approximately 1.0% (w/v) NaCl. Major cellular fatty acids were iso-C15:0, iso-C17:0 3-OH, Summed feature 4 and Summed feature 9. The predominant respiratory quinone was MK-6. The predominant polar lipids in strain BDHS18T were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, one unidentified aminolipid and one unidentified lipid. The DNA G + C content was 36.9 mol%. According to the phylogenetic analysis, physiological and phenotypic characteristics, strain BDHS18T represents a novel species of the genus Moheibacter, for which the name Moheibacter lacus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is BDHS18T (= KCTC 72160T = MCCC 1H00369T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang RG, Tan X, Zhao XM, Deng J, Lv J (2014) Moheibacter sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from sediment, and emended descriptions of Empedobacter brevis, Wautersiella falsenii and Weeksella virosa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1481–1487
Schauss T, Busse HJ, Golke J, Kämpfer P, Glaeser SP (2016) Moheibacter stercoris sp. nov., isolated from an input sample of a biogas plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2585–2591
Liu QQ, Wang Y, Li J, Du ZJ, Chen GJ (2014) Saccharicrinis carchari sp. nov., isolated from a shark, and emended descriptions of the genus Saccharicrinis and Saccharicrinis fermentans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(7):2204–2209
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017) Introducing EzBio-Cloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution (N Y) 39:783–791
Bowman JP (2000) Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. Nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1861–1868
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Determination of biochemical characteristics. Manual for the systematic identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398 (In Chinese)
Collins MD, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1980) Fatty acids, isoprenoid quinone and polar lipid composition in the classification of Curtobacterium and related taxa. J Gen Microbiol 118:29–37
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367
Xu XW, Wu YH, Wang CS, Oren A, Zhou PJ et al (2007) Haloferax larsenii sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:717–720
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Acknowledgements
This work of scanning electron microscope was supported by the Physical-Chemical Materials Analytical and Testing Center of Shandong University at Weihai.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070002, 31770002) and National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2019FY100700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. The strain BDHS18T was isolated by YC. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YL and CNW. The manuscript was written by YL. Project guidance and critical revision of manuscripts was performed by ZD, MY and MW. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chang, YQ., Wang, CN. et al. Moheibacter lacus sp. nov., Isolated from Freshwater Lake Sediment. Curr Microbiol 78, 2160–2164 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02465-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02465-1