Abstract.
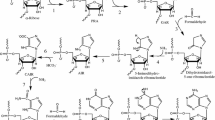
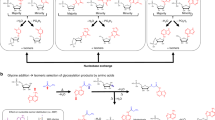
Purine biosynthesis requires ten enzymatic transformations to generate inosine monophosphate. PurF, PurD, PurL, PurM, PurC, and PurB are common to all pathways, while PurN or PurT, PurK/PurE-I or PurE-II, PurH or PurP, and PurJ or PurO catalyze the same steps in different organisms. X-ray crystal structures are available for all 15 purine biosynthetic enzymes, including 7 ATP-dependent enzymes, 2 amidotransferases and 2 tetrahydrofolate-dependent enzymes. Here we summarize the structures of the purine biosynthetic enzymes, discuss similarities and differences, and present arguments for pathway evolution. Four of the ATP-dependent enzymes belong to the ATP-grasp superfamily and 2 to the PurM superfamily. The amidotransferases are unrelated, with one utilizing an N-terminal nucleophileglutaminase and the other utilizing a triad glutaminase. Likewise the tetrahydrofolate-dependent enzymes are unrelated. Ancestral proteins may have included a broad specificity enzyme instead of PurD, PurT, PurK, PurC, and PurP, and a separate enzyme instead of PurM and PurL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 26 May 2008; received after revision 30 June 2008; accepted 9 July 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Morar, M. & Ealick, S.E. Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 3699–3724 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8295-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8295-8