Abstract
Rationale
In view of the difficulties in using antidepressant agents as training drugs in drug discrimination research, it was reasoned that tianeptine, because of its short duration of action and its lack of toxicity associated with long-term administration, would be well-suited to establish a discriminative stimulus cue in rats and, hence, a valuable tool in the investigation of the neural basis of depression.
Objectives
A drug discrimination procedure was used to determine whether tianeptine was associated with a specific discriminative stimulus effect, and substitution tests were conducted to determine whether this effect was mediated by serotonergic mechanisms.
Method
Rats were trained to discriminate 10 mg/kg tianeptine from saline and were tested with fluoxetine, a selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitor; venlafaxine, a 5-HT/noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor; 8-hydroxy-(2-di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), a selective 5-HT1A agonist; and caffeine, a nonselective antagonist of adenosine receptors.
Results
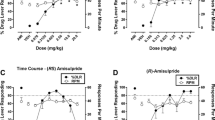
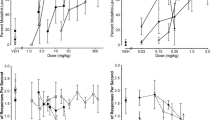
Tianeptine induced a specific, robust, and sustained discriminative stimulus in rats. Fluoxetine and 8-OH-DPAT partially substituted for tianeptine by producing >50% of tianeptine-appropriate lever responding. In contrast, venlafaxine and caffeine induced responding on a saline-associated lever.
Conclusion
The discriminative stimulus effect of tianeptine is mediated by serotonergic mechanisms, but what is surprising is that this mechanism seems to be, at least partially, enhanced by serotonergic transmission.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alby JM, Ferret M, Jabane J (1993) Efficacy of tianeptine in the treatment of major depression and dysthymia with somatic complaints. Ann Psychiatr 8:136–144
Antoniou K, Kafetzopoulos E, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z, Hyphantis T, Marselos M (1998) d-amphetamine, cocaine and caffeine: a comparative study of acute effects on locomotor activity and behavioural patterns in rats. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:189–196
Barrett JE, Zhang L (1991) Involvement of 5HT1A activity in the discriminative stimulus effects of imipramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:407–410
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1997) Indirect in vivo 5HT1A agonistic effects of the new antidepressant mirtazapine. Psychopharmacology 133:275–282
Ceyhan M, Kayir H, Uzbay IT (2005) Effects of tianeptine and fluoxetine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in rats. J Psychiatr Res 39:191–196
Dekeyne A, Millan MJ (2003) Discriminative stimulus properties of antidepressant agents: a review. Behav Pharmacol 14:391–407
Dekeyne A, Gobert A, Lob L, Cistarelli L, Melon C, Millan MC (2001) Discriminative stimulus properties of the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, reboxetine in rats. Psychopharmacology 154:213–218
Demotes-Mainard F, Galley P, Manciet G, Vinson G, Salvadori C (1991) Pharmacokinetics of the antidepressant tianeptine at steady state in the elderly. J Clin Pharmacol 31:174–178
Flip M, Chojnacka-Wojcik E, Przegalinski E (1993) Discriminative stimulus properties of ()-oxaprotiline in rats. Pol J Pharmacol 45:151–154
Garrett BE, Holtzman SG (1994) D1 and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists block caffeine-induced stimulation of locomotor activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:89–94
Glennon RA (1991) Discriminative stimulus properties of hallucinogens and related designer drugs. In: Glennon RA, Jarbe TUC, Frankenheim J (eds) Drug discrimination: applications to drug abuse research. NIDA Research Monograph, Washington, DC, pp 25–45
Goudie AJ, Leathley MJ (1993) Drug discrimination assays. In: Sahgal A (ed) Behavioural neuroscience. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 145–167
Hamon M, Bourgoin S, Gozlan H (1989) Effect de la tianeptine sur la liberation in vitro de H 5-HT et sur les divers types de recepteurs serotoninergiques dans le system nerveux central chez le rat. J Psychiat Biol Ther 48–51
Kasper S, Olie JP (2002) A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of tianeptine versus SSRI in the short-term treatment of depression. Eur Psychiatry 17(Suppl 3):331–340
Kato G, Weitsch AF (1988) Neurochemical profile of tianeptine, a new antidepressant drug. Clin Neuropharmacol 11(Suppl 2):43–50
Lane R, Baldwin D, Preskorn S (1995) The SSRIs: advantages, disadvantages and differences. J Psychopharmacol 9:163–178
Loo H, Saiz-Ruiz J, Costa e Silva JACE et al (1999) Efficacy and safety of tianeptine in the treatment of depressive disorders in comparison with fluoxetine. J Affect Disord 56:109–118
Marona-Lewicka D, Nichols DE (1998) Drug discrimination studies of the introceptive cues produced by selective serotonin uptake inhibitors and selective serotonin releasing agents. Psychopharmacology 138:67–75
Mennini T, Mocaer E, Garattini S (1987) Tianeptine, a new selective enhancer of serotonin reuptake in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 336:478–482
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Girardon S, Dekeyne A (1999) Citalopram elicits a discriminative stimulus in rats at a dose selectively increasing extracellular levels of serotonin vs. dopamine and noradrenaline. Eur J Pharmacol 364:147–150
Millan MJ, Dekeyne A, Rapp M, Drieu La Rochelle C, Macsweeny C, Peglion J-L, Brocco M (2001) S33005, a novel ligand at both serotonin and norepinephrine transporters: II. Behavioral profile in comparison with venlefaxine, reboxetine, citalopram and clomipramine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:581–591
Mocaer E, Rettori MC, Kamoun A (1988) Pharmacological antidepressive effects and tianeptine-induced 5-HT uptake increase. Clin Neuropharmacol 11:S32–S42
Preskorn SH (1997) Clinically relevant pharmacology of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. An overview with emphasis on pharmocokinetics and effects on oxidative drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacokinet 32(Suppl 1):1–21
Redrobe JP, MacSweeney CP, Bourin M (1996) The role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors in antidepressant drug actions in the mouse forced swimming test. Eur J Pharmacol 318:213–220
Rover RJ, Rover-Morrot, MJ, Paille F, Barrucand D, Schmit J, Defrance R, Salvadori C (1988) Tianeptine and its main metabolite pharmacokinetics in chronic alcoholism and cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacokinet 3:186–191
Schweizer E, Thielen RJ, Frazer A (1997) Venlafaxine, a novel antidepressant compound. Exp Opin Invest Drugs 6:65–78
Shearman G, Miksic S, Lal H (1978) Discriminative stimulus properties of desipramine. Neuropharmacology 17:1045–1048
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1987) Manual of pharmacological calculations with computer programs. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Tianpetine (S1574) Investigators' Brochure (1993) Version no. 5, p 13
Uzbay IT, Cinar MG, Aytemir M, Tuglular I (1999) Analgesic effect of tianeptine in mice. Life Sci 64:1313–1319
Waintraub L, Septien L, Azoulay P (2000) Efficacy and safety of tianeptine in major depression: evidence from a 3-month controlled clinical trial vs. paroxetine. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 10(Suppl 2):51
Wolf MC, Leander JD (1998) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors potentiate 8-OH-DPAT-induced stimulus control in the pigeon. Eur J Pharmacol 345:35–39
Wolf MC, Leander JD (1999) Discriminative stimulus properties of LW233708, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in pigeon. Psychopharmacology 146:275–279
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Baris Acikmese, Mr. Ugur Yazgan, and Mr. Selami Alan for their valuable technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alici, T., Kayir, H., Aygoren, M.O. et al. Discriminative stimulus properties of tianeptine. Psychopharmacology 183, 446–451 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0210-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0210-5