Abstract
Rationale and Objectives
Relapse to alcohol use during abstinence or maladaptive eating habits during dieting is often provoked by stress. The anxiogenic drug yohimbine, which causes stress-like responses in humans and non-humans, reliably reinstates alcohol and food seeking in a rat relapse model. Yohimibine is a prototypical alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist, but results from studies on noradrenaline's role in yohimbine-induced reinstatement of drug and food seeking are inconclusive. Here, we further addressed this issue by studying the effect of the alpha-1 adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin and the alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist guanfacine on yohimbine-induced reinstatement.
Methods
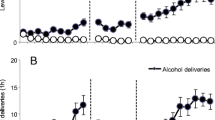
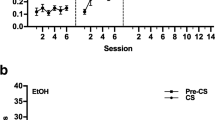
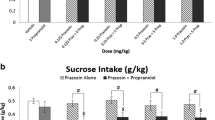
In exp. 1, we trained rats to self-administer alcohol (12% w/v, 1 h/day), and after extinction of alcohol-reinforced lever pressing, we tested prazosin's (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg/kg, i.p.) or guanfacine's (0.125, 0.25, and 0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) effect on yohimbine (1.25 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced reinstatement; we also examined prazosin's effect on intermittent-footshock-stress-induced reinstatement. In exp. 2, we trained food-restricted rats to self-administer 45 mg food pellets and first examined prazosin's or guanfacine's effects on food-reinforced responding, and then, after extinction of lever presses, on yohimbine-induced reinstatement.
Results
Prazosin (0.5–2.0 mg/kg) blocked yohimbine-induced reinstatement of food and alcohol seeking, as well as footshock-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Guanfacine attenuated yohimbine-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking at the highest dose (0.5 mg/kg), but its effect on yohimbine-induced reinstatement of food seeking was not significant. Neither prazosin nor guanfacine affected high-rate food-reinforced responding.
Conclusions
Results demonstrate an important role of postsynaptic alpha-1 adrenoceptors in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol and food seeking.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie ED, Keller RW Jr, Zigmond MJ (1988) Characterization of hippocampal norepinephrine release as measured by microdialysis perfusion: pharmacological and behavioral studies. Neuroscience 27:897–904
Aghajanian GK, VanderMaelen CP (1982) Alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated hyperpolarization of locus coeruleus neurons: intracellular studies in vivo. Science 215:1394–1396
Aston-Jones G, Delfs JM, Druhan J, Zhu Y (1999) The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: a target site for noradrenergic actions in opiate withdrawal. Ann NY Acad Sci 877:486–498
Bing G, Stone EA, Zhang Y, Filer D (1992) Immunohistochemical studies of noradrenergic-induced expression of c-fos in the rat CNS. Brain Res 592:57–62
Bossert JM, Ghitza UE, Lu L, Epstein DH, Shaham Y (2005) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: an update and clinical implications. Eur J Pharmacol 526:36–50
Boyajian CL, Leslie FM (1987) Pharmacological evidence for alpha-2 adrenoceptor heterogeneity: differential binding properties of [3H]rauwolscine and [3H]idazoxan in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:1092–1098
Breese GR, Sinha R, Heilig M (2010) Chronic alcohol neuroadaptation and stress contribute to susceptibility for alcohol craving and relapse. Pharmacol Ther (in press)
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Southwick SM, Charney DS (1996a) Noradrenergic mechanisms in stress and anxiety: I. preclinical studies. Synapse 23:28–38
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Southwick SM, Charney DS (1996b) Noradrenergic mechanisms in stress and anxiety: II. clinical studies. Synapse 23:39–51
Brown SA, Vik PW, Patterson TL, Grant I, Schuckit MA (1995) Stress, vulnerability and adult alcohol relapse. J Stud Alcohol 56:538–545
Brown ZJ, Tribe E, D'Souza NA, Erb S (2009) Interaction between noradrenaline and corticotrophin-releasing factor in the reinstatement of cocaine seeking in the rat. Psychopharmacology Berl 203:121–130
Buffalari DM, See RE (2010) Inactivation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in an animal model of relapse: effects on conditioned cue-induced reinstatement and its enhancement by yohimbine. Psychopharmacology Berl 213:19–27
Byers MG, Allison KM, Wendel CS, Lee JK (2010) Prazosin versus quetiapine for nighttime posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in veterans: an assessment of long-term comparative effectiveness and safety. J Clin Psychopharmacol 30:225–229
Byrne S, Cooper Z, Fairburn C (2003) Weight maintenance and relapse in obesity: a qualitative study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:955–962
Cohen BM (1970) Prazosin hydrochloride (CP-12, 299–1), an oral anti-hypertensive agent: preliminary clinical observations in ambulatory patients. J Clin Pharmacol J New Drugs 10:408–417
Curran T, Morgan JI (1995) Fos: an immediate-early transcription factor in neurons. J Neurobiol 26:403–412
Dekeyne A, Millan MJ (2006) Discriminative stimulus properties of the selective and highly potent alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, S18616, in rats: mediation by the alpha2A subtype, and blockade by the atypical antidepressants, mirtazapine and mianserin. Neuropharmacology 51:718–726
Doxey JC, Lane AC, Roach AG, Virdee NK (1984) Comparison of the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist profiles of idazoxan (RX 781094), yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 325:136–144
Drew GM, Gower AJ, Marriott AS (1979) Alpha 2-adrenoceptors mediate clonidine-induced sedation in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 67:133–141
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology 189:1–16
Erb S, Stewart J (1999) A role for the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, but not the amygdala, in the effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 19:35
Erb S, Hitchcott PK, Rajabi H, Mueller D, Shaham Y, Stewart J (2000) Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists block stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:138–150
Foote SL, Bloom FE, Aston-Jones G (1983) Nucleus locus coeruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity. Physiol Rev 63:844–914
Forget B, Wertheim C, Mascia P, Pushparaj A, Goldberg SR, Le Foll B (2010) Noradrenergic alpha1 receptors as a novel target for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1751–1760
Fritschy JM, Grzanna R (1991) Selective effects of DSP-4 on locus coeruleus axons: are there pharmacologically different types of noradrenergic axons in the central nervous system? Prog Brain Res 88:257–268
Funk D, Li Z, Le AD (2006) Effects of environmental and pharmacological stressors on c-fos and corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in rat brain: relationship to the reinstatement of alcohol seeking. Neuroscience 138:235–243
Ghitza UE, Gray SM, Epstein DH, Rice KC, Shaham Y (2006) The anxiogenic drug yohimbine reinstates palatable food seeking in a rat relapse model: a role of CRF(1) receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2188–2196
Ghitza UE, Nair SG, Golden SA, Gray SM, Uejima JL, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2007) Peptide YY3-36 decreases reinstatement of high-fat food seeking during dieting in a rat relapse model. J Neurosci 27:11522–11532
Grilo CM, Shiffman S, Wing RR (1989) Relapse crises and coping among dieters. J Consult Clin Psychol 57:488–495
Handley SL, Mithani S (1984) Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists in a maze-exploration model of ‘fear’-motivated behaviour. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 327:1–5
Holmberg G, Gershon S (1961) Autonomic and psychic effects of yohimbine hydrochloride. Psychopharmacologia 2:93–106
Ji XH, Ji JZ, Zhang H, Li BM (2008) Stimulation of alpha2-adrenoceptors suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex of rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2263–2271
Kostrzewa RM, Kostrzewa JP, Brus R (2003) Dopamine receptor supersensitivity: an outcome and index of neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 5:111–118
Lang WJ, Gershon S (1963) Effects of psychoactive drugs on yohimbine induced responses in conscious dogs. A proposed screening procedure for anti-anxiety agents. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 142:457–472
Le A, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to alcohol in rats. Pharmacol Ther 94:137–156
Le AD, Quan B, Juzystch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y (1998) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:169–174
Le AD, Poulos CX, Harding S, Watchus W, Juzytsch W, Shaham Y (1999) Effects of naltrexone and fluoxetine on alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:435–444
Le AD, Harding S, Watchus W, Juzytsch W, Shalev U, Shaham Y (2000) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in stress-induced relapse to alcohol-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 150:317–324
Le AD, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Funk D, Shaham Y (2005) Role of alpha-2 adrenoceptors in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking and alcohol self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 179:366–373
Le AD, Funk D, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Fletcher PJ (2009) The role of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine in yohimbine-induced increases in alcohol-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 204:477–488
Lee B, Tiefenbacher S, Platt DM, Spealman RD (2004) Pharmacological blockade of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors induces reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in squirrel monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:686–693
Leri F, Flores J, Rodaros D, Stewart J (2002) Blockade of stress-induced, but not cocaine-induced reinstatement, by infusion of noradrenergic antagonists into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the central nucleus of the amygdala. J Neurosci 22:5713–5718
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–7861
Manion ST, Gamble EH, Li H (2007) Prazosin administered prior to inescapable stressor blocks subsequent exaggeration of acoustic startle response in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:559–565
Mantsch JR, Weyer A, Vranjkovic O, Beyer CE, Baker DA, Caretta H (2010) Involvement of noradrenergic neurotransmission in the stress- but not cocaine-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice: role for beta-2 adrenergic receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2165–2178
Marinelli PW, Funk D, Juzytsch W, Harding S, Rice KC, Shaham Y, Le AD (2007) The CRF(1) receptor antagonist antalarmin attenuates yohimbine-induced increases in operant alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 195:345–355
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Cussac D, Lejeune F, Nicolas JP, Coge F, Galizzi JP, Boutin JA, Rivet JM, Dekeyne A, Gobert A (2000) Agonist and antagonist actions of yohimbine as compared to fluparoxan at alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors (AR)s, serotonin (5-HT)(1A), 5-HT(1B), 5-HT(1D) and dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors. Significance for the modulation of frontocortical monoaminergic transmission and depressive states. Synapse 35:79–95
Moore RY, Bloom FE (1979) Central catecholaimine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci 2:113–168
Munzar P, Goldberg SR (1999) Noradrenergic modulation of the discriminative-stimulus effects of methamphetamine in rats. Psychopharmacology Berl 143:293–301
Nair SG, Golden SA, Shaham Y (2008) Differential effects of the hypocretin 1 receptor antagonist SB 334867 on high-fat food self-administration and reinstatement of food seeking in rats. Br J Pharmacol 154:406–416
Nair SG, Adams-Deutsch T, Epstein DH, Shaham Y (2009a) The neuropharmacology of relapse to food seeking: methodology, main findings, and comparison with relapse to drug seeking. Prog Neurobiol 89:18–45
Nair SG, Adams-Deutsch T, Pickens CL, Smith DG, Shaham Y (2009b) Effects of the MCH1 receptor antagonist SNAP 94847 on high-fat food-reinforced operant responding and reinstatement of food seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 205:129–140
Nair SG, Navarre BM, Cifani C, Pickens CL, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2011) Role of dorsal medial prefrontal cortex dopamine D1-family receptors in relapse to high-fat food seeking induced by the anxiogenic drug yohimbine. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:497–510
Newman-Tancredi A, Nicolas JP, Audinot V, Gavaudan S, Verriele L, Touzard M, Chaput C, Richard N, Millan MJ (1998) Actions of alpha2 adrenoceptor ligands at alpha2A and 5-HT1A receptors: the antagonist, atipamezole, and the agonist, dexmedetomidine, are highly selective for alpha2A adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 358:197–206
Pacak K, Palkovits M, Kopin IJ, Goldstein DS (1998) Stress-induced norepinephrine release in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and pituitary-adrenocortical and sympathoadrenal activity: in vivo microdialysis studies. Front Neuroendocrinol 16:89–150
Pappas BA, Ings R (1987) Neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of spinal noradrenergic terminals: nociception, clonidine analgesia and spinal alpha two adrenoceptors. Brain Res Bull 18:221–225
Peterson CB, Mitchell JE (1999) Psychosocial and pharmacological treatment of eating disorders: a review of research findings. J Clin Psychol 55:685–697
Rasmussen DD, Alexander LL, Raskind MA, Froehlich JC (2009) The alpha1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, prazosin, reduces alcohol drinking in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:264–272
Richards JK, Simms JA, Steensland P, Taha SA, Borgland SL, Bonci A, Bartlett SE (2008) Inhibition of orexin-1/hypocretin-1 receptors inhibits yohimbine-induced reinstatement of ethanol and sucrose seeking in Long-Evans rats. Psychopharmacology 199:109–117
Robinson TE, Whishaw IQ (1988) Normalization of extracellular dopamine in striatum following recovery from a partial unilateral 6-OHDA lesion of the substantia nigra: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats. Brain Res 450:209–224
Sagvolden T (2006) The alpha-2A adrenoceptor agonist guanfacine improves sustained attention and reduces overactivity and impulsiveness in an animal model of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Behav Brain Funct 2:41
Sallee FR, Eaton K (2010) Guanfacine extended-release for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:2549–2556
Scholtysik G, Lauener H, Eichenberger E, Burki H, Salzmann R, Muller-Schweinitzer E, Waite R (1975) Pharmacological actions of the antihypertensive agent N-amidino-2-(2, 6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide hydrochloride (BS 100–141). Arzneimittelforschung 25:1483–1491
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1995) Stress reinstates heroin self-administration behavior in drug-free animals: an effect mimicking heroin, not withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 119:334–341
Shaham Y, Erb S, Stewart J (2000a) Stress-induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking in rats: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:13–33
Shaham Y, Highfield D, Delfs JM, Leung S, Stewart J (2000b) Clonidine blocks stress-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in rats: an effect independent of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 12:292–302
Shaham Y, Shalev U, Lu L, De Wit H, Stewart J (2003) The reinstatement model of drug relapse: history, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology 168:3–20
Shalev U, Erb S, Shaham Y (2010) Role of CRF and other neuropeptides in stress-induced reinstatement of drug seeking. Brain Res 1314:15–28
Shepard JD, Bossert JM, Liu SY, Shaham Y (2004) The anxiogenic drug yohimbine reinstates methamphetamine seeking in a rat model of drug relapse. Biol Psychiatry 55:1082–1089
Shields AD, Wang Q, Winder DG (2009) Alpha2A-adrenergic receptors heterosynaptically regulate glutamatergic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Neuroscience 163:339–351
Sinha R (2007) The role of stress in addiction relapse. Curr Psychiatry Rep 9:388–395
Tassin JP, Studler JM, Herve D, Blanc G, Glowinski J (1986) Contribution of noradrenergic neurons to the regulation of dopaminergic (D1) receptor denervation supersensitivity in rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 46:243–248
Walker BM, Rasmussen DD, Raskind MA, Koob GF (2008) Alpha1-noradrenergic receptor antagonism blocks dependence-induced increases in responding for ethanol. Alcohol 42:91–97
Wang X, Cen X, Lu L (2001) Noradrenaline in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis is critical for stress-induced reactivation of morphine-conditioned place preference in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 432:153–161
Weiss F, Ciccocioppo R, Parsons LH, Katner S, Liu X, Zorrilla EP, Valdez GR, Ben-Shahar O, Angeletti S, Richter RR (2001) Compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse. Neuroadaptation, stress, and conditioning factors. Ann NY Acad Sci 937:1–26
Yamada H, Bruijnzeel AW (2010) Stimulation of alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala attenuates stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking in rats. Neuropharmacology 60:303–311
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the NIAAA (AA13108) to A.D. Lê and by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse. We thank Dr. Donna Calu and Ms. Thi Kuch for their help in conducting exp. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lê, A.D., Funk, D., Juzytsch, W. et al. Effect of prazosin and guanfacine on stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol and food seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 218, 89–99 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2178-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2178-7