Summary
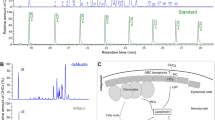
Using a radioimmunoassay developed for the determination of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP), immunoreactive material was detected in extracts of locust nervous tissue. Serial dilutions of a brain extract gave a displacement curve parallel to the CCAP standard curve. One locust nervous system was calculated to contain approximately 1.4 pmol CCAP-like material.
In order to investigate whether the immunoreactive substance was similar or identical to the crustacean neuropeptide, isolation and complete characterization was carried out using 800 locust nervous systems. The isolation procedure consisted of pre-purification of the crude extract on a Sep-Pak cartridge, affinity chromatography on a column which was prepared by coupling of anti-CCAP antibody to CNBr-activated Sepharose, and reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In the HPLC-profile immunoreactivity was confined to a single peak which co-chromatographed with authentic CCAP. The peptide was carboxymethylated and analyzed in an automated gas-phase sequencer. Its amino acid sequence, is identical to that of CCAP fromCarcinus maenas.
Synthetic CCAP was tested on the isolated locust hindgut in vitro. The peptide proved to be a potent enhancer of gut contractions, with a significant effect being observable at concentrations of 10−10 M. It is concluded that in the locust CCAP may function as a myotropic peptide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett HPJ, Browne CA, Goltzman D, Solomon S (1979) In: Gross E, Meienhofer J (eds) Peptides: structure and biological function. Pierce Chemical Co, Rockford, IL, p 121
Bishop CA, O'Shea M, Miller RJ (1981) Neuropeptide proctolin (H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr-OH): immunological detection and neuronal localization in insect central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 5899–5902
Bishop CA, Wine JJ, O'Shea M (1984) Neuropeptide proctolin in postural motoneurons of the crayfish. J Neurosci 4: 2001–2009
Brown BE, Starratt AN (1975) Isolation of proctolin, a myotropic peptide fromPeriplaneta americana. J Insect Physiol 21: 1879–1881
Dircksen H, Keller R (1988) Immunocytochemical localization of CCAP, a novel crustacean cardioactive peptide in the nervous system of the shore crab,Carcinus maenas. Cell Tissue Res 254: 347–360
Hirs CHW (1967) Reduction and S-carboxymethylation and proteins. Methods Enzymol 11: 199–203
Jones BN (1986) Amino acid analysis by o-phthaldialdehyde precolumn derivatization and reversed phase HPLC. In: Shively JE (ed) Methods of protein microcharacterization, a practical handbook. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ
Keshishian H, O'Shea M (1985) The distribution of a peptide neurotransmitter in the postembryonic grasshopper central nervous system. J Neurosci 4: 992–1004
Kingan T, Timus M (1983) Radioimmunologic detection of proctolin in arthropods. Comp Biochem Physiol 1: 75–78
Rao KR, Mohrherr CJ, Riehm JP, Zahnow CA, Norton S, Johnson L, Tarr GE (1987) Primary structure of an analog of crustacean pigment-dispersing hormone from the lubber grasshopperRomalea microptera. J Biol Chem 6: 2672–2675
Schwarz TL, Lee G, Kravitz EA (1981) Proctolin-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the lobster,Homarus americanus. Soc Neurosci Abstr 7: 253
Schwarz TL, Lee G, Siwicki K, Standaert DG, Kravitz EA (1984) Proctolin in the lobster: the distribution, release and chemical characterization of a likely neurohormone. J Neurosci 4: 1300–1311
Stangier J, Dircksen H, Keller R (1986) Identification and immunocytochemical localization of proctolin in pericardial organs of the shore crab,Carcinus maenas. Peptides 7: 67–72
Stangier J, Hilbich C, Beyreuther K, Keller R (1987) Unusual cardioactive peptide (CCAP) from pericardial organs of the shore crabCarcinus maenas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 575–579
Stangier J, Hilbich C, Dircksen H, Keller R (1988) Distribution of a novel cardioactive neuropeptide (CCAP) in the nervous system of the shore crabCarcinus maenas. Peptides 9: 795–800
Sullivan RE (1979) A proctolin-like peptide in crab pericardial organs. J Exp Zool 210: 543–552
Usherwood PNR, Grundfest H (1988) Peripheral inhibition in skeletal muscle of insects. J Neurophysiol 28: 497–518
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stangier, J., Hilbich, C. & Keller, R. Occurrence of crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the nervous system of an insect,Locusta migratoria . J Comp Physiol B 159, 5–11 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692677
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692677