Abstract
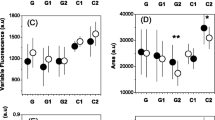
The photosynthetic adaptive features of non-dormant seeds in Posidonia oceanica were studied in order to evaluate the effects of light on germination success. Transmission electron micrographs showed the presence of chloroplasts in the epidermal cells, close to the nucleus at the periphery of the cytoplasm. The well-developed thylakoid membranes and the presence of starch granules indicated that the chloroplasts were photosynthetically active. The relationship between photosynthesis versus irradiance in P. oceanica seeds incubated at 15 and 21°C was analysed. The net photosynthesis in the non-dormant seed of P. oceanica was positive and compensated its respiration demand (90 μmol quanta m−2 s−1) at both temperatures. Net photosynthesis was negative at the other irradiance values. To test the effects of light on germination success, seeds were placed both in dark and light conditions. Germination success was significantly higher in light rather than in dark condition. The characteristics observed in the photosynthesis in P. oceanica seed could be a mechanism to guarantee seedling survival in temperate waters, demonstrating though the specialized nature of this species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberte RS, Suba GK, Procaccini G, Zimmerman RC, Fain SR (1994) Assessment of genetic diversity of seagrass population using DNA fingerprinting: implications for population stability and management. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1049–1053
Alcoverro T, Manzanera M, Romero J (1998) Seasonal and age-dependent variability of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile photosynthetic parameters. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 230(1):1–13
Balestri E, Lardicci C (2008) First evidence of a massive recruitment event in Posidonia oceanica: spatial variation in first-year seedling abundance on a heterogeneous substrate. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 76:634–641
Balestri E, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (1998) In vitro germination and seedling development of Posidonia oceanica. Aquat Bot 60:83–93
Balestri E, Cinelli F, Lardicci C (2003) Spatial variation in Posidonia oceanica structural, morphological and dynamic features in a northwestern Mediterranean coastal area: a multi-scale analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 250:51–60
Balestri E, Gobert S, Lepoint G, Lardicci C (2009) Seed nutrient content and nutritional status of Posidonia oceanica seedlings in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 388:99–109
Belzunce M, Navarro RM, Rapaport HF (2005) Seed and early plantlet structure of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Aquat Bot 82:269–283
Buia MC, Mazzella L (1991) Reproductive phenology of the Mediterranean seagrasses Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Aschers., and Zostera noltii Hornem. Aquat Bot 40:343–362
Caye G, Meinesz A (1989) Cultures en milieu artificial de Posidonia oceanica a partir de graines. In: Boudouresque CF, Meinesz A, Fresi E, Gravez V (eds) Int. Workshop on Posidonia oceanica Beds, vol. 2, GIS Posidonie Publ., pp 293–299
Drew A (1978) Factors affecting photosynthesis and its seasonal variation in the seagrasses Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Aschers, and Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in the Mediterranean. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 31:173–194
Duarte CM (1989) Temporal biomass variability and production/biomass relationships of seagrass communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 51:269–276
Pattanayak GK, Biswal AK, Reddy VS, Tripathy BC (2005) Light-dependent regulation of chlorophyll b biosynthesis in chlorophyllide a oxygenase overexpressing tobacco plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:466–471
Hocking PJ, Cambridge ML, McComb AJ (1981) Nutrient accumulation in the fruits of two species of seagrasses Posidonia australis and Posidonia sinuosa. Ann Bot 45:149–161
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls A, B, C1 and C2 in higher-plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:191–194
Kaldy JE, Dunton KH (1999) Ontogenic photosynthetic changes, dispersal and survival of Thalassia testudinum (turtle grass) seedling in a sub-tropical lagoon. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 240:193–212
Kuo J, Kirkman H (1990) Anatomy of viviparous seagrasses seedlings of Amphibolis and Thalassodendron and their nutrient supply. Bot Mar 33:117–126
Kuo J, McComb AJ (1989) Seagrass Taxonomy, Structure and Development. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Molinier R, Picard J (1952) Recherches sur les herbiers de phanérogames marines du littoral mediterranéen français. Ann Inst Oceánogr 27:157–234
Orth RJ, Harwell MC, Fishman JR (1999) A rapid and simple method for thransplanting eelgrass using single, unanchored shoots. Aquat Bot 64:77–85
Ott JA (1980) Growth and production in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar Ecol 1:47–64
Pergent G, Romero J, Pergent-Martini C, Mateo MA, Boudouresque CF (1994) Primary production, stocks and fluxes in the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 106:139–146
Pergent-Martini C, Pergent G (1995) Impact of a sewage treatment plant on the Posidonia oceanica meadow: assessment criteria. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on the Mediterranean coastal environment. MEDCOAST’95, pp 1389–1399
Piazzi L, Acunto S, Cinelli F (1999) In situ survival and development of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile seedlings. Aquat Bot 63:103–112
Pirc H (1986) Seasonal aspect of photosynthesis in Posidonia oceanica: influence of depth, temperature and light intensity. Aquat Bot 26:203–212
Procaccini G, Orsini L, Ruggiero MV, Scardi M (2001) Spatial pattern of genetic diversity in Posidonia oceanica, an endemic Mediterranean seagrass. Mol Ecol 10:1413–1421
Tomlinson PB (1982) Anatomy of the Monocotyledons VII. Helobiae (Alismatidae). Claredon Press, Oxford
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino from Spain (project code 116/SGTB/2007/1.3). The authors kindly thank Javier Lloret for the constructive criticism on this paper. This work was supported by a grant (D. Celdrán) from Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (Programa Nacional de Formación de Profesorado Universitario).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Ralph.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celdrán, D., Marín, A. Photosynthetic activity of the non-dormant Posidonia oceanica seed. Mar Biol 158, 853–858 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1612-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1612-4