Abstract
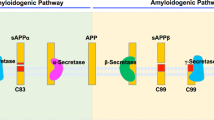
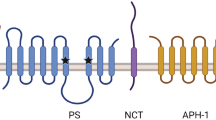
Genetic and biological studies provide evidence that the production and deposition of amyloid-β peptides (Aβ) contribute to the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease. β- and γ-secretases, which are responsible for the generation of Aβ, are plausible molecular targets for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. γ-Secretase is an unusual aspartic protease that cleaves the scissile bond within the transmembrane domain. This unusual enzyme is composed of a high molecular weight membrane protein complex containing presenilin, nicastrin, Aph-1 and Pen-2. Drugs that regulate the production of Aβ by inhibiting or modulating γ-secretase activity could provide a disease-modifying effect on Alzheimer’s disease, although recent studies suggest that γ-secretase plays important roles in cellular signaling including Notch. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanism whereby γ-secretase recognizes and cleaves its substrate is a critical issue for the development of compounds that specifically regulate Aβ-generating γ-secretase activity. This review focuses on the structure and function relationship of γ-secretase complex and the mode of action of the γ-secretase inhibitors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barten DM, Guss VL, Corsa JA, Loo A, Hansel SB, Zheng M, Munoz B, Srinivasan K, Wang B, Robertson BJ, Polson CT, Wang J, Roberts SB, Hendrick JP, Anderson JJ, Loy JK, Denton R, Verdoorn TA, Smith DW, Felsenstein KM (2005) Dynamics of β-amyloid reductions in brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma of β-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice treated with a γ-secretase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:635–643
Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, Lee MK, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada CM, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, Slunt HH, Wang R, Seeger M, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Younkin SG, Sisodia SS (1996) Familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Aβ1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron 17:1005–1013
Chen F, Hasegawa H, Schmitt-Ulms G, Kawarai T, Bohm C, Katayama T, Gu Y, Sanjo N, Glista M, Rogaeva E, Wakutani Y, Pardossi-Piquard R, Ruan X, Tandon A, Checler F, Marambaud P, Hansen K, Westaway D, St George-Hyslop P, Fraser P (2006) TMP21 is a presenilin complex component that modulates γ-secretase but not ɛ-secretase activity. Nature 440:1208–1212
De Strooper B, Saftig P, Craessaerts K, Vanderstichele H, Guhde G, Annaert W, Von Figura K, Van Leuven F (1998) Deficiency of presenilin-1 inhibits the normal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. Nature 391:387–390
Edbauer D, Winkler E, Regula JT, Pesold B, Steiner H, Haass C (2003) Reconstitution of γ-secretase activity. Nat Cell Biol 5:486–488
Esler WP, Kimberly WT, Ostaszewski BL, Diehl TS, Moore CL, Tsai JY, Rahmati T, Xia W, Selkoe DJ, Wolfe MS (2000) Transition-state analogue inhibitors of γ-secretase bind directly to presenilin-1. Nat Cell Biol 2:428–434
Francis R, McGrath G, Zhang J, Ruddy DA, Sym M, Apfeld J, Nicoll M, Maxwell M, Hai B, Ellis MC, Parks AL, Xu W, Li J, Gurney M, Myers RL, Himes CS, Hiebsch R, Ruble C, Nye JS, Curtis D (2002) aph-1 and pen-2 are required for Notch pathway signaling, γ-secretase cleavage of βAPP, and presenilin protein accumulation. Dev Cell 3:85–97
Fuwa H, Hiromoto K, Takahashi Y, Yokoshima S, Kan T, Fukuyama T, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Natsugari H (2006) Synthesis of biotinylated photoaffinity probes based on arylsulfonamide γ-secretase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:4184–4189
Fuwa H, Takahashi Y, Konno Y, Watanabe N, Miyashita H, Sasaki M, Natsugari H, Kan T, Fukuyama T, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2007) Divergent synthesis of multifunctional molecular probes to elucidate the enzyme specificity of dipeptidic γ-secretase inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol 2:408–418
Goutte C, Tsunozaki M, Hale VA, Priess JR (2002) APH-1 is a multipass membrane protein essential for the Notch signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:775–779
Hayashi I, Urano Y, Fukuda R, Isoo N, Kodama T, Hamakubo T, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2004) Selective reconstitution and recovery of functional γ-secretase complex on budded baculovirus particles. J Biol Chem 279:38040–38046
Herreman A, Serneels L, Annaert W, Collen D, Schoonjans L, De Strooper B (2000) Total inactivation of γ-secretase activity in presenilin-deficient embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 2:461–462
Ilagan MX, Kopan R (2007) SnapShot: notch signaling pathway. Cell 128:1246
Isoo N, Sato C, Miyashita H, Shinohara M, Takasugi N, Morohashi Y, Tsuji S, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2007) Aβ42 overproduction associated with structural changes in the catalytic pore of γ-secretase: common effects of Pen-2 N-terminal elongation and fenofibrate. J Biol Chem 282:12388–12396
Iwatsubo T, Odaka A, Suzuki N, Mizusawa H, Nukina N, Ihara Y (1994) Visualization of Aβ 42(43) and Aβ 40 in senile plaques with end-specific Aβ monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is Aβ 42(43). Neuron 13:45–53
Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2004) γ-Secretase: proteasome of the membrane? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:499–504
Lazarov VK, Fraering PC, Ye W, Wolfe MS, Selkoe DJ, Li H (2006) Electron microscopic structure of purified, active γ-secretase reveals an aqueous intramembrane chamber and two pores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6889–6894
Li YM, Lai MT, Xu M, Huang Q, DiMuzio-Mower J, Sardana MK, Shi XP, Yin KC, Shafer JA, Gardell SJ (2000a) Presenilin 1 is linked with γ-secretase activity in the detergent solubilized state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6138–6143
Li YM, Xu M, Lai MT, Huang Q, Castro JL, DiMuzio-Mower J, Harrison T, Lellis C, Nadin A, Neduvelil JG, Register RB, Sardana MK, Shearman MS, Smith AL, Shi XP, Yin KC, Shafer JA, Gardell SJ (2000b) Photoactivated γ-secretase inhibitors directed to the active site covalently label presenilin 1. Nature 405:689–694
Lleo A, Berezovska O, Herl L, Raju S, Deng A, Bacskai BJ, Frosch MP, Irizarry M, Hyman BT (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs lower Aβ42 and change presenilin 1 conformation. Nat Med 10:1065–1066
Morohashi Y, Kan T, Tominari Y, Fuwa H, Okamura Y, Watanabe N, Sato C, Natsugari H, Fukuyama T, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T (2006) C-terminal fragment of presenilin is the molecular target of a dipeptidic γ-secretase-specific inhibitor DAPT. J Biol Chem 281:14670–14676
Netzer WJ, Dou F, Cai D, Veach D, Jean S, Li Y, Bornmann WG, Clarkson B, Xu H, Greengard P (2003) Gleevec inhibits β-amyloid production but not Notch cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12444–12449
Niimura M, Isoo N, Takasugi N, Tsuruoka M, Ui-Tei K, Saigo K, Morohashi Y, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2005) Aph-1 contributes to the stabilization and trafficking of the γ-secretase complex through mechanisms involving intermolecular and intramolecular interactions. J Biol Chem 280:12967–12975
Ogura T, Mio K, Hayashi I, Miyashita H, Fukuda R, Kopan R, Kodama T, Hamakubo T, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Sato C (2006) Three-dimensional structure of the γ-secretase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343:525–534
Okochi M, Fukumori A, Jiang J, Itoh N, Kimura R, Steiner H, Haass C, Tagami S, Takeda M (2006) Secretion of the Notch-1 Aβ-like peptide during Notch signaling. J Biol Chem 281:7890–7898
Parks AL, Curtis D (2007) Presenilin diversifies its portfolio. Trends Genet 23:140–150
Petit A, Bihel F, Alves da Costa C, Pourquie O, Checler F, Kraus JL (2001) New protease inhibitors prevent γ-secretase-mediated production of Aβ40/42 without affecting Notch cleavage. Nat Cell Biol 3:507–511
Sato C, Morohashi Y, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2006) Structure of the catalytic pore of γ-secretase probed by the accessibility of substituted cysteines. J Neurosci 26:12081–12088
Schmidt B, Baumann S, Braun HA, Larbig G (2006) Inhibitors and modulators of β- and γ-secretase. Curr Top Med Chem 6:377–392
Searfoss GH, Jordan WH, Calligaro DO, Galbreath EJ, Schirtzinger LM, Berridge BR, Gao H, Higgins MA, May PC, Ryan TP (2003) Adipsin, a biomarker of gastrointestinal toxicity mediated by a functional γ-secretase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 278:46107–46116
Shah S, Lee SF, Tabuchi K, Hao YH, Yu C, LaPlant Q, Ball H, Dann CE 3rd, Sudhof T, Yu G (2005) Nicastrin functions as a γ-secretase-substrate receptor. Cell 122:435–447
Siemers E, Skinner M, Dean RA, Gonzales C, Satterwhite J, Farlow M, Ness D, May PC (2005) Safety, tolerability, and changes in amyloid β concentrations after administration of a γ-secretase inhibitor in volunteers. Clin Neuropharmacol 28:126–132
Siemers ER, Quinn JF, Kaye J, Farlow MR, Porsteinsson A, Tariot P, Zoulnouni P, Galvin JE, Holtzman DM, Knopman DS, Satterwhite J, Gonzales C, Dean RA, May PC (2006) Effects of a γ-secretase inhibitor in a randomized study of patients with Alzheimer disease. Neurology 66:602–604
Steiner H, Than M, Bode W, Haass C (2006) Pore-forming scissors? A first structural glimpse of γ-secretase. Trends Biochem Sci 31:491–493
Takahashi Y, Hayashi I, Tominari Y, Rikimaru K, Morohashi Y, Kan T, Natsugari H, Fukuyama T, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2003) Sulindac sulfide is a noncompetitive γ-secretase inhibitor that preferentially reduces Aβ42 generation. J Biol Chem 278:18664–18670
Takasugi N, Tomita T, Hayashi I, Tsuruoka M, Niimura M, Takahashi Y, Thinakaran G, Iwatsubo T (2003) The role of presenilin cofactors in the γ-secretase complex. Nature 422:438–441
Thinakaran G, Borchelt DR, Lee MK, Slunt HH, Spitzer L, Kim G, Ratovitsky T, Davenport F, Nordstedt C, Seeger M, Hardy J, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS (1996) Endoproteolysis of presenilin 1 and accumulation of processed derivatives in vivo. Neuron 17:181–190
Tolia A, Chavez-Gutierrez L, De Strooper B (2006) Contribution of presenilin transmembrane domains 6 and 7 to a water-containing cavity in the γ-secretase complex. J Biol Chem 281:27633–27642
Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2006) γ-Secretase as a therapeutic target for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 12:661–670
Tomita T, Maruyama K, Saido TC, Kume H, Shinozaki K, Tokuhiro S, Capell A, Walter J, Grunberg J, Haass C, Iwatsubo T, Obata K (1997) The presenilin 2 mutation (N141I) linked to familial Alzheimer disease (Volga German families) increases the secretion of amyloid β protein ending at the 42nd (or 43rd) residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2025–2030
Weggen S, Eriksen JL, Das P, Sagi SA, Wang R, Pietrzik CU, Findlay KA, Smith TE, Murphy MP, Bulter T, Kang DE, Marquez-Sterling N, Golde TE, Koo EH (2001) A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Aβ42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity. Nature 414:212–216
Wolfe MS (2006) The γ-Secretase complex: membrane-embedded proteolytic ensemble. Biochemistry 45:7931–7939
Wolfe MS, Xia W, Ostaszewski BL, Diehl TS, Kimberly WT, Selkoe DJ (1999) Two transmembrane aspartates in presenilin-1 required for presenilin endoproteolysis and γ-secretase activity. Nature 398:513–517
Yu G, Nishimura M, Arawaka S, Levitan D, Zhang L, Tandon A, Song YQ, Rogaeva E, Chen F, Kawarai T, Supala A, Levesque L, Yu H, Yang DS, Holmes E, Milman P, Liang Y, Zhang DM, Xu DH, Sato C, Rogaev E, Smith M, Janus C, Zhang Y, Aebersold R, Farrer LS, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Fraser P, St George-Hyslop P (2000) Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and βAPP processing. Nature 407:48–54
Zhou S, Zhou H, Walian PJ, Jap BK (2005) CD147 is a regulatory subunit of the γ-secretase complex in Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-peptide production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7499–7504
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Dr. Takeshi Iwatsubo (The University of Tokyo) and all colleagues who collaborated in the studies cited in this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomita, T. At the frontline of Alzheimer’s disease treatment: γ-secretase inhibitor/modulator mechanism. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 377, 295–300 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0206-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0206-2