Abstract
Background
Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) is an autosomal-recessive inborn error of metabolism.
Objective
To recognize the CT and MR brain sectional imaging findings in children with MMA.
Materials and methods
Brain imaging studies (47 MR and 5 CT studies) from 52 children were reviewed and reported by a neuroradiologist. The clinical data were collected for each patient.
Results
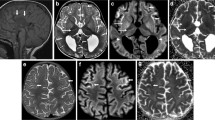
The most common findings were ventricular dilation (17 studies), cortical atrophy (15), periventricular white matter abnormality (12), thinning of the corpus callosum (8), subcortical white matter abnormality (6), cerebellar atrophy (4), basal ganglionic calcification (3), and myelination delay (3). The brain images in 14 patients were normal.
Conclusion
Radiological findings of MMA are nonspecific. A constellation of common clinical and radiological findings should raise the suspicion of MMA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsui SM, Mahoney MJ, Rosenberg LE (1983) The natural history of the inherited methylmalonic acidemias. N Engl J Med 308:857–861
Coulombe JT, Shih VE, Levy HL (1981) Massachusetts metabolic disorders screening program. II. Methylmalonic aciduria. Pediatrics 67:26–31
Mahoney MJ, Bick D (1987) Recent advances in the inherited methylmalonic acidemias. Acta Paediatr Scand 76:689–696
Saudubray JM, Ogier H, Bonnefont JP et al (1989) Clinical approach to inherited metabolic diseases in the neonatal period: a 20-year survey. J Inherit Metab Dis 12 [Suppl 1]:25–41
Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Valle S (eds) (2001) The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York
Naidu S, Moser HW (1991) Value of neuroimaging in metabolic diseases affecting the CNS. AJNR 12:413–416
Yue NC, Arnold AM, Longstreth WT et al (1997) Sulcal, ventricular, and white matter changes at MR imaging in the aging brain: data from the cardiovascular health study. Radiology 202:33–39
Kanaumi T, Takashima S, Hirose S et al (2006) Neuropathology of methylmalonic acidemia in a child. Pediatr Neurol 34:156–159
Brismar J, Ozand PT (1994) CT and MR of the brain in disorders of the propionate and methylmalonate metabolism. AJNR 15:1459–1473
Biancheri R, Cerone R, Schiaffino MC et al (2001) Cobalamin (Cbl) C/D deficiency: clinical, neurophysiological and neuroradiologic findings in 14 cases. Neuropediatrics 32:14–22
Lachman RS (2007) Taybi and Lachman’s radiology of syndromes, metabolic disorders, and skeletal dysplagias. 5th edn. Mosby-Elsevier, Philadelphia, p 507
Enns GM, Barkovich AJ, Rosenblatt DS et al (1999) Progressive neurological deterioration and MRI changes in cblC methylmalonic acidaemia treated with hydroxocobalamin. J Inherit Metab Dis 22:599–607
Barkovich AJ (2000) Pediatric neuroimaging. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 138–139
Rutherford M (2002) MRI of the neonatal brain. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA
Jin H, Zou LP, Zhang CH et al (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of methylmalonic acidemia in 14 cases. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 42:581–584
Gebarski SS, Gabrielsen TO, Knake JE et al (1983) Cerebral CT findings in methylmalonic acid propionic acidemias. AJNR 4:955–957
Heidenreich R, Natowicz M, Hainline BE et al (1988) Acute extrapyramidal syndrome in methylmalonic acidemia: “metabolic stroke” involving the globus pallidus. J Pediatr 113:1022–1027
de Sousa C, Piesowicz AT, Brett EM et al (1989) Focal changes in the globi pallidi associated with neurological dysfunction in methylmalonic acidaemia. Neuropediatrics 20:199–201
Korf B, Wallman JK, Levy HL (1986) Bilateral lucency of the globus pallidus complicating methylmalonic acidemia. Ann Neurol 20:364–366
Yesildag A, Ayata A, Baykal B et al (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in methylmalonic acidemia. Acta Radiol 46:101–103
Trinh BC, Melhem ER, Barker PB (2001) Multi-slice proton MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging in methylmalonic acidemia: report of two cases and review of the literature. AJNR 22:831–833
Rosenberg NL (1987) Methylmalonic acid, methanol, metabolic acidosis and lesions of the basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 22:96–97
Shimoizumi H, Okabe I, Kodama H et al (1993) Methylmalonic acidemia with bilateral MRI high intensities of the globus pallidus. No To Hattatsu 25:554–557
Roodhooft AM, Baumgartner ER, Martin JJ et al (1990) Symmetrical necrosis of the basal ganglia in methylmalonic acidaemia. Eur J Pediatr 149:582–584
Barkovich AJ (1995) Pediatric neuroradiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 463–465
Rossi A, Cerone R, Biancheri R et al (2001) Early-onset combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria: neuroradiologic findings. AJNR 22:554–563
Dave P, Curless RG, Steinman L (1984) Cerebellar hemorrhage complicating methylmalonic and propionic acidemia. Arch Neurol 41:1293–1296
Fischer AQ, Challa VR, Burton BK et al (1981) Cerebellar hemorrhage complicating isovaleric academia: a case report. Neurology 31:746–748
Barkovich AJ, Ali F, Rowley HA et al (1998) Imaging patterns of neonatal hypoglycemia. AJNR 19:523–528
Lyon G, Kolodny EH, Pastores GM (2006) Neurology of hereditary metabolic diseases of children. McGraw-Hill, New York
Takeuchi M, Harada M, Matsuzaki K et al (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in a patient with treated methylmalonic acidemia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:547–551
Michel SJ, Given CA 2nd, Robertson WC Jr (2004) Imaging of the brain, including diffusion-weighted imaging in methylmalonic acidemia. Pediatr Radiol 34:580–582
Andruela CF, De Blasi R, Carella A (1991) CT and MR studies of methylmalonic acidemia. AJNR 12:410–412
Gropman AL (2005) Expanding the diagnostic and research toolbox for inborn errors of metabolism: the role of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Mol Genet Metab 86:2–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radmanesh, A., Zaman, T., Ghanaati, H. et al. Methylmalonic acidemia: brain imaging findings in 52 children and a review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol 38, 1054–1061 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0940-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0940-8