Abstract
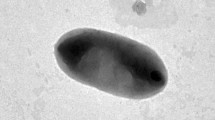
Strain SZY PN-1 T, representing a novel Gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, rod-shaped and yellow-pigmented bacterium, was isolated from a skin sample of a healthy Chinese male. Growth occurred at pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum, pH 7.0) and 10–37 ℃ (optimum, 30 ℃) with 0–1.0% (w/v) NaCl in R2A agar. Comparative analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain SZY PN-1 T shared high similarities with two invalid-published species, “Sandaracinobacter sibiricus” RB16-17 (97.1%) and “Sandaracinobacter neustonicus” JCM 30734 (96.6%), respectively. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences together with protein-concatemer tree showed that SZY PN-1 T formed a separate branch within the family Sphingosinicellaceae. The DNA G + C content of the strain SZY PN-1 T was 65.0% (genome). The polar lipid profile included phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, two sphingoglycolipids, diphosphatidylglycerol, five unidentified glycolipids, and seven unidentified lipids. The predominant fatty acids (> 10.0%) were identified as C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c, C17:1 ω6c, C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c. The major respiratory quinone was Q-10. Based on the phenotypic and genotypic features, a novel genus and species, Sandaracinobacteroides hominis gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed, with type strain SZY PN-1 T (= KCTC 82150 T = NBRC 114675 T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas MM, Malluhi QM, Balakrishnan P (2014) Assessment of de novo assemblers for draft genomes: a case study with fungal genomes. BMC Genomics 15:S10
Aslanzadeh J (2006) Biochemical profile-based microbial identification systems. In: Tang YW, Stratton CW (eds) Advanced techniques in diagnostic microbiology. Springer, New York, pp 87–121
Cai H, Cui H, Zeng Y, An M, Jiang H (2018) Sandarakinorhabdus cyanobacteriorum sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from cyanobacterial aggregates in a eutrophic lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:730–735
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466
Collins MD, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycan based on 2,4-diaminobutyric acid. J Appl Bacteriol 48:459–470
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–223
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Biol 20:406–416
Fukuda W, Chino Y, Araki S, Kondo Y, Imanaka H, Kanai T, Atomi H, Imanka T (2014) Polymorphobacter multimanifer gen. nov., sp. nov., a polymorphic bacterium isolated from Antarctic white rock. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2034–2040
Gich F, Overmann J (2006) Sandarakinorhabdus limnophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacteriochlorophyll α-containing, obligately aerobic bacterium isolated from freshwater lakes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:847–854
Giovannoni SJ (1991) The polymerase chain reaction. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Modern microbiological methods: nucleic acids techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 177–203
Hansen GH, Sørheim R (1991) Improved method for phenotypical characterization of marine bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 13:231–241
Hördt A, López MG, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Weinhold LM, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020) Analysis of 1000+ type-strain genomes substantially improves taxonomic classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front Microbiol 11:468
Jia L, Feng X, Zheng Z, Han L, Hou X, Lu Z, Lv J (2015) Polymorphobacter fuscus sp. nov., isolated from permafrost soil, and emended description of the genus Polymorphobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3920–3925
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351
Kim M, Kang O, Zhang Y, Ren L, Chang X, Jiang F, Fan C, Zheng C, Peng F (2016) Sphingoaurantiacus polygranulatus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from high-Arctic tundra soil, and emended descriptions of the genera Sandarakinorhabdus, Polymorphobacter and Rhizorhabdus and the species Sandarakinorhabdus limnophila, Rhizorhabdus argentea and Sphingomonas wittichii. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:91–100
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, Mcgettigan PA (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lee I, Jang GI, Cho Y, Yoon SJ, Pham HM, Nguyen AV, Lee YM, Park H, Rhee TS, Kim SH, Hwang CY (2020) Sandaracinobacter neustonicus sp. nov., isolated from the sea surface microlayer in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean, and emended description of the genus Sandaracinobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:4698–4703
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China), and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Liu K, Li S, Jiao N, Tang K (2014) Pacificamonas flava gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Sphingomonadaceae isolated from the Southeastern Pacific. Curr Microbiol 69:96–101
Logan NA, Vos PD (2009) The genus Bacillus. In: Vos PD, Garrity GM, Jones D, Krieg ND, Ludwig W, Rainey FA, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB (eds) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, p 62
Maruyama T, Park HD, Ozawa TY, Sumino T, Hamana K, Hiraishi A, Kato K (2006) Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:85–89
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60
Minnikin DE, CollinsGoodfellow MDM (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25:1043–1055
Phurbu D, Liu ZX, Liu HC, Lhamo Y, Yangzom P, Li AH, Zhou YG (2020) Polymorphobacter arshaanensis sp. nov., containing the photosynthetic gene pufML, isolated from a volcanic lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:1093–1098
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2015) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931
Saga Y, Osumi S, Higuchi H, Tamiaki H (2005) Bacteriochlorophyll-c homolog composition in green sulfur photosynthetic bacterium Chlorobium vibrioforme dependent on the concentration of sodium sulfide in liquid cultures. Photosynth Res 86:123–130
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA et al (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313
Thompson CC, Chimetto L, Edwards RA, Swings J, Stackebrandt E, Thompson FL (2013) Microbial genomic taxonomy. BMC Genomics 14:913
Wu M, Scott AJ (2012) Phylogenomic analysis of bacterial and archaeal sequences with AMPHORA2. Bioinformatics 28:1033–1034
Xing T, Liu Y, Wang N, Xu B, Shen L, Liu K, Gu Z, Guo B, Zhou Y, Liu H (2017) Polymorphobacter glacialis sp. nov., isolated from ice core. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:617–620
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Chen GZ, Chen HH, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family 'Oxalobacteraceae’ isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB, Euzéby J, Amann R, Rosselló-Móra R (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:635–645
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Yurkov V, Stackebrandt E, Buss O, Vermeglio A, Gorlenko V, Beatty JT (1997) Reorganization of the genus Erythromicrobium: description of Erythromicrobium sibiricum as Sandaracinobacter sibiricus gen. nov., sp. nov., and of Erythromicrobium ursincola as Erythromonas ursincola gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1172–1178
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Refractory Chronic Diseases (2018B030322012) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972856).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and CC designed the research and project outline. PHQ, HML, JHF, SL, LD and YZM performed isolation, deposition, and identification. PHQ, HML and JHF analyzed the data. PHQ, HML and WJL drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments involving human subjects were carried out according to the institutional review board protocols approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine in China (BE2019-165). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, PH., Luo, HM., Feng, JH. et al. Sandaracinobacteroides hominis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human skin. Arch Microbiol 203, 5067–5074 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02454-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02454-9