Abstract
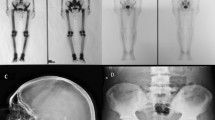
We report a new case of hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis (HCAO). The clinical presentation of the patient was an acquired deep severe bone pain with increased serum bone alkaline phosphatase activity (up to 12 times the upper limit of normal), and generalized bone sclerosis, temporally related to the hepatitis C-virus (HCV) infection. We documented in this patient an increase of circulating osteoprotegerin (OPG), and a concentration of circulating receptor activator for nuclear factor-kB ligand (RANKL) below the lower limit of the reference range. The observed abnormalities of the OPG/RANKL system may contribute to the maintenance of the positive balance of bone remodeling that characterizes patients with HCAO.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choo QL, Weiner AJ, Overby LR (1990) Hepatitis C virus: the major causative agent of viral non-A, non-B hepatitis. Br Med Bull 46:423-441
Villareal DT, Murphy WA, Teitelbaum SL, Arens MQ, Whyte MP (1992) Painful diffuse osteosclerosis after intravenous drug abuse. Am J Med 93:371–381
Beyer HS, Anderson Q, Shih MS, Parfitt AM, Heath H (1993) Diffuse osteosclerosis in intravenous drug abusers. Am J Med 95:660–661
Whyte MP, Teitelbaum SL, Reinus WR (1996) Doubling skeletal mass during adult life: the syndrome of diffuse osteosclerosis after intravenous drug abuse. J Bone Miner Res 11:554–558
Diamond T, Depczysnki B (1996) Acquired osteosclerosis associated with intravenous drug use and hepatitis C infection. Bone 19:679–683
Whyte MP, Reasner CA (1997) Hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis after blood transfusion. Am J Med 102:219–229
Hassoun AAK, Nippoldt TB, Tiegs RD, Khosla S (1997) Hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis: an unusual syndrome of acquired osteosclerosis in adults. Am J Med 103:70–73
Shaker JL, Reims WR, Whyte MP (1998) Hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis: late onset after blood transfusion in an elderly woman. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:93–98
Wakitani S, Hattori T, Nakaya H, Chae YM, Murata N, Tanigami A (2003) Clinical images: hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 48:268
Khosla S, Hassoun AAK, Baker BK, Liu F, Zein NN, Whyte MP, Reasner CA, Nippoldt TB, Tiegs RD, Hintz RL (1998) Insulin-like growth factor system abnormalities in hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis. J Clin Invest 101:2165–2173
Khosla S, Ballard FJ, Conover CA (2002) Use of site-specific antibodies to characterize the circulating form of big insulin-like growth factor II in patients with hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3867–3870
Khosla S (2001) Minireview: the OPG/RANK/RANKL system. Endocrinology 142:5050–5055
Shaker JL, Moore BP, Whyte MP (1999) Hyperparathyroidism and increased serum IGF-binding protein-2 levels in hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:384–385
Whyte MP, Chines A, Silva DP, Landt Y, Ladenson JH (1996) Creatine kinase brain isoenzyme (BB-CK) presence in serum distinguishes osteopetroses among the sclerosing bone disorders. J Bone Miner Res 11:1438–1443
Pennisi P, Signorelli SS, Riccobene S, Celotta G, Di Pino L, La Malfa T, Fiore CE (2004) Low bone density and abnormal bone turnover in patients with atherosclerosis of peripheral vessels. Osteoporos Int 15:389–395
Szalay F, Hegedus D, Lakatos PL, Tornai I, Bajnock E, Dunkel K, Lakatos P (2003) High serum osteoprotegerin and low RANKL in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol 38:395–400
Burgess TL, Qian YX, Kaufman S, Ring BD, Van G, Capparelli C (1999) The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol 145:527–538
Bekker PJ, Holloway DL, Rasmussen AS, Murphy R, Martin SW, Leese PT, Holmes GB, Dunstan CR, DePaoli AM (2004) A single-dose placebo-controlled study of AMG 162, a fully human monoclonal antibody to RANKL, in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 19:1059–1066
Tappero G, Farina M, Negro F, Anfossi G, Mattiello L, Giuli PD, Colombatto P, Brunetto MR, Angeli A, Bonino F (1997) Intrahepatic expression of c-fos, c-myb and c-myc oncogenes: correlation with virus-induced chronic liver disease and response to interferon. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:148–154
Sabatakos G, Sims NA, Chen K, Aoki K, Kelz MB, Amling M, Bouali V, Mukhopadhyay K, Ford K, Nestler EJ, Baron R (2000) Overexpression of ΔFos B transcription factor(s) increases bone formation and inhibits adipogenesis. Nat Med 6:985–990
Jochum W, David JP, Elliot C, Wutz A, Plenk H, Matsuo K, Wagner EF (2000) Increased bone formation and osteosclerosis in mice overexpressing the transcription factor Fra-1. Nat Med 6:980–984
Matsuo K, Owens JM, Tonko M, Elliot C, Chambers TJ, Wagner EF (2000) Fos-1 is a transcriptional target of c-Fos during osteoclast differentiation. Nat Genet 24:184–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiore, C.E., Riccobene, S., Mangiafico, R. et al. Hepatitis C-associated osteosclerosis (HCAO): report of a new case with involvement of the OPG/RANKL system. Osteoporos Int 16, 2180–2184 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-005-1858-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-005-1858-8